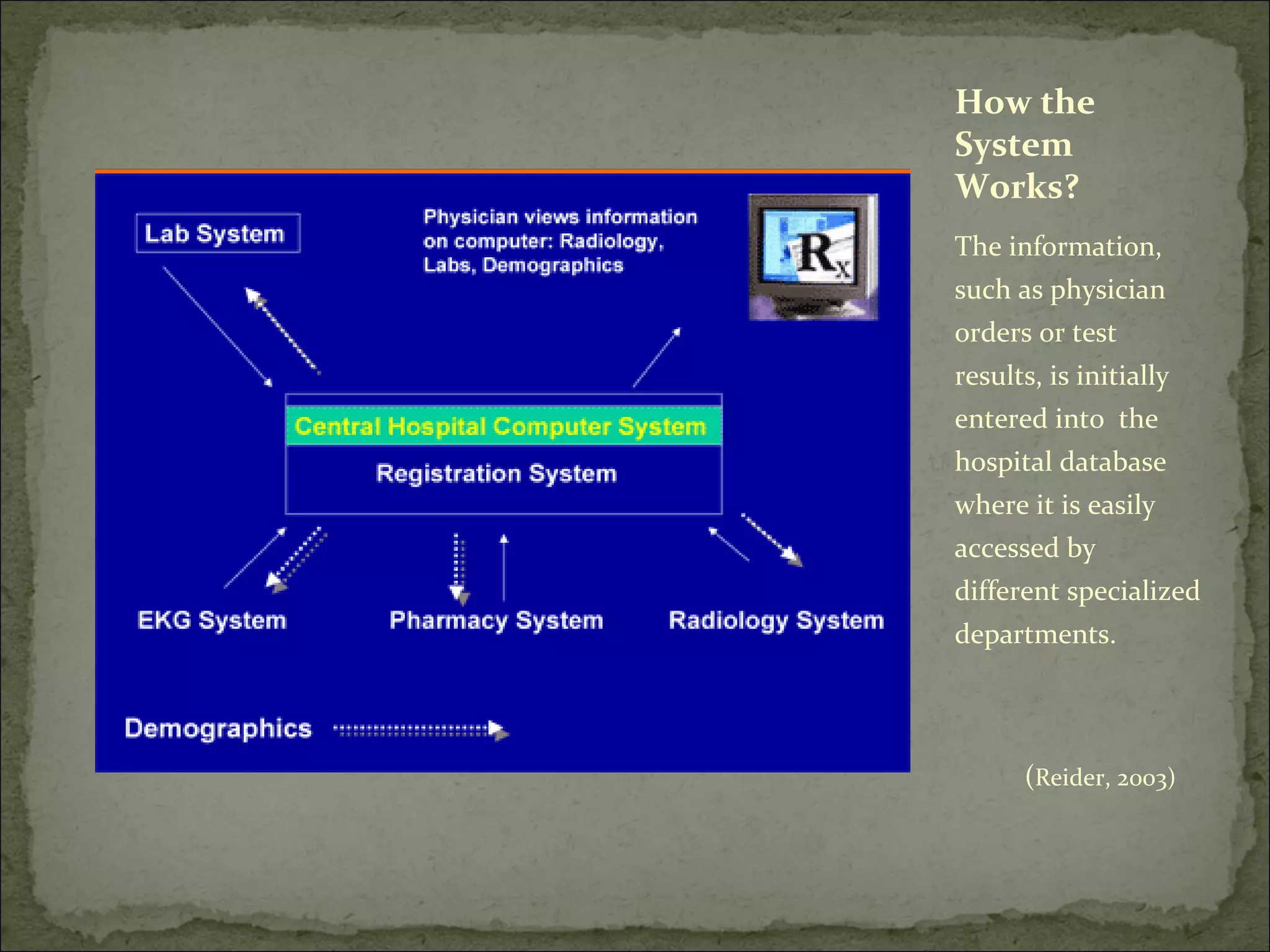
The document discusses Computerized Physician Order Entry (CPOE) systems, which allow physicians to directly enter medical orders like medications, tests, and procedures into a hospital's information system. CPOE provides benefits like real-time access to patient records, clinical decision support, and elimination of transcription errors. However, successful implementation requires addressing legal/ethical issues and gaining physician acceptance. Nurses will need new competencies and responsibilities in utilizing CPOE, such as entering orders and updating patient information.