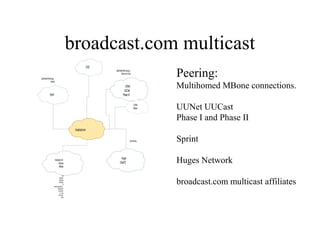
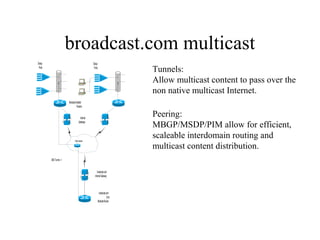
The document discusses multicast technology and strategies used by broadcast.com for efficient routing and content distribution across networks. It highlights the importance of peering protocols such as mbgp/msdp and pim for scalability, as well as the challenges posed by vendor support and application limits. Future prospects in 1999 include wider enterprise deployment, improved quality of service, and the need for standardized tools to enhance interoperability.