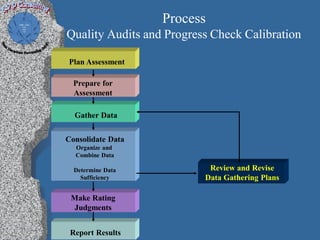
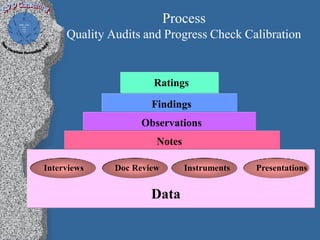
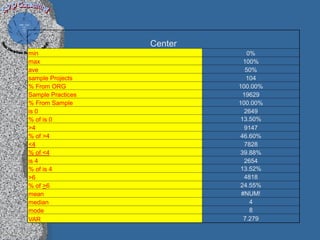
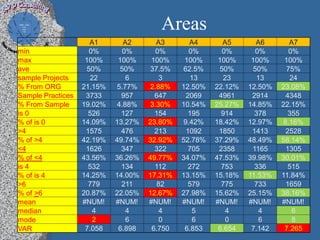
This document discusses process performance models and provides a case study. It summarizes:
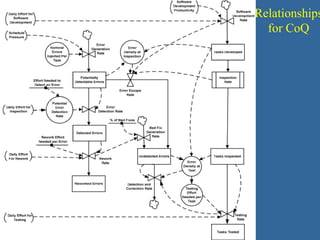
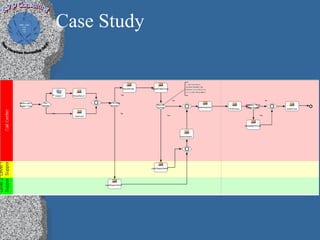
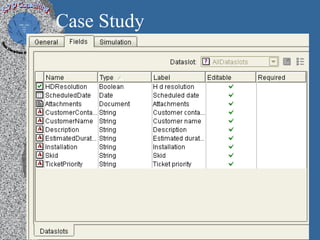
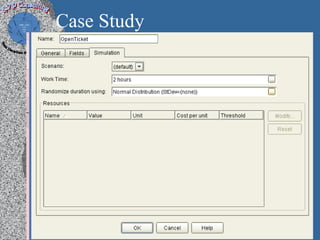
1) A process performance case study based on 450 project feasibility checks that discusses organizational background, ROI, quality audits, and call/incident center performance.
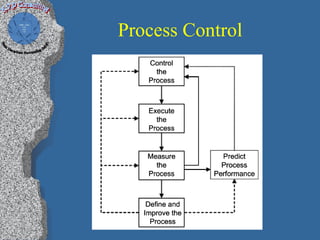
2) The main steps identified for high maturity process improvement, including building an action plan and services roadmap using CMMI-SVC to manage transformation.
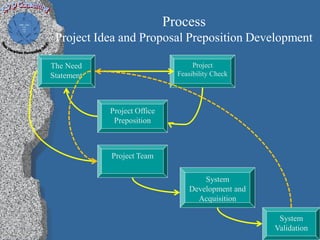
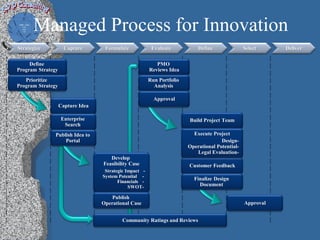
3) A case study on a managed process for innovation that strategizes, captures, formulates, evaluates, defines, selects, and delivers ideas through a multi-step review and approval process.