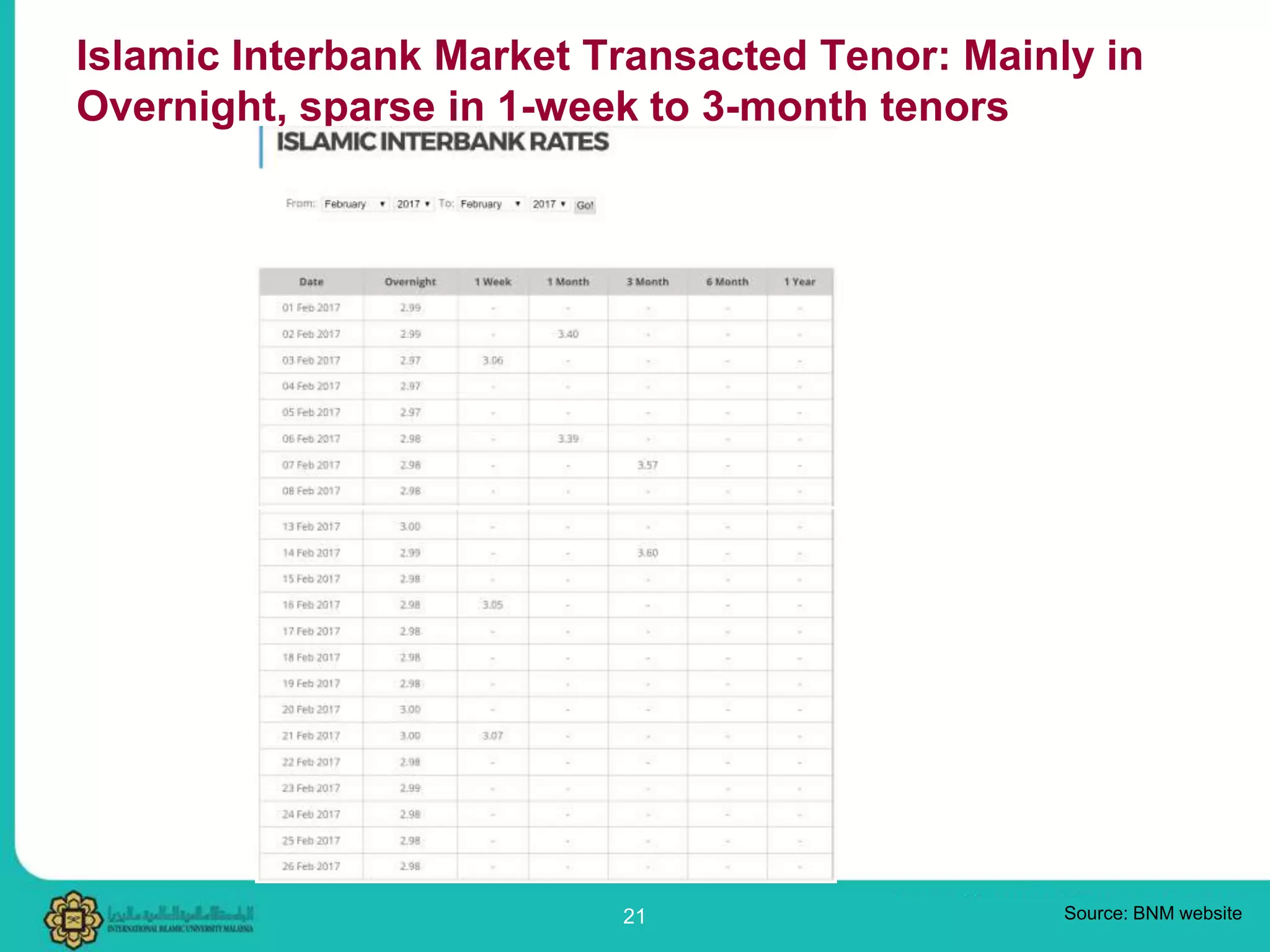
The document provides an overview of the Islamic money market, including its functions, instruments, and calculations. It discusses:
1. The key functions of the Islamic money market are to facilitate the transfer of funds between surplus and deficit parties in accordance with Shariah principles. It also plays a role in liquidity management and as a channel for central banks to conduct monetary policy.
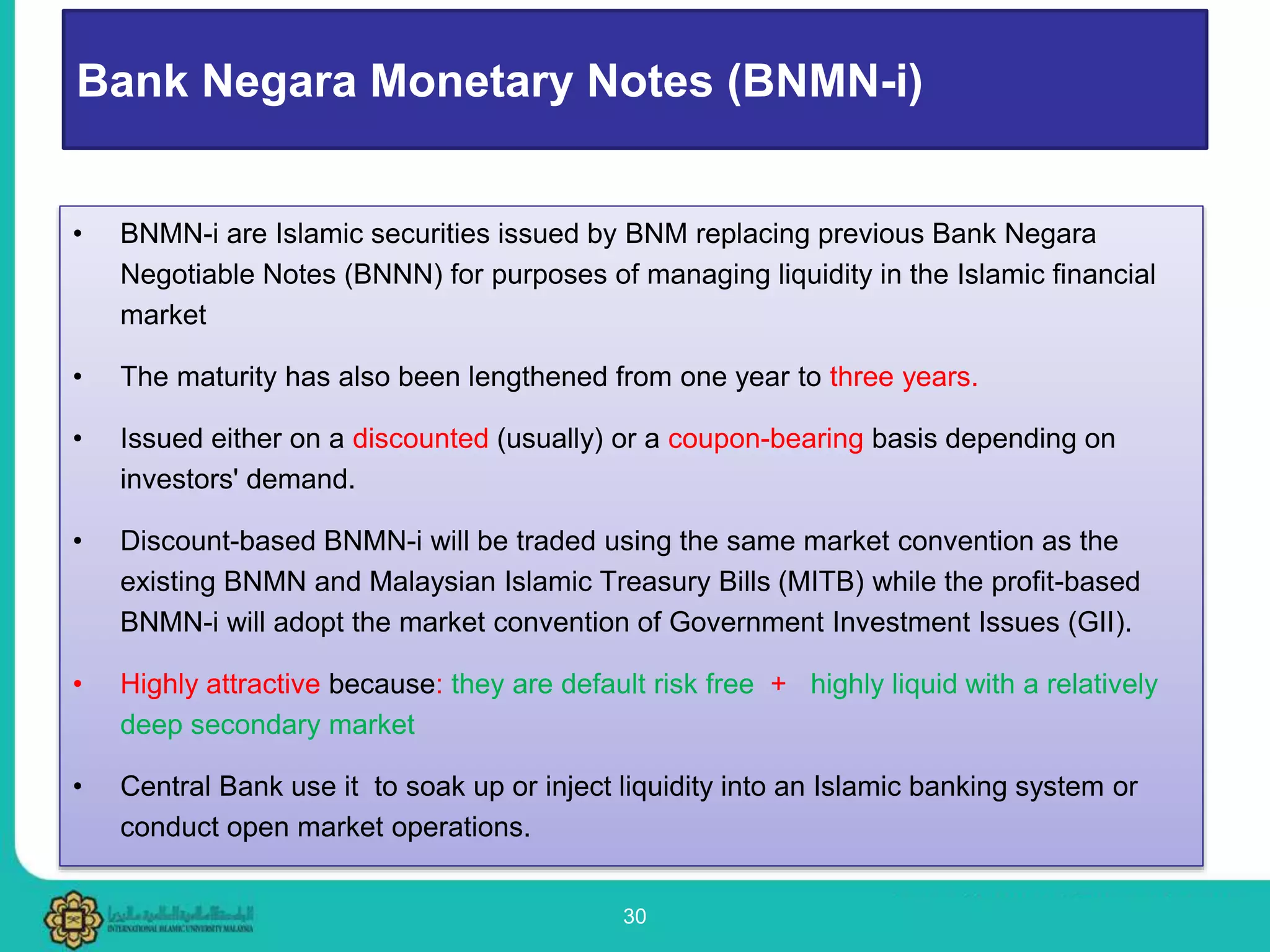
2. Popular Islamic money market instruments discussed include Mudarabah Interbank Investments, Wadiah acceptances, Qard, Commodity Murabahah programs, and Bank Negara Monetary Notes-i.
3. Calculations for profit on various instruments are explained, such as using profit rates, discount rates,