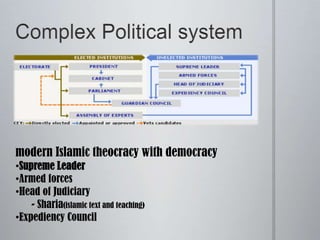
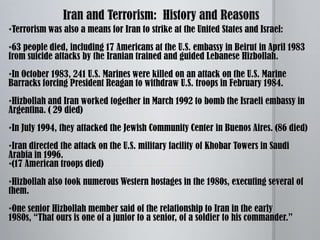
The document provides an overview of various topics related to Iran, including its government and politics, human rights record, terrorism activities, and nuclear program. It discusses Iran's history from the Pahlavi era in the 1920s through the 1979 revolution and Iran-Iraq war. It notes Iran has a complex political system as an Islamic theocracy with elected aspects. The document also examines Iran's sponsorship of terrorism, particularly its close ties to Hezbollah, and support for Palestinian groups. In addition, it provides details on Iran's nuclear program and the debate around how the U.S. should respond.




















![Iran’s Supreme Leader Ayatollah Khomeini declared shortly after taking power that, “We should try hard to export our revolution to the world….we [shall] confront the world with our ideology.”-Daniel Byman, The Saban Center for Middle East Policy.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iran-091121100612-phpapp02/85/Iran-23-320.jpg)