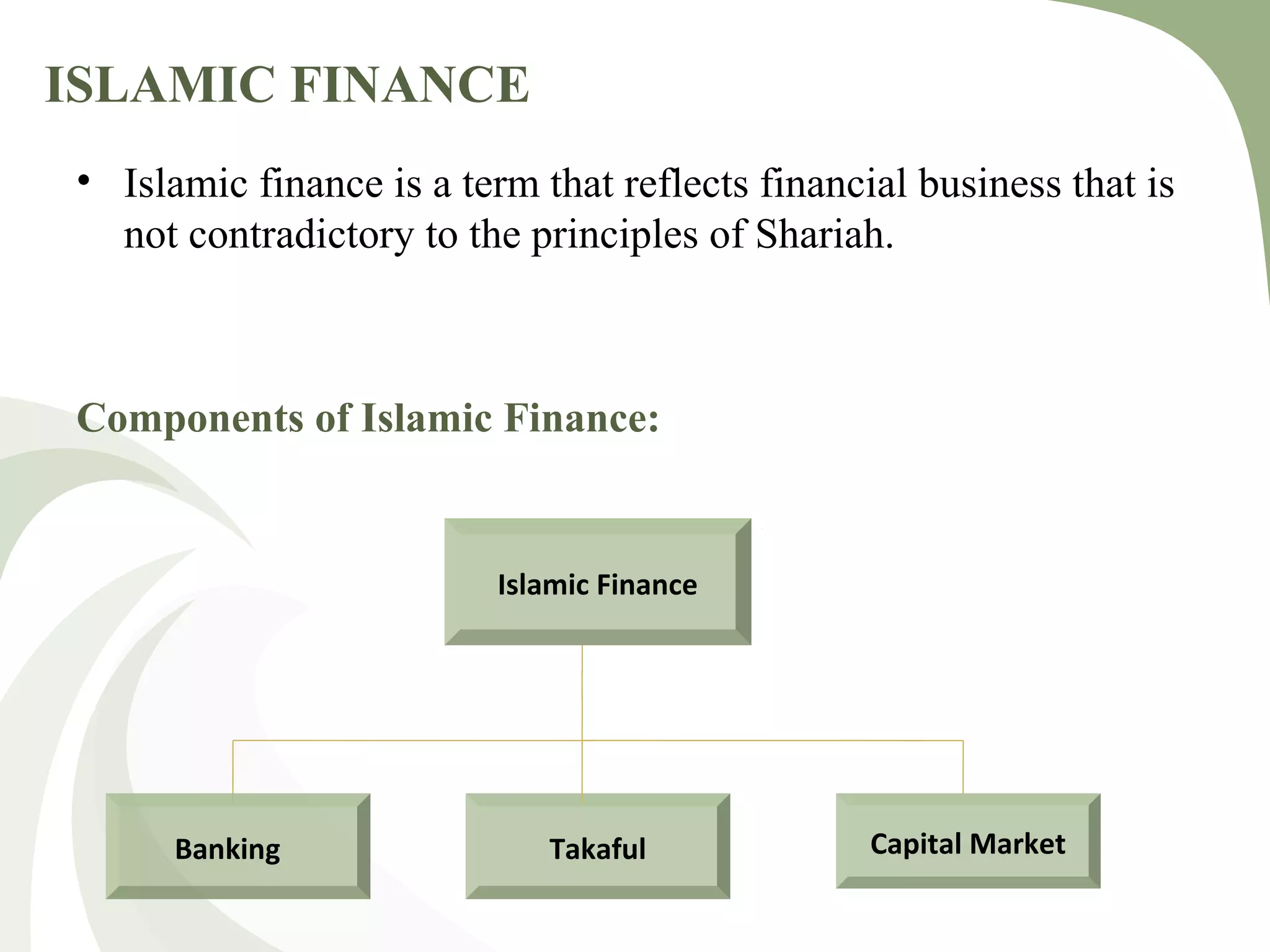
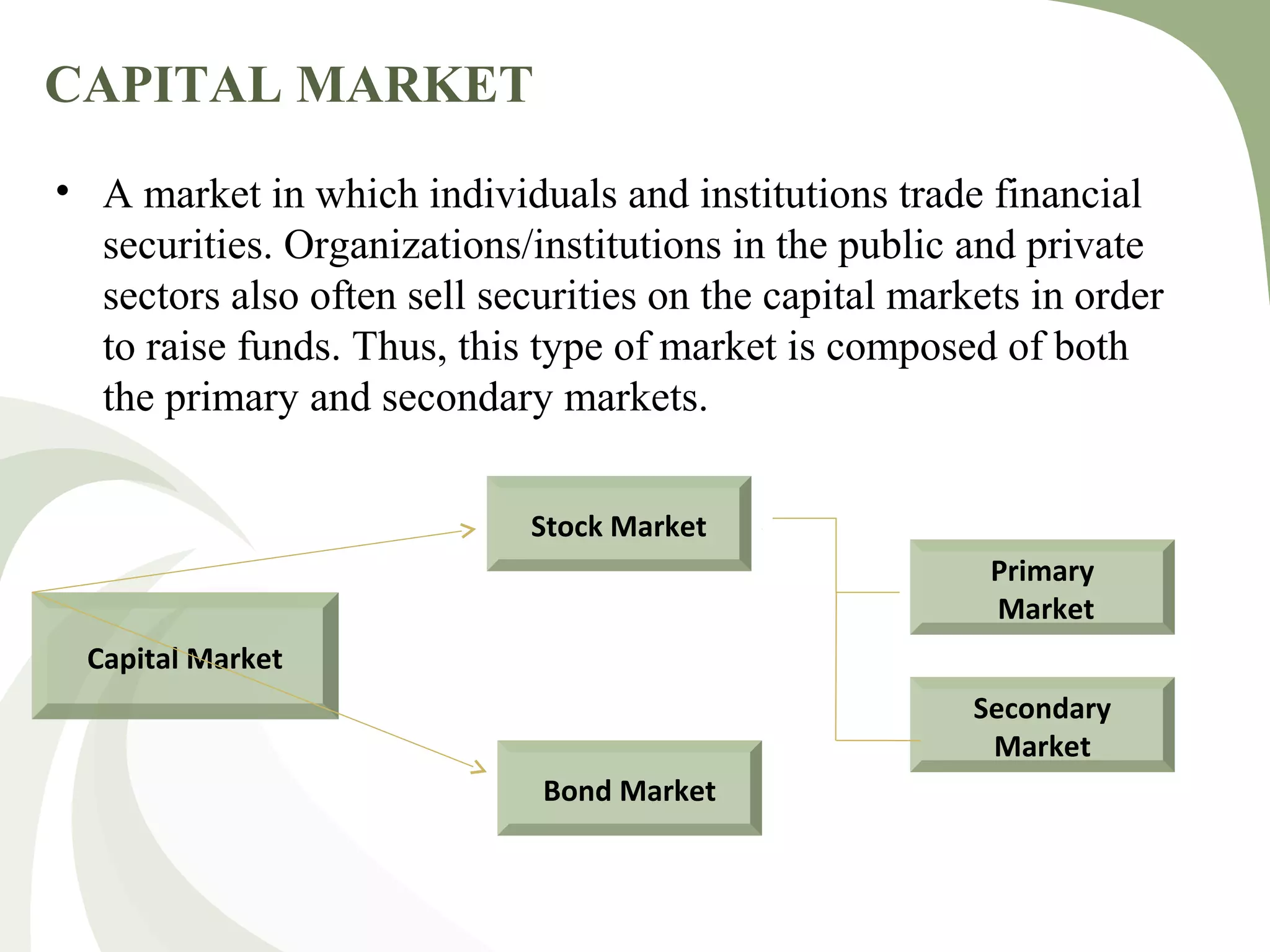
The document provides a comprehensive overview of Islamic capital markets, detailing their foundation in Shariah principles and their growth since the establishment of the first Islamic bank in 1961. It discusses the components, functions, and development challenges of these markets, as well as the role of various regulatory authorities in standardizing Islamic financial products. Key issues include regulatory frameworks and investor education, with suggestions for addressing these through capacity building and market development initiatives.




![HISTORY OF ICM
Islamic Finance starts in 1961 in Egypt by establishing the
earliest Islamic Bank [Mit Ghimar Bank]
Structured Involvement of Islamic Finance in Financial
Markets started in the decades of 1970 and 1980’s by
establishing many Islamic Banks, Takaful and Investment
companies.
Boost in Islamic Capital Markets came after financial
liberalization. ICM started in 1980s in Malaysia while in
Bahrain, Pakistan and some other countries in early 1990s](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/islamiccapitalmarkets-150922065049-lva1-app6892/75/Islamic-Capital-Markets-7-2048.jpg)



![STANDARDISING And REGULATORY
AUTHORITIES
International Islamic Financial Market (IIFM) [2002]
Its primary focus lies in the standardization of Islamic financial
products, documentation and related processes at the global level.
The Islamic Financial Services Board (IFSB) [2003]
It is an international standard-setting organization that promotes
and enhances the soundness and stability of the Islamic financial
services industry by issuing global prudential standards and
guiding principles for the industry, broadly defined to include
banking, capital markets and insurance sectors.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/islamiccapitalmarkets-150922065049-lva1-app6892/75/Islamic-Capital-Markets-11-2048.jpg)
![STANDARDISING And REGULATORY
AUTHORITIES Cont…….
The Shariah board [2003]
It has the responsibility for ensuring that all products and services
offered by that institution are compliant with the principles of
Shariah law
The Accounting and Auditing Organization for Islamic
Financial Institution. (AAOIFI) [1990]
It sets compliance standards for institutions that wish to gain
access to the Islamic banking market.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/islamiccapitalmarkets-150922065049-lva1-app6892/75/Islamic-Capital-Markets-12-2048.jpg)
![STANDARDISING And REGULATORY
AUTHORITIES Cont…….
The Islamic capital markets Task Force of the International
Organization of Securities Commission (IOSCO)
It assist relevant regulators in assessing the extent of the
development and potential regulatory issues relating to Islamic
Capital Market, as well as to gather information on Islamic
financial products.
The International Islamic Rating Agency (IIRA) [2002]
evaluate and provide independent assessments and opinions on
the likelihood of any future loss by Islamic Financial Institutions,](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/islamiccapitalmarkets-150922065049-lva1-app6892/75/Islamic-Capital-Markets-13-2048.jpg)


