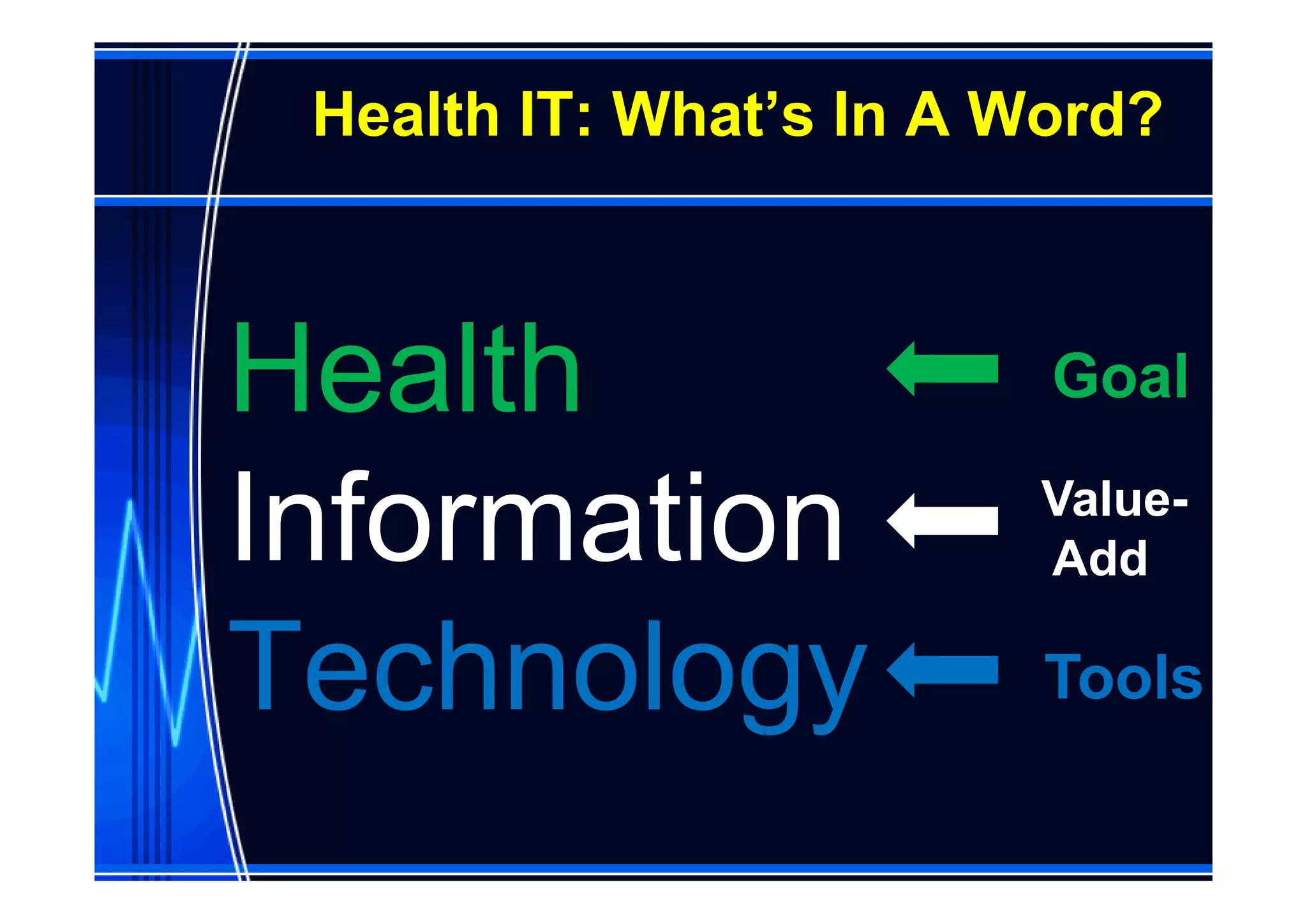
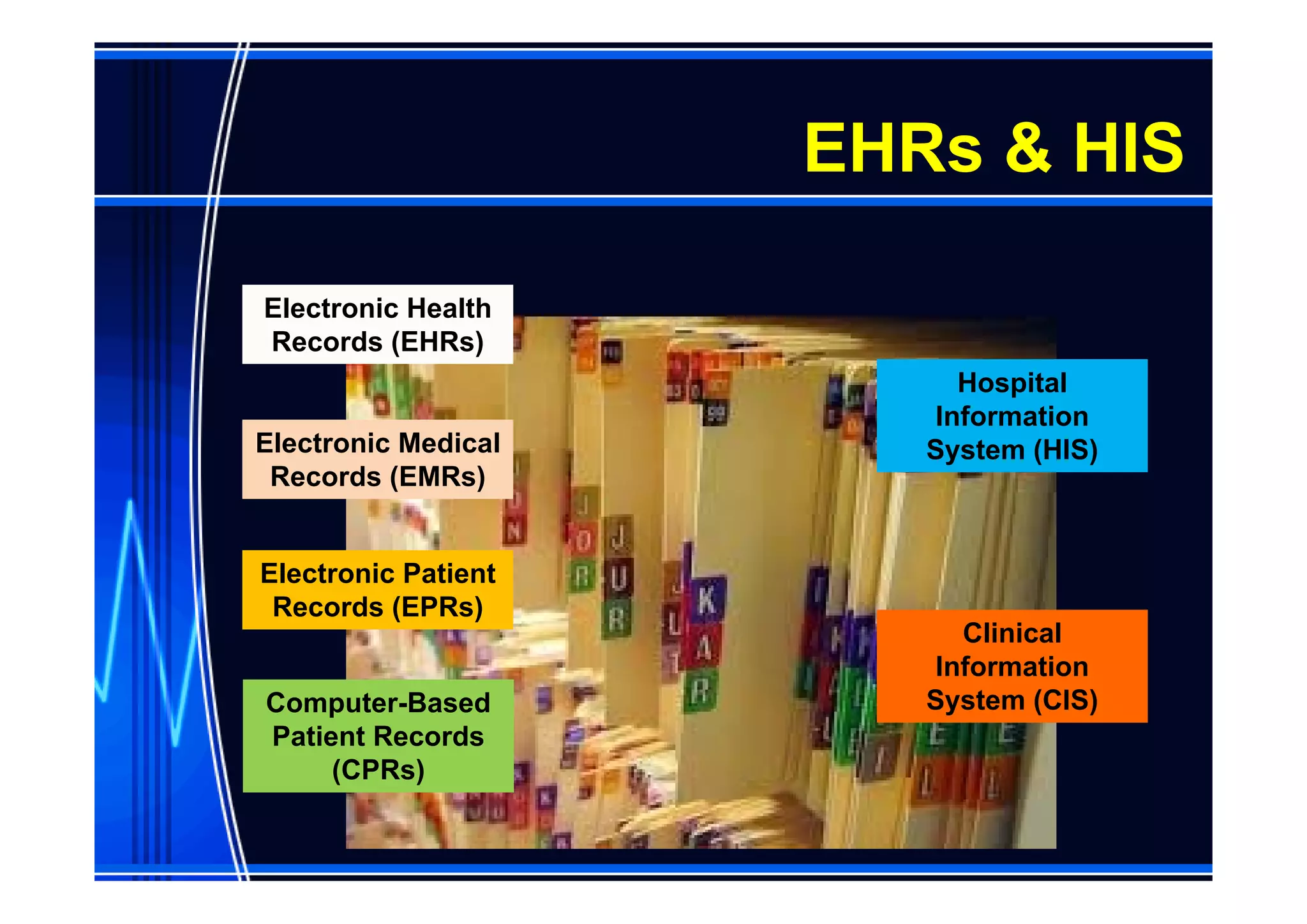
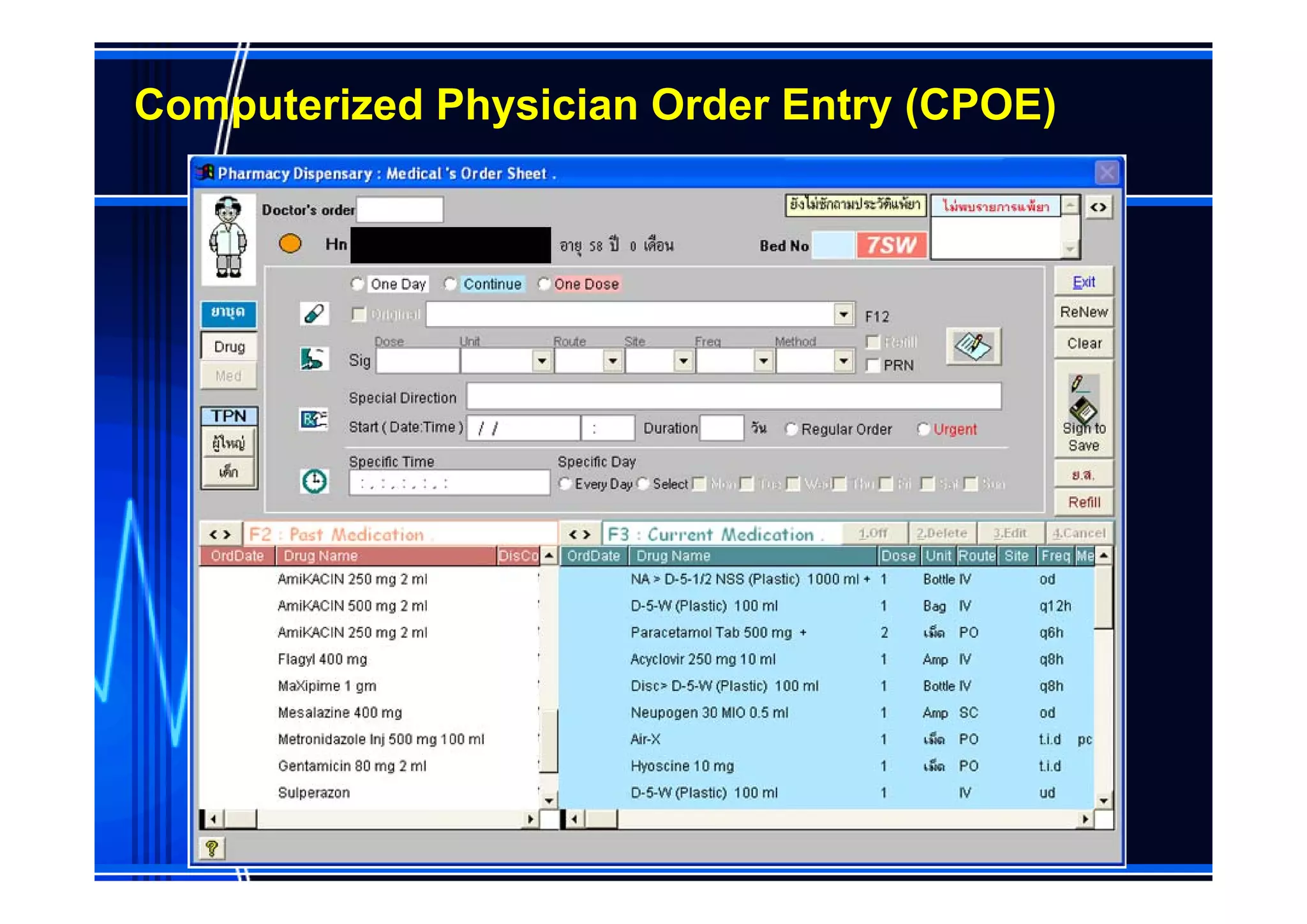
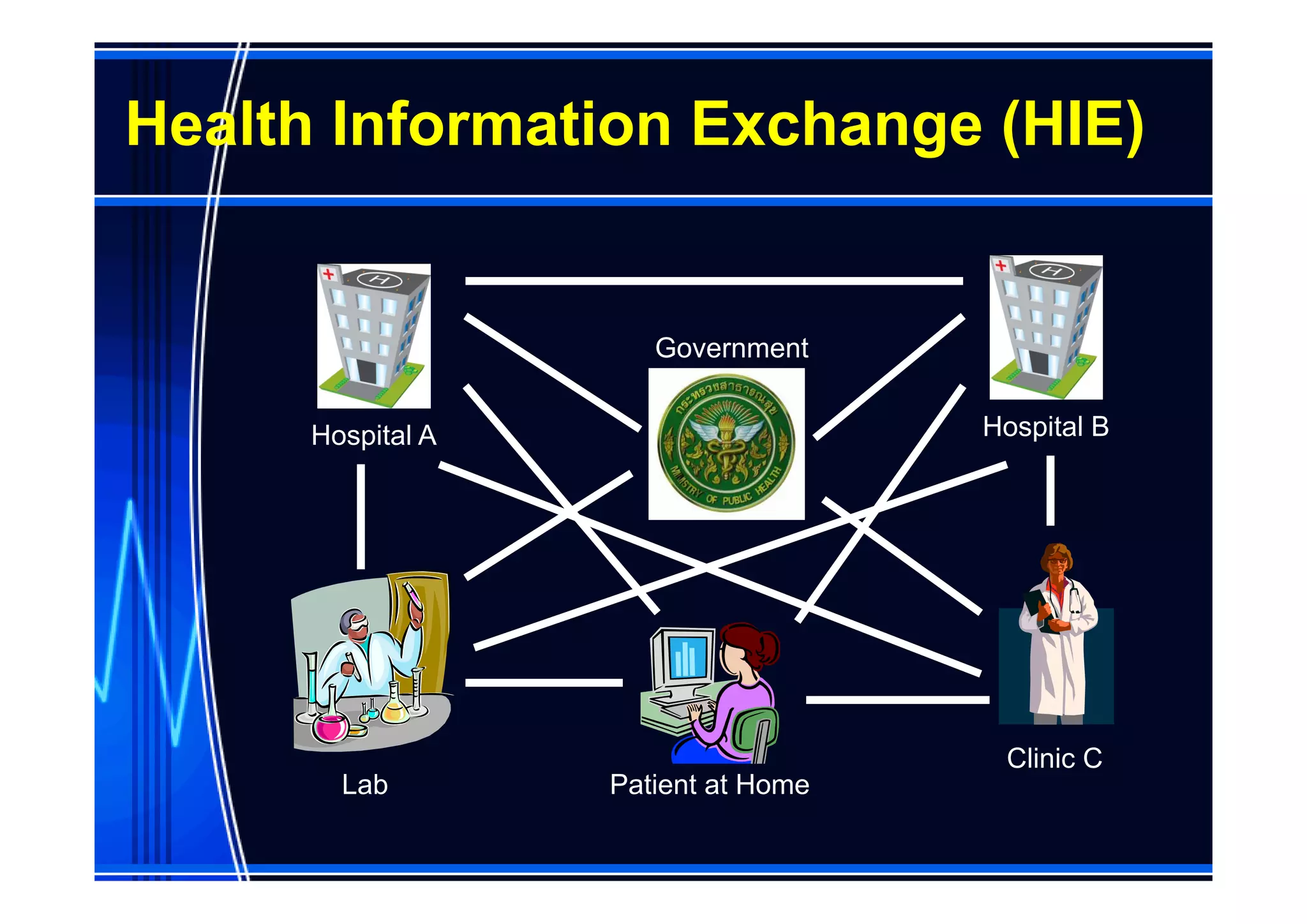
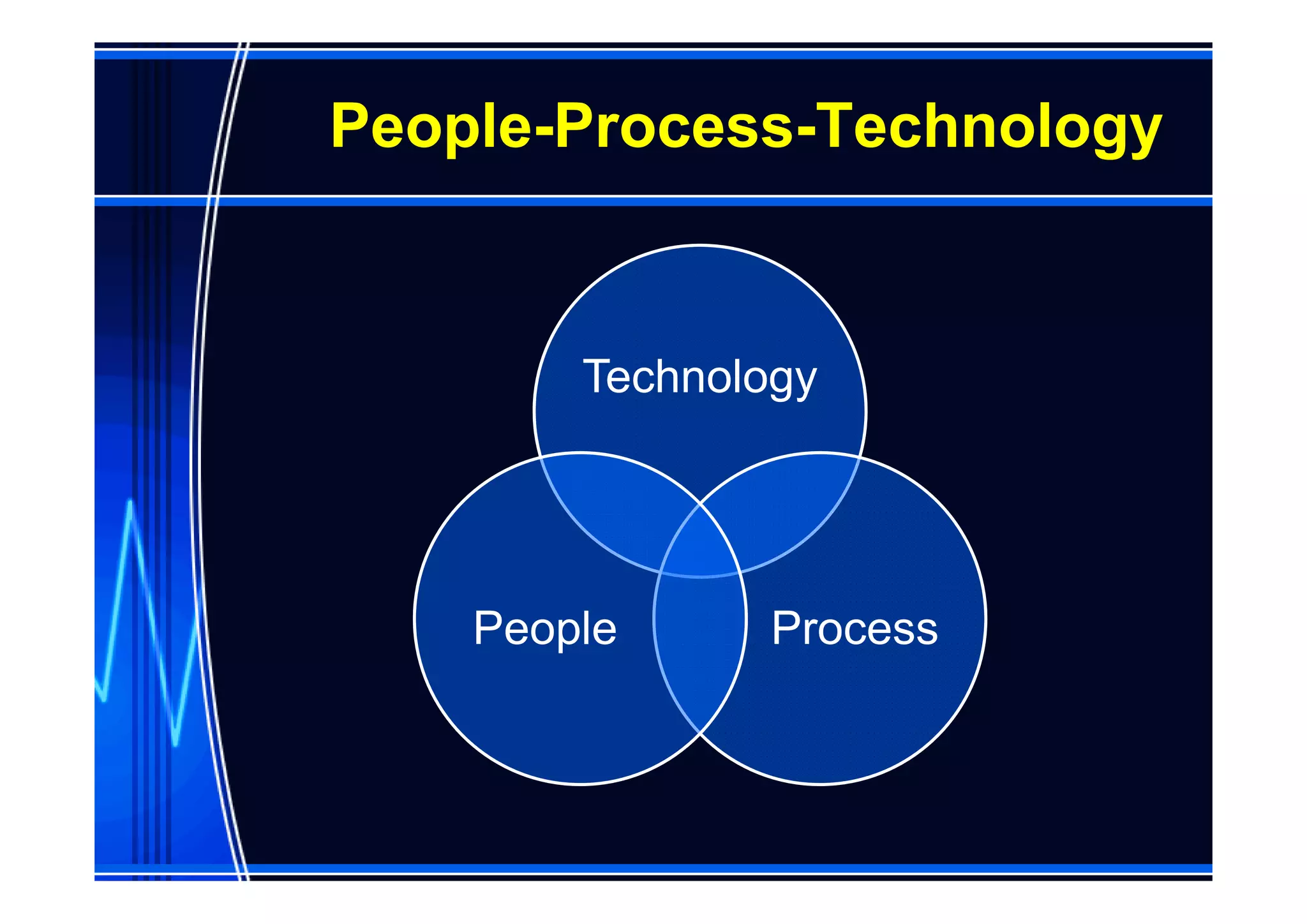
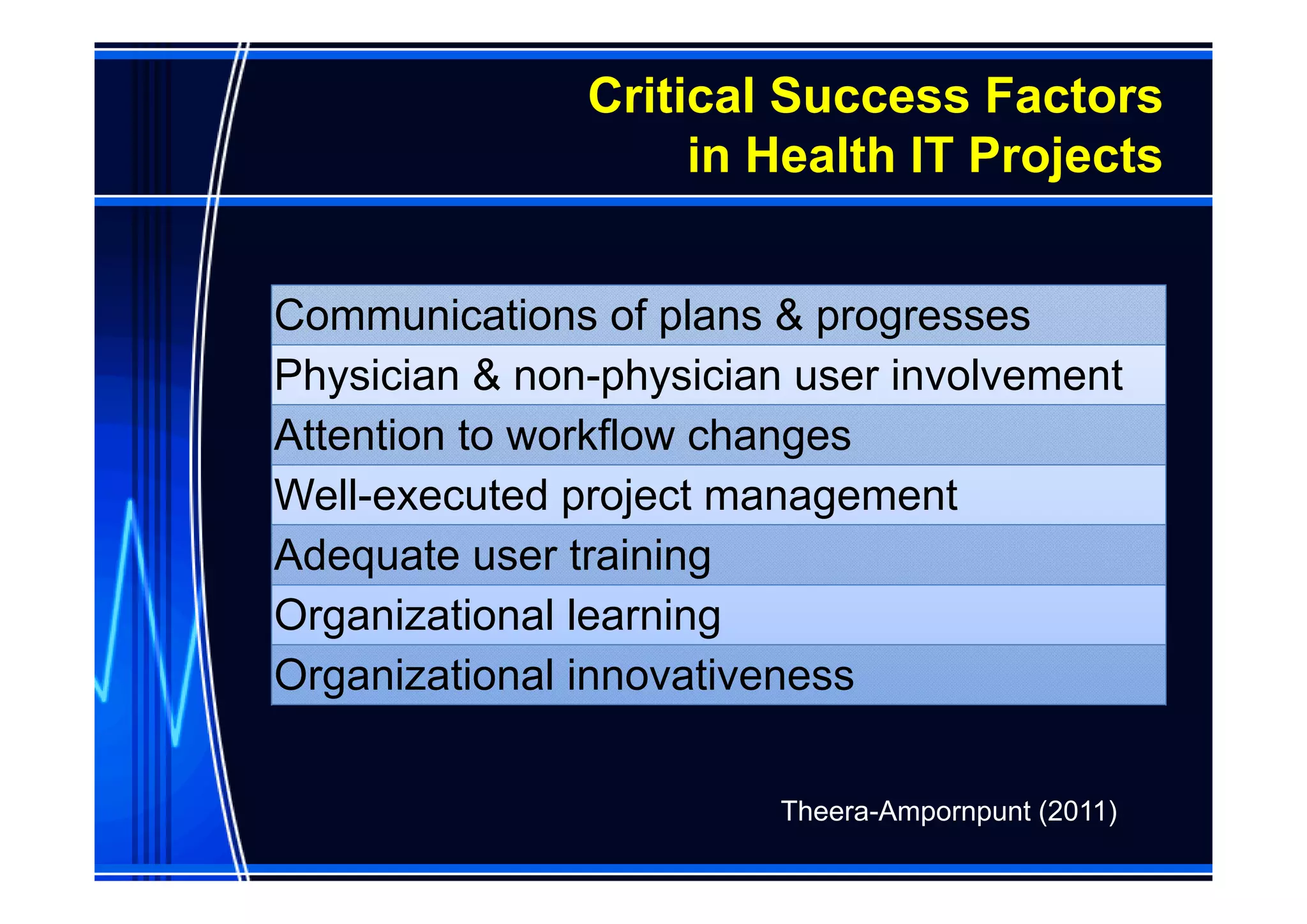
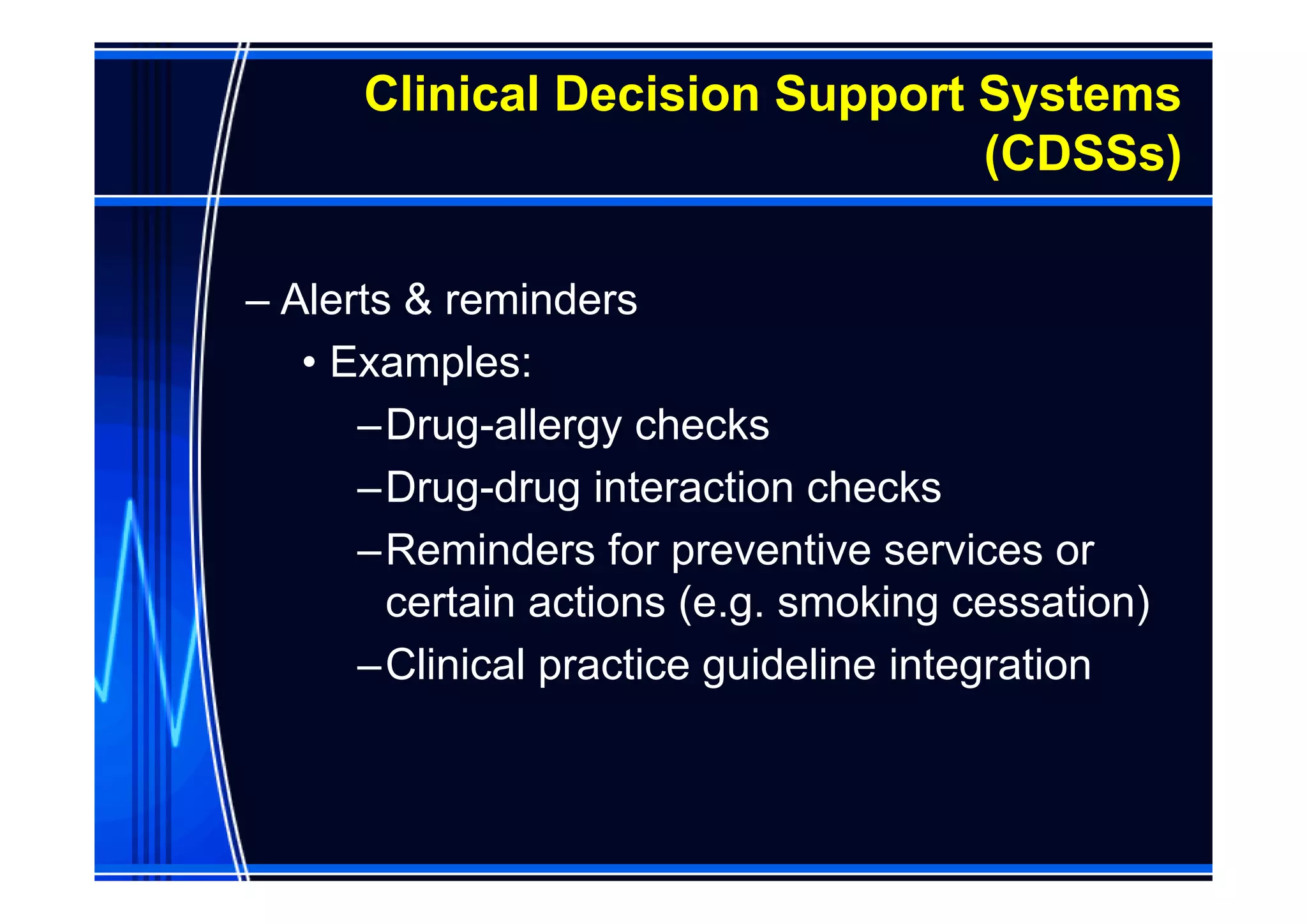
This document discusses information management and health IT systems in emergency rooms. It outlines the unique information needs of ERs, including patient history, safety information, treatment details, and patient tracking. Common ER information problems like limited availability and reliability are described. The document then discusses health IT systems that can help, such as electronic health records, order entry tools, clinical decision support systems, and health information exchange. It notes both the values of health IT in areas like safety and efficiency, as well as potential risks like alert fatigue if not implemented correctly. Overall, the document examines how information technology can address ER information problems, but also requires careful management to achieve benefits.