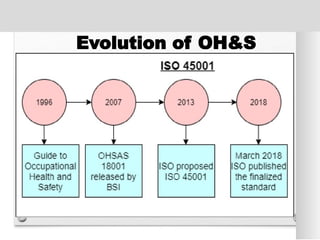
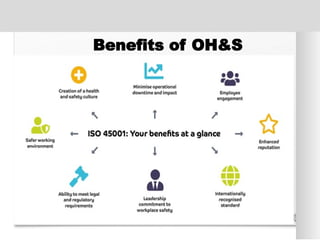
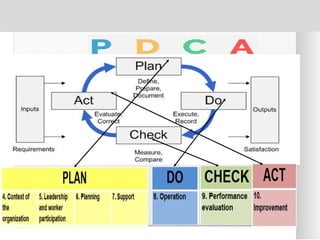
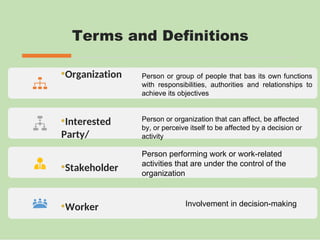
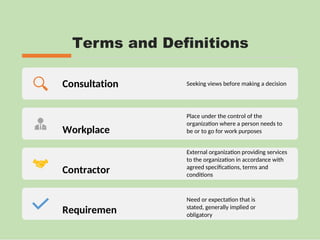
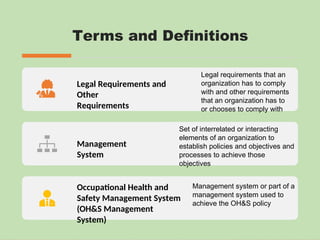
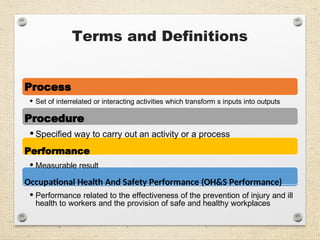
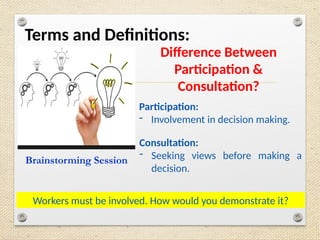
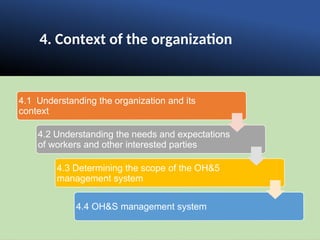
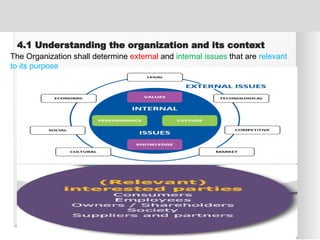
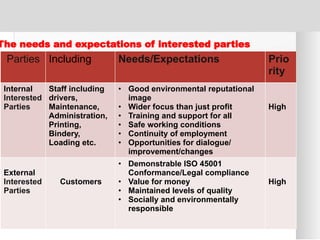
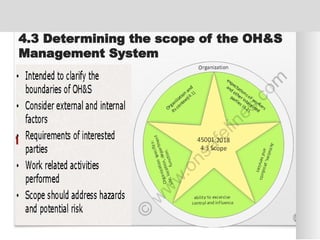
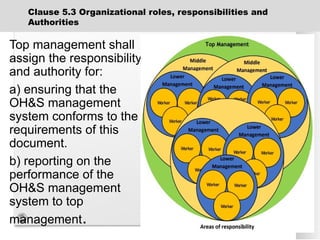
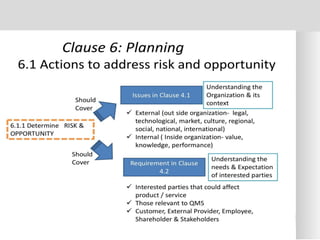
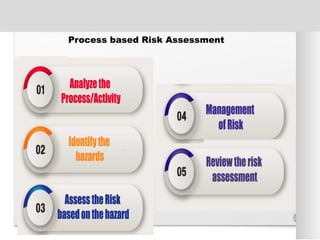
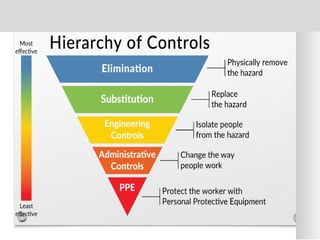
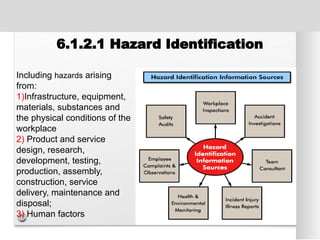
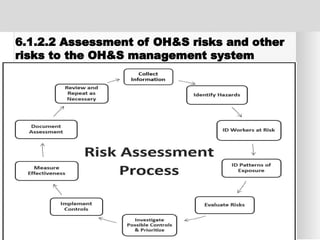
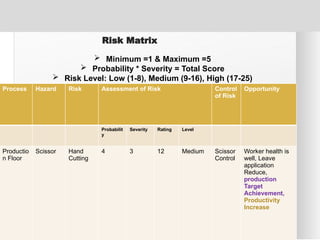
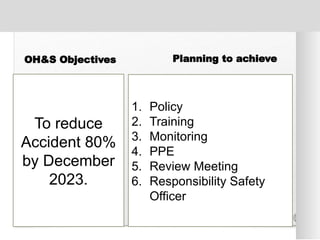
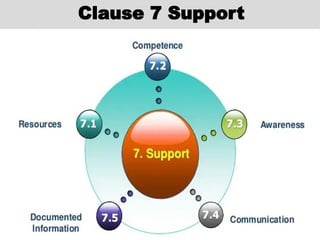
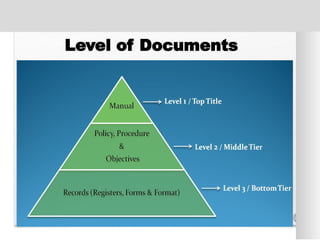
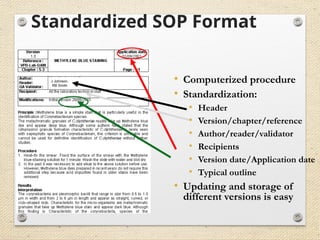
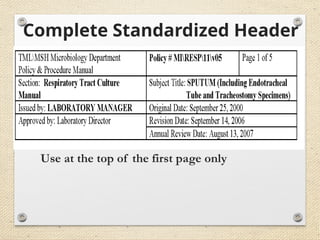
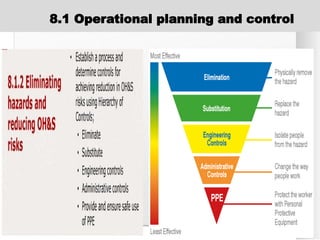
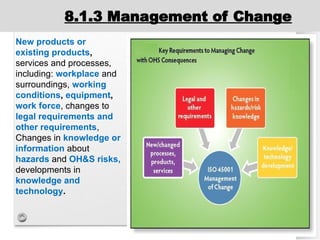
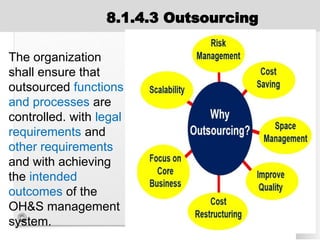
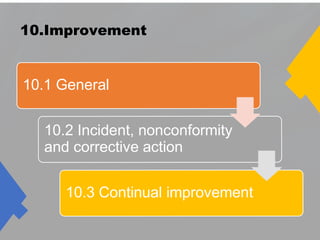
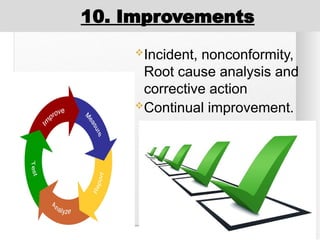
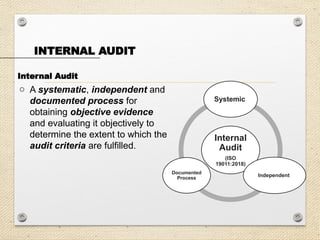
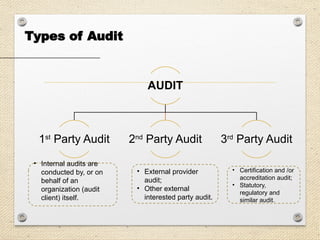
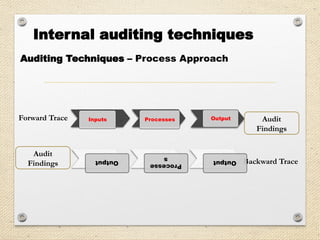
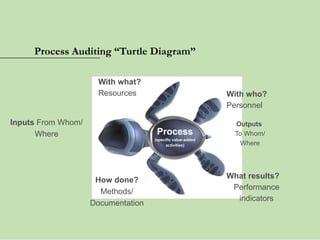
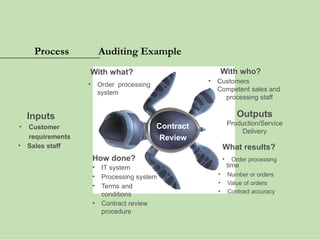
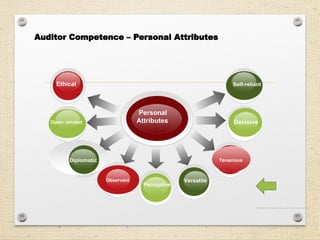
The document outlines the ISO 45001:2018 Occupational Health and Safety Management Systems (OHSMS), detailing its framework, benefits, and clauses aimed at improving worker safety. It emphasizes the importance of leadership, worker participation, and continual improvement in managing occupational health and safety risks within organizations of any size. Key components include planning, performance evaluation, and the necessity for organizations to adapt to challenges while fulfilling legal requirements and achieving safety objectives.