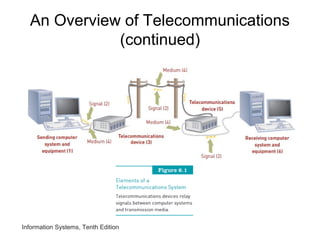
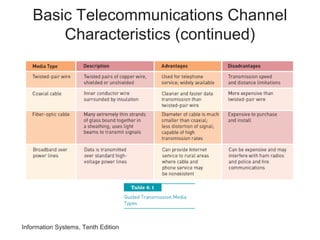
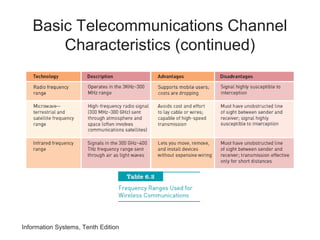
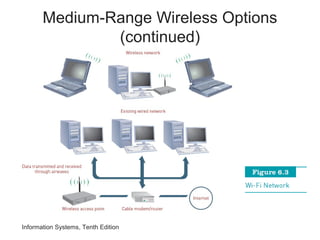
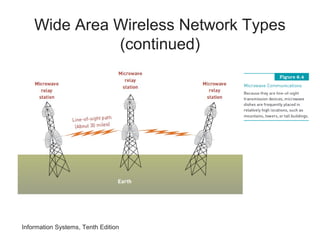
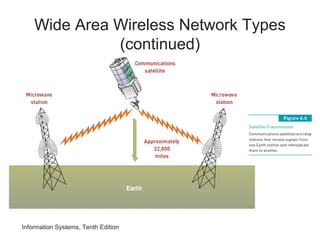
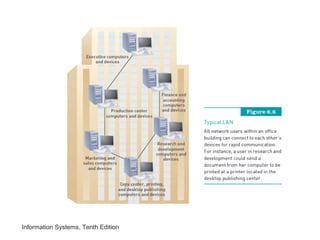
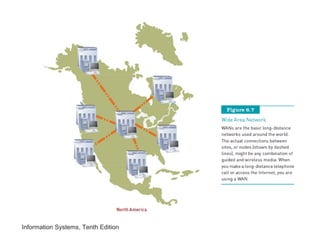
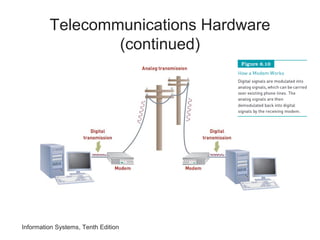
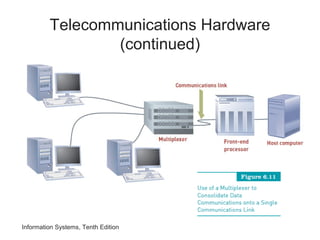
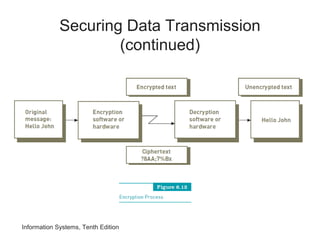
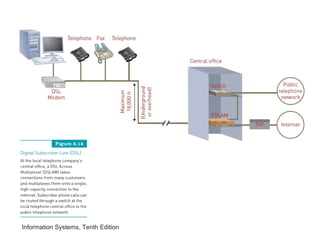
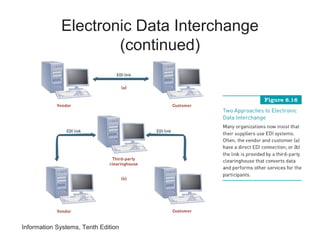
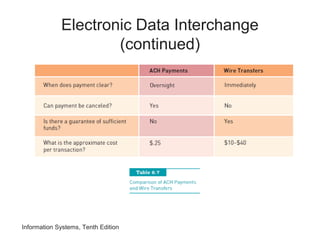
The document provides an overview of telecommunications and networks. It defines key concepts like telecommunications, networks, bandwidth, and different types of network ranges. It describes the components of a basic telecommunications system and different telecommunications media. It also discusses network applications, security, and how telecommunications and networks are transforming organizations by removing barriers of time and distance and allowing sharing of resources.