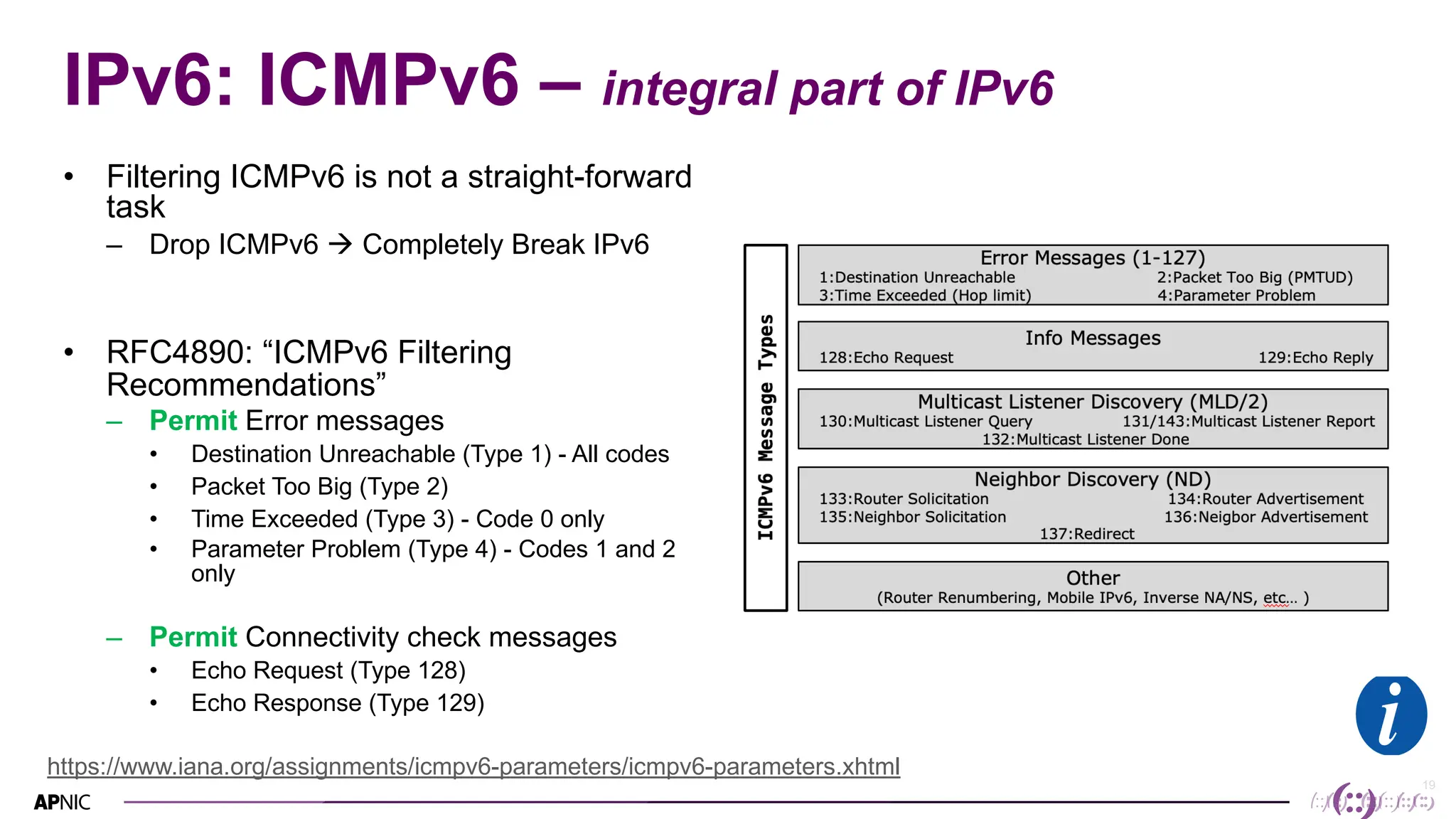
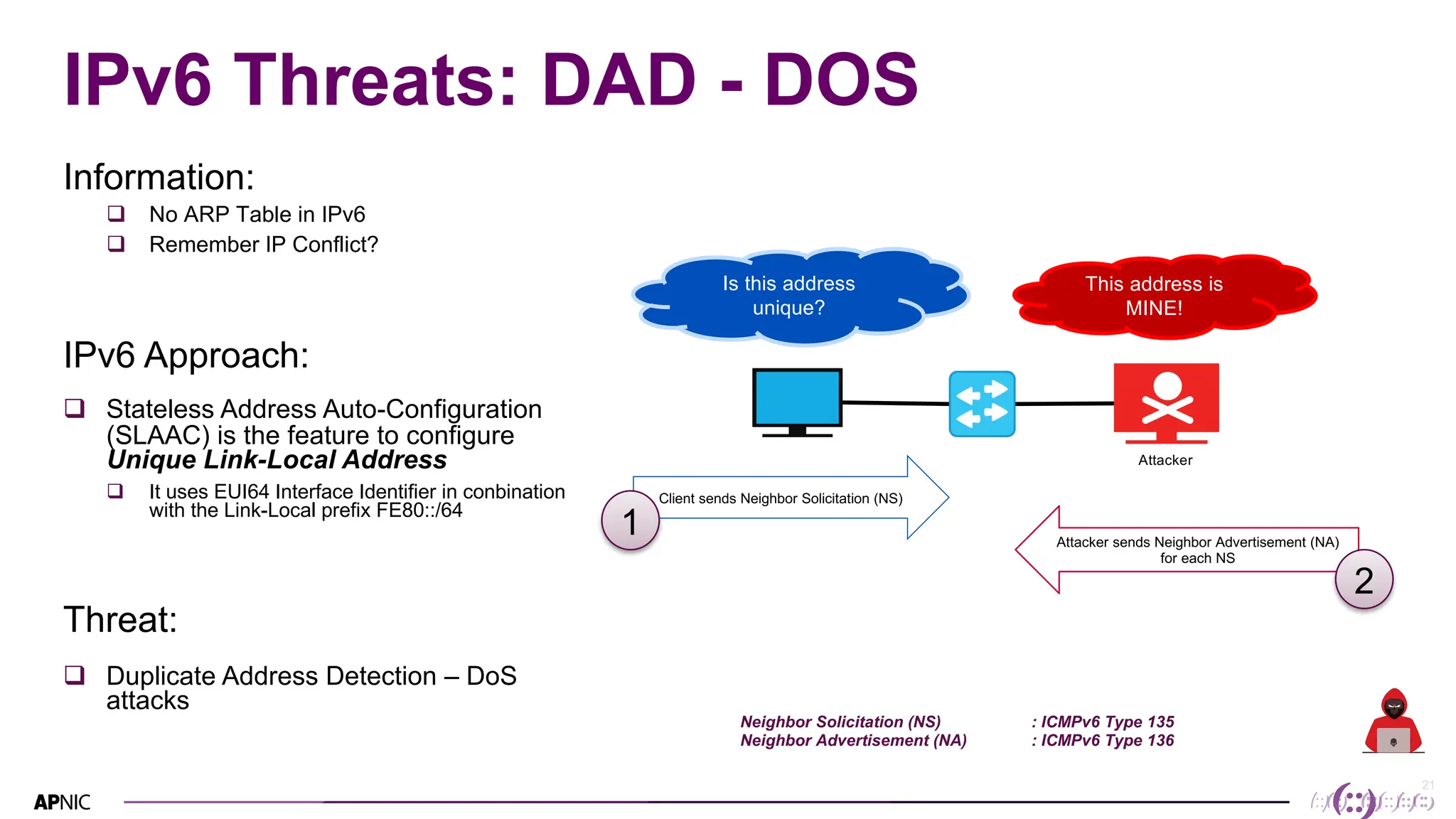
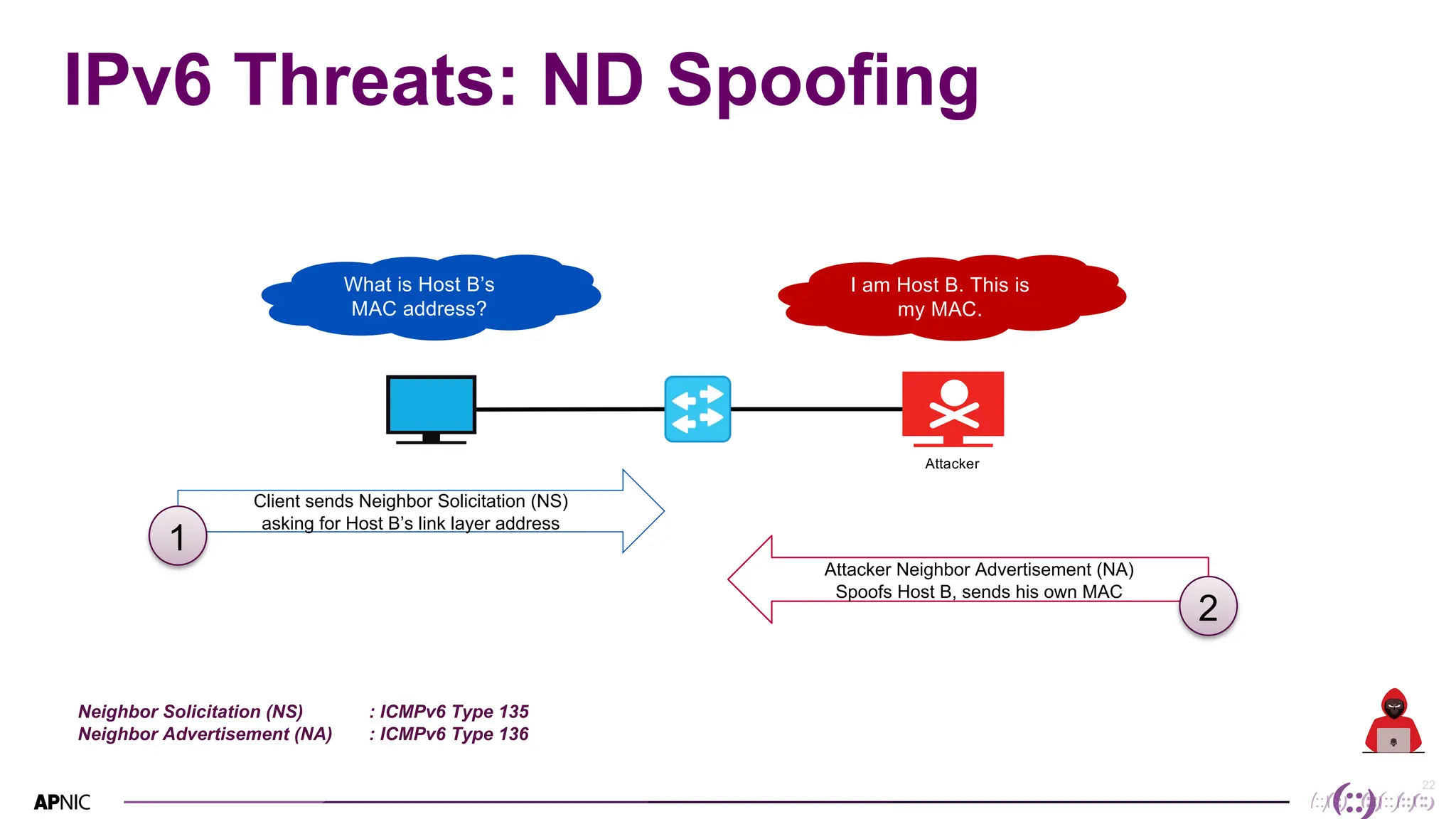
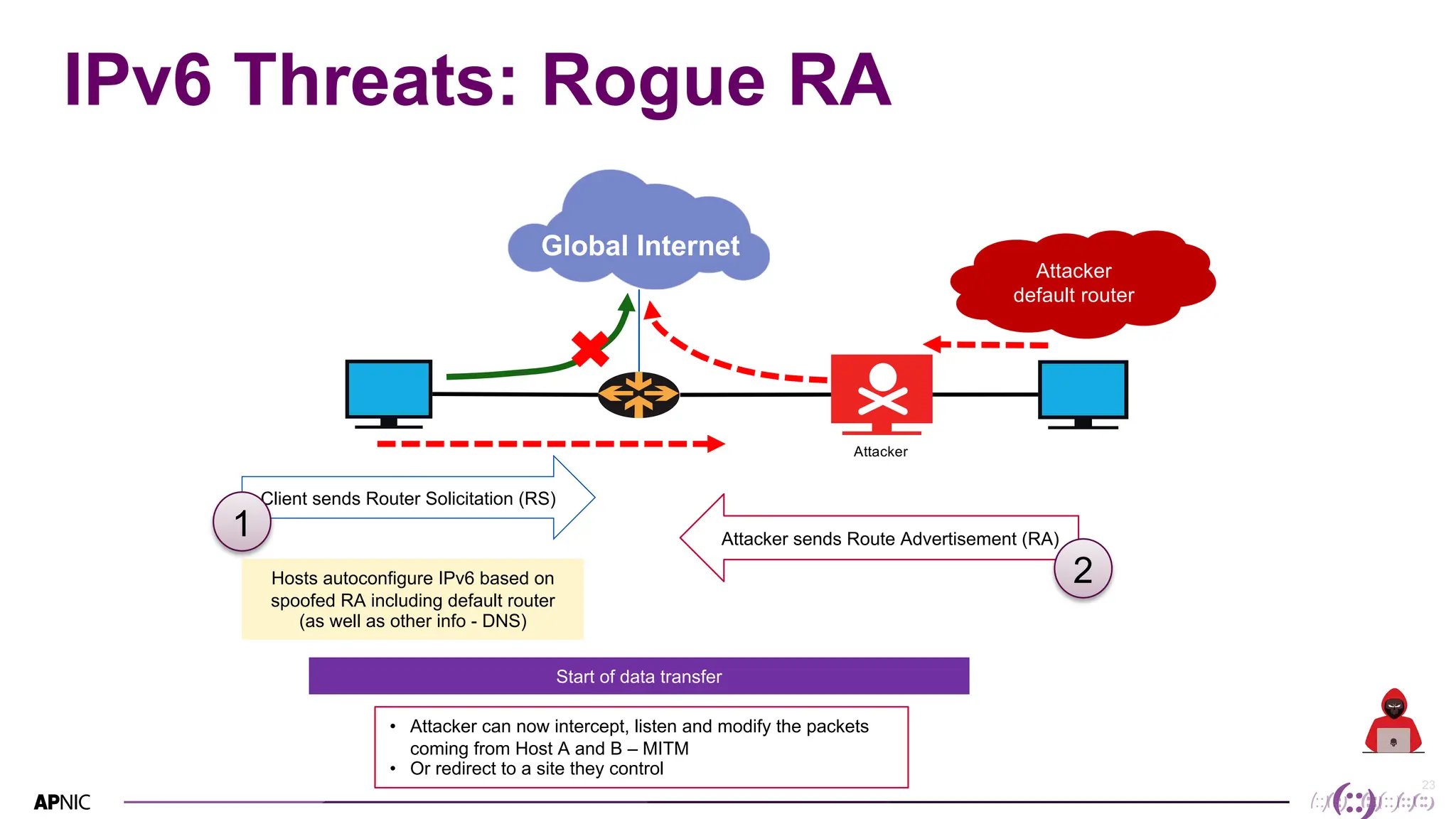
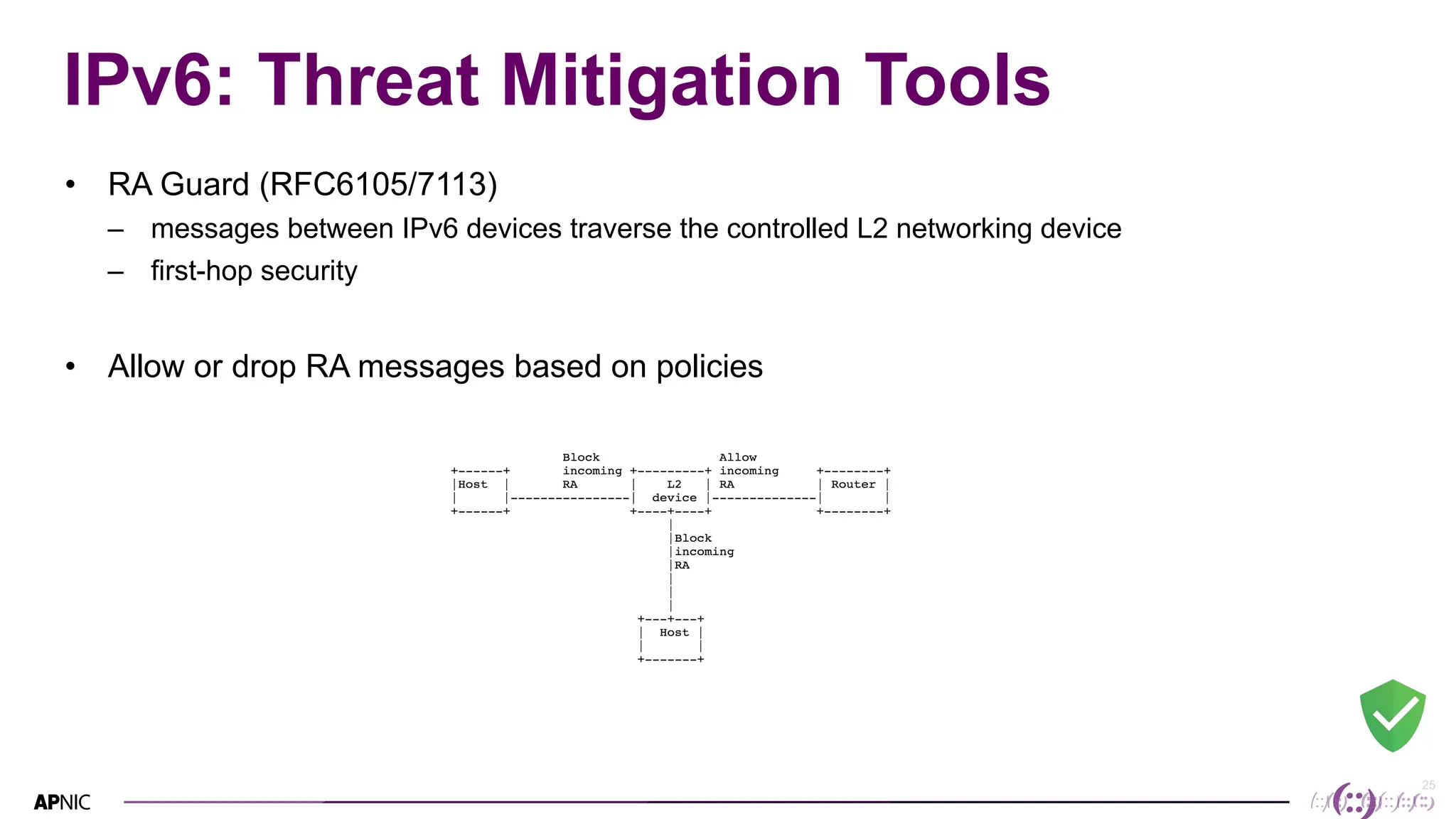
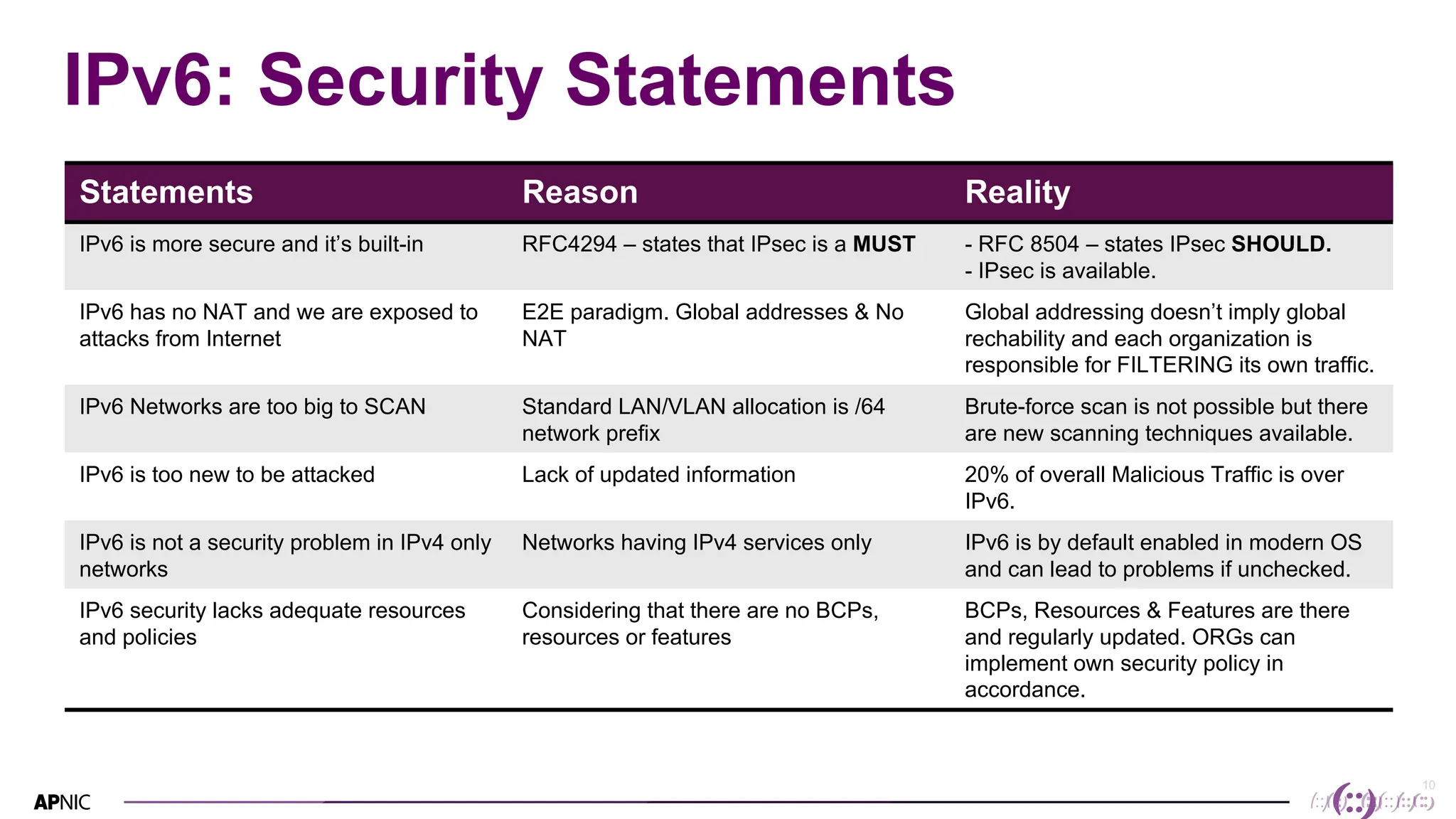
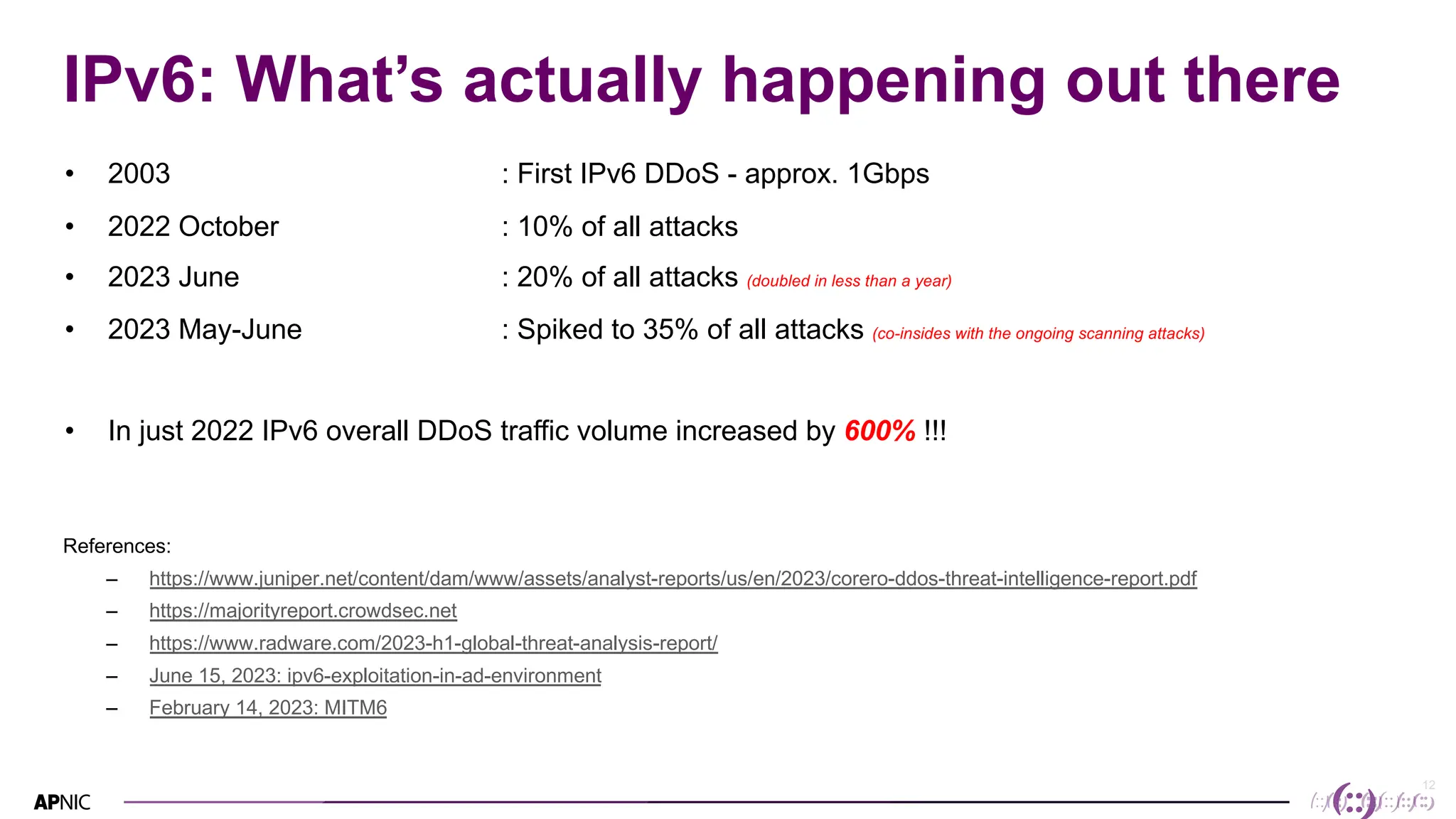
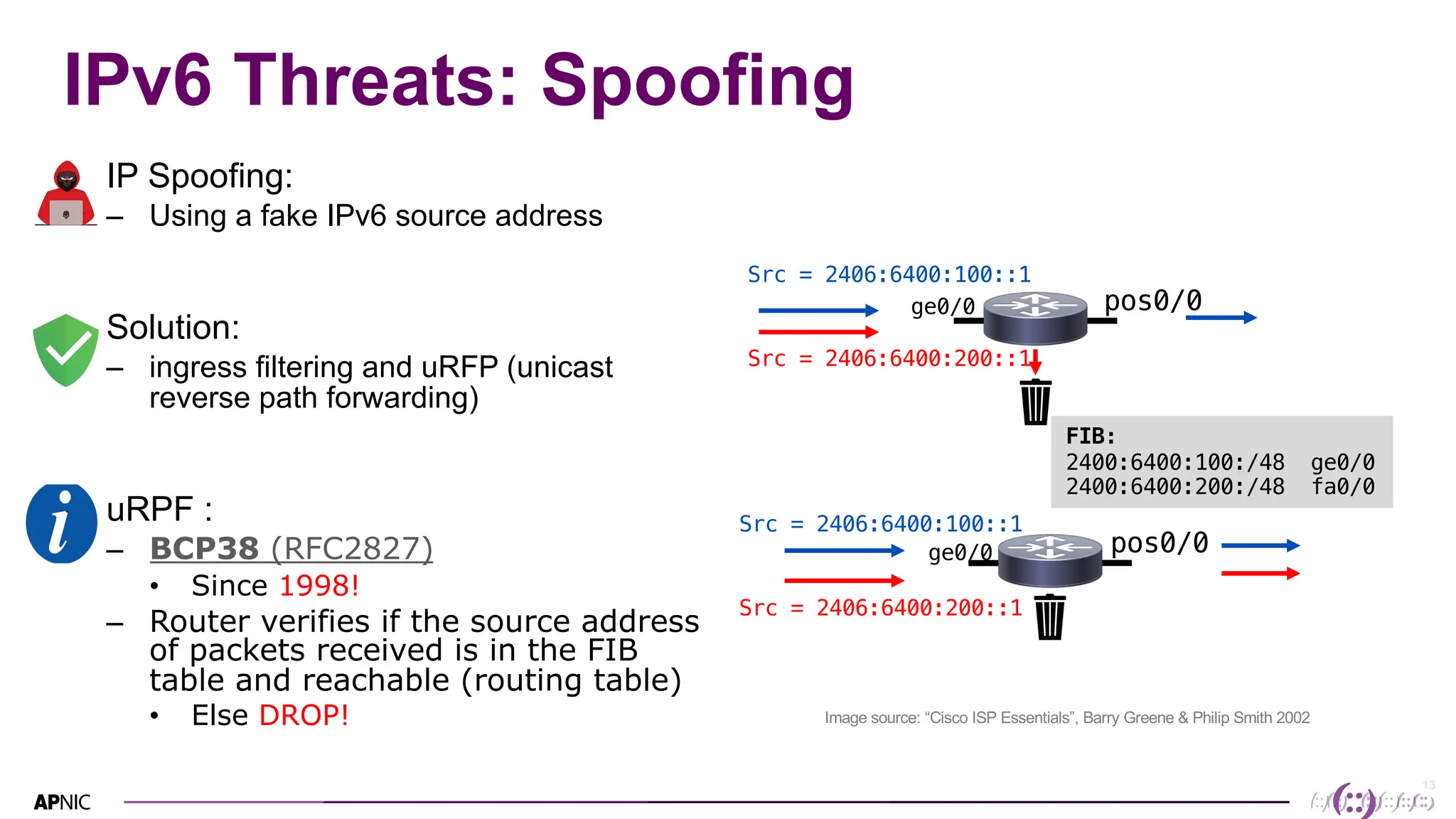
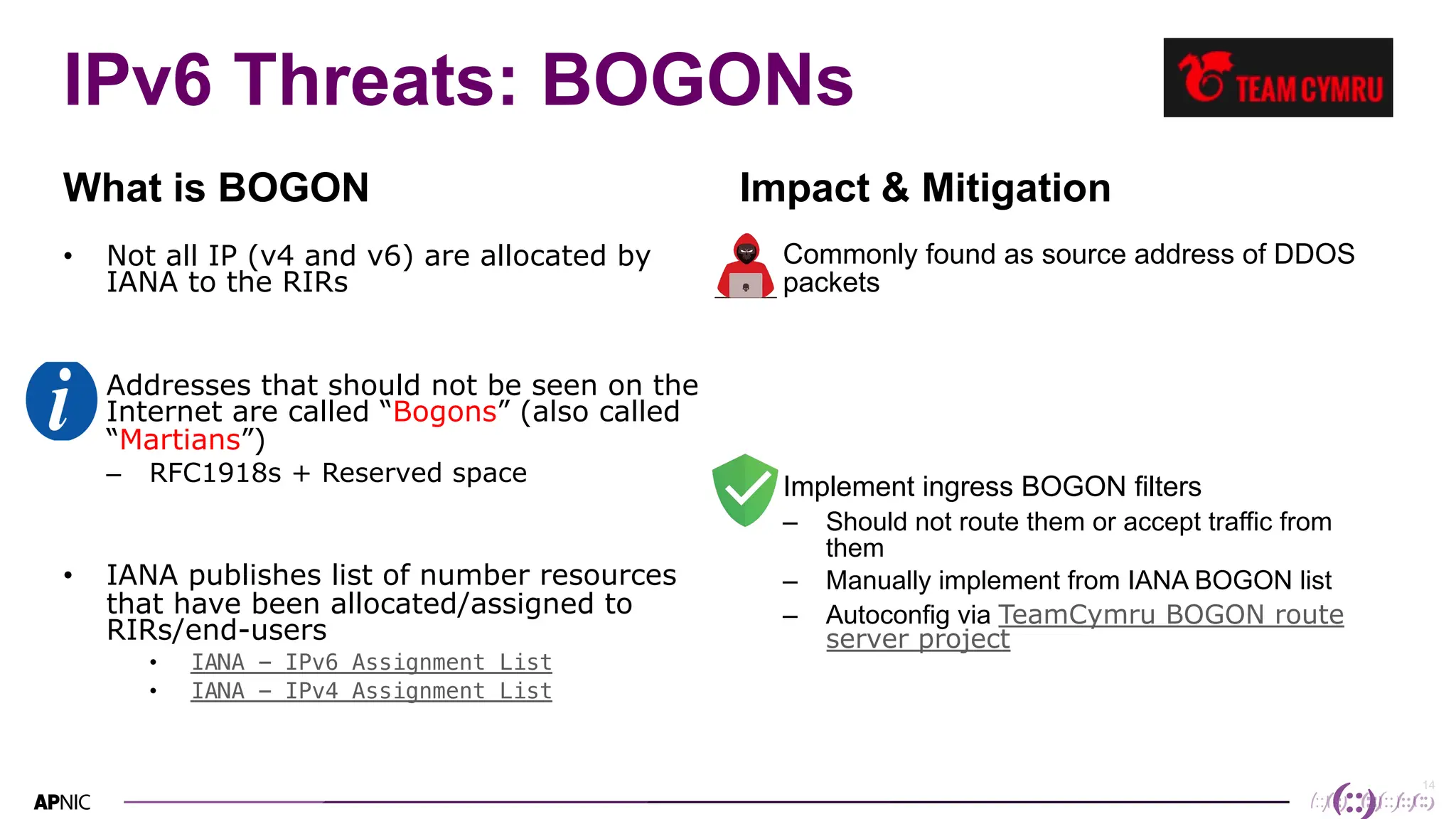
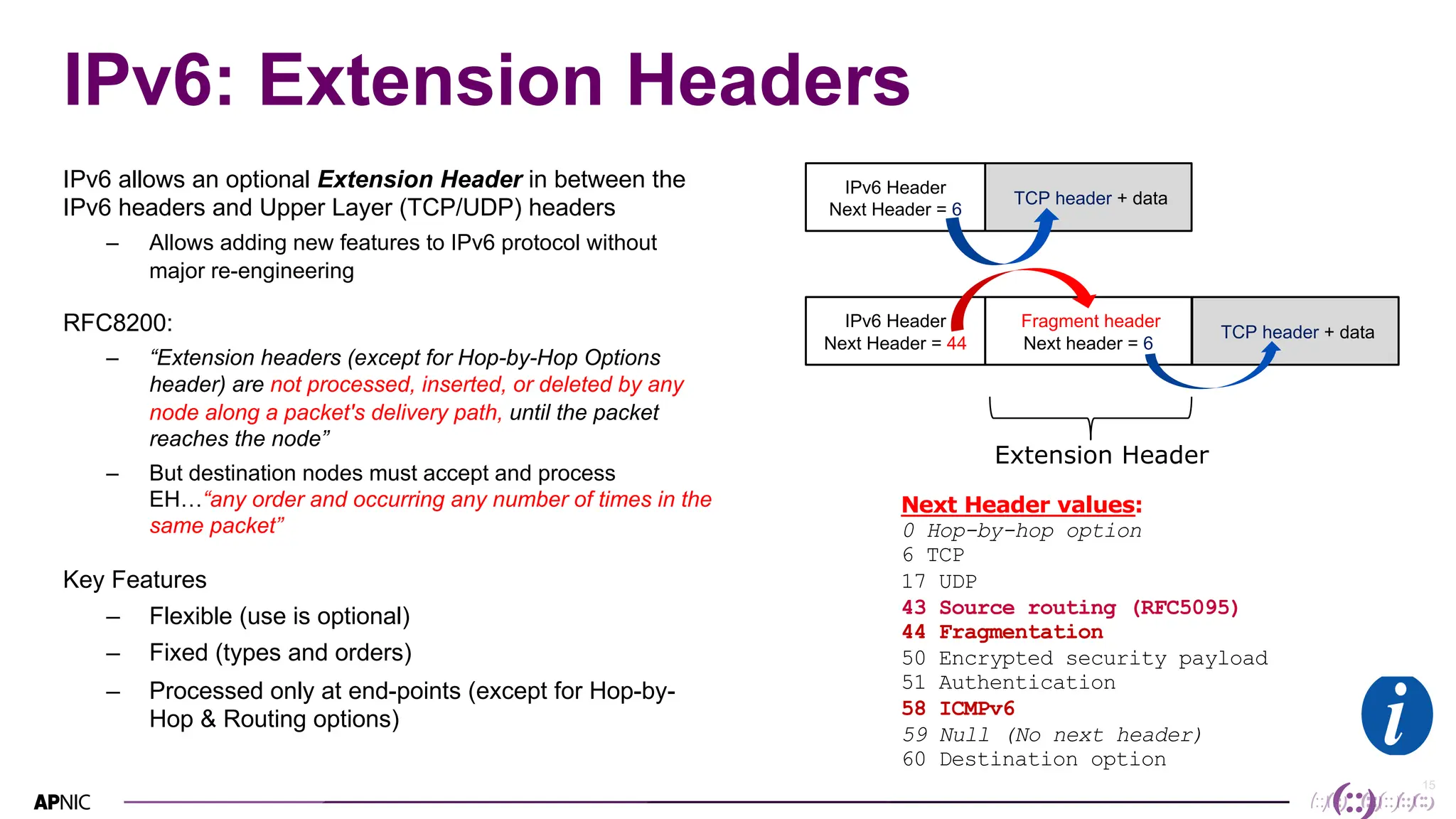
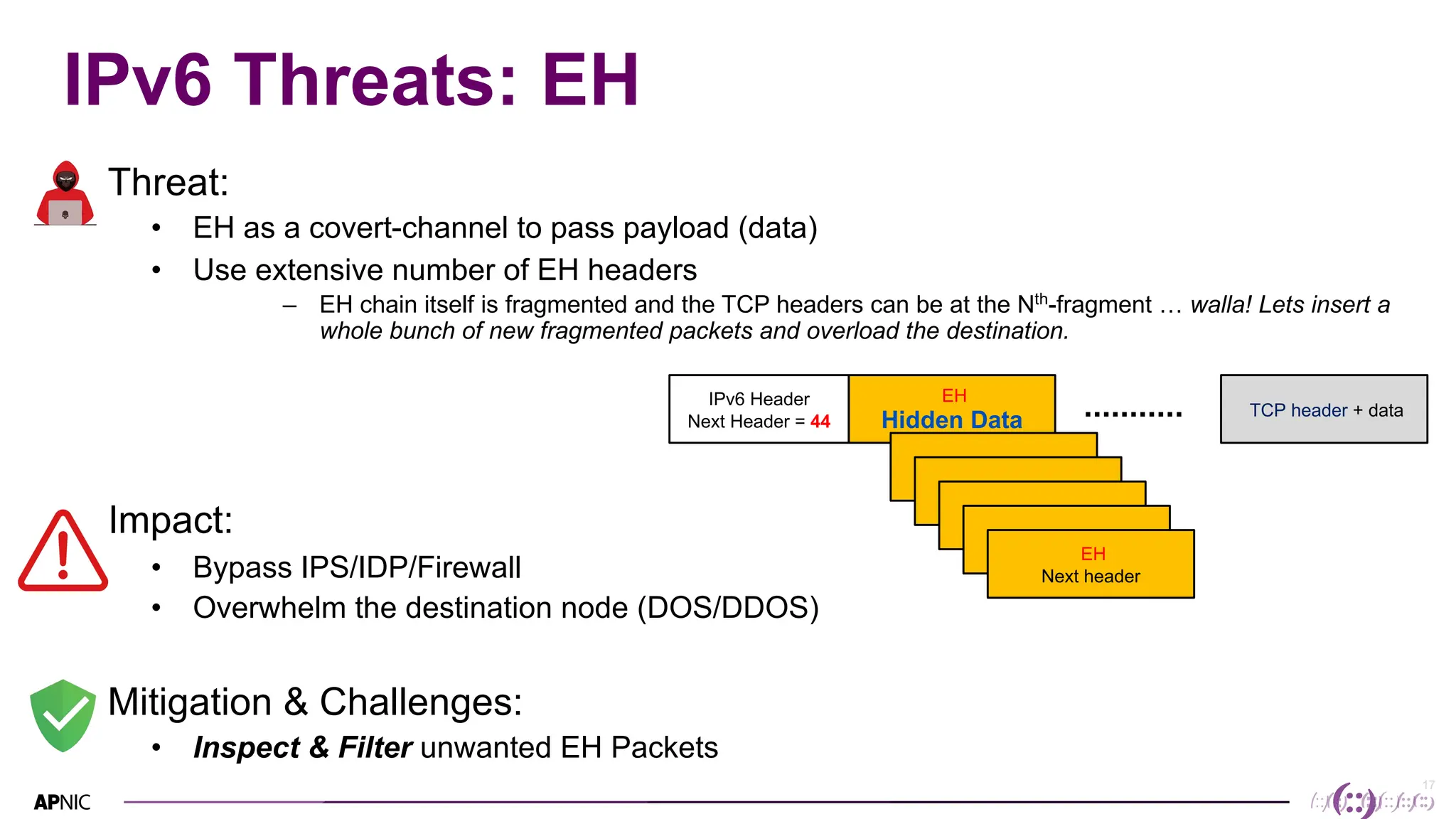
This document discusses IPv6 security. It begins with an overview of IPv6 address types and headers. It then notes that some initial assumptions about IPv6 security being more robust have been disproven in reality. Specifically, IPv6 is now the target of around 20% of malicious attacks. The document outlines several IPv6 security threats such as address spoofing, extension header attacks, neighbor discovery spoofing, and rogue router advertisements. It recommends approaches like ingress filtering, RA guard, and SEND to help detect and mitigate these threats. Tools like NDPMon can monitor for anomalies in neighbor discovery behavior. Overall, network operators must apply similar security practices to IPv6 as with IPv4, including access controls, host hardening, and







![18
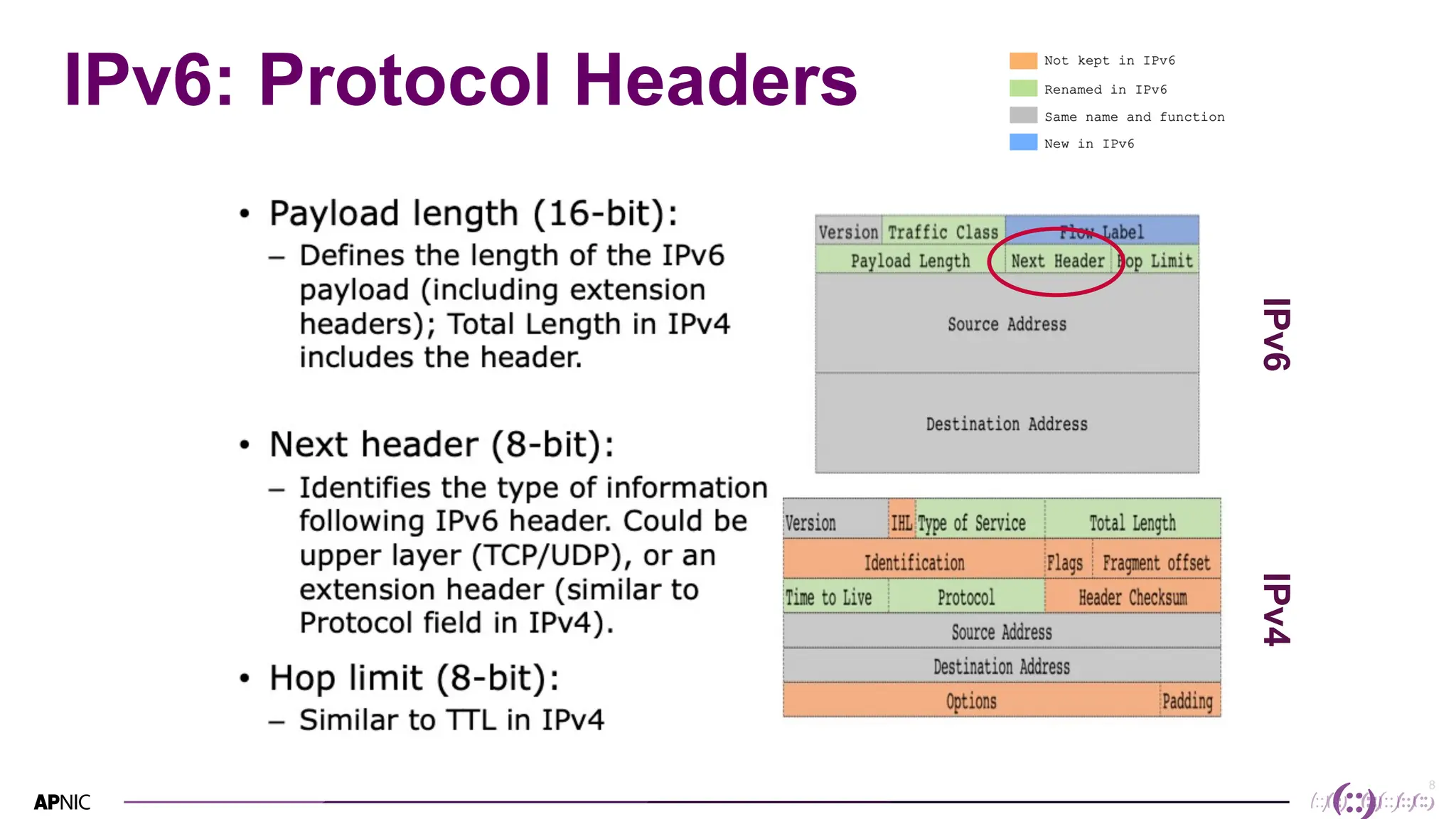
IPv6 Threats: EH - Routing Headers
• Include one or more IPs that
should be visited in the path
– Processed by the visited router
• Routing Header (Type 0):
– RH0 can be used for traffic
amplification over a remote path
• RH0 Deprecated [RFC5095]
– Disable IPv6 Source Routing
– Filter RH0 Packets
A B
Attacker
DST
RH0 Fields Addr[S]
S D
E F
Addr[A]
Addr[B]
Addr[A]
Addr[B]
Addr[A]
Addr[B]
Addr[D] DST
Targetted Link – BW usage](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ipv6sec-bdnog171698994097-231212045549-8e0d85fc/75/IPv6-Security-Overview-by-QS-Tahmeed-APNIC-RCT-18-2048.jpg)