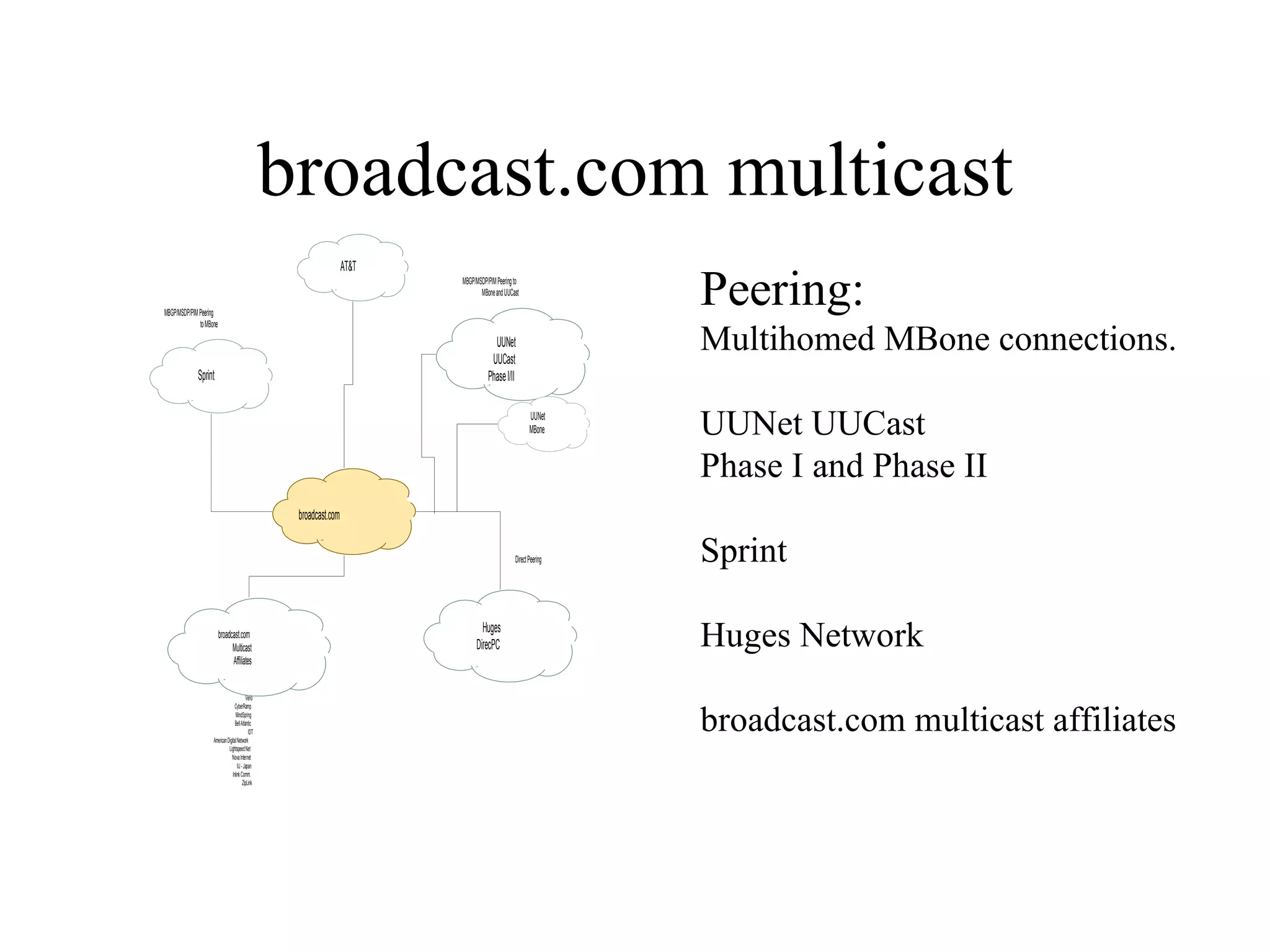
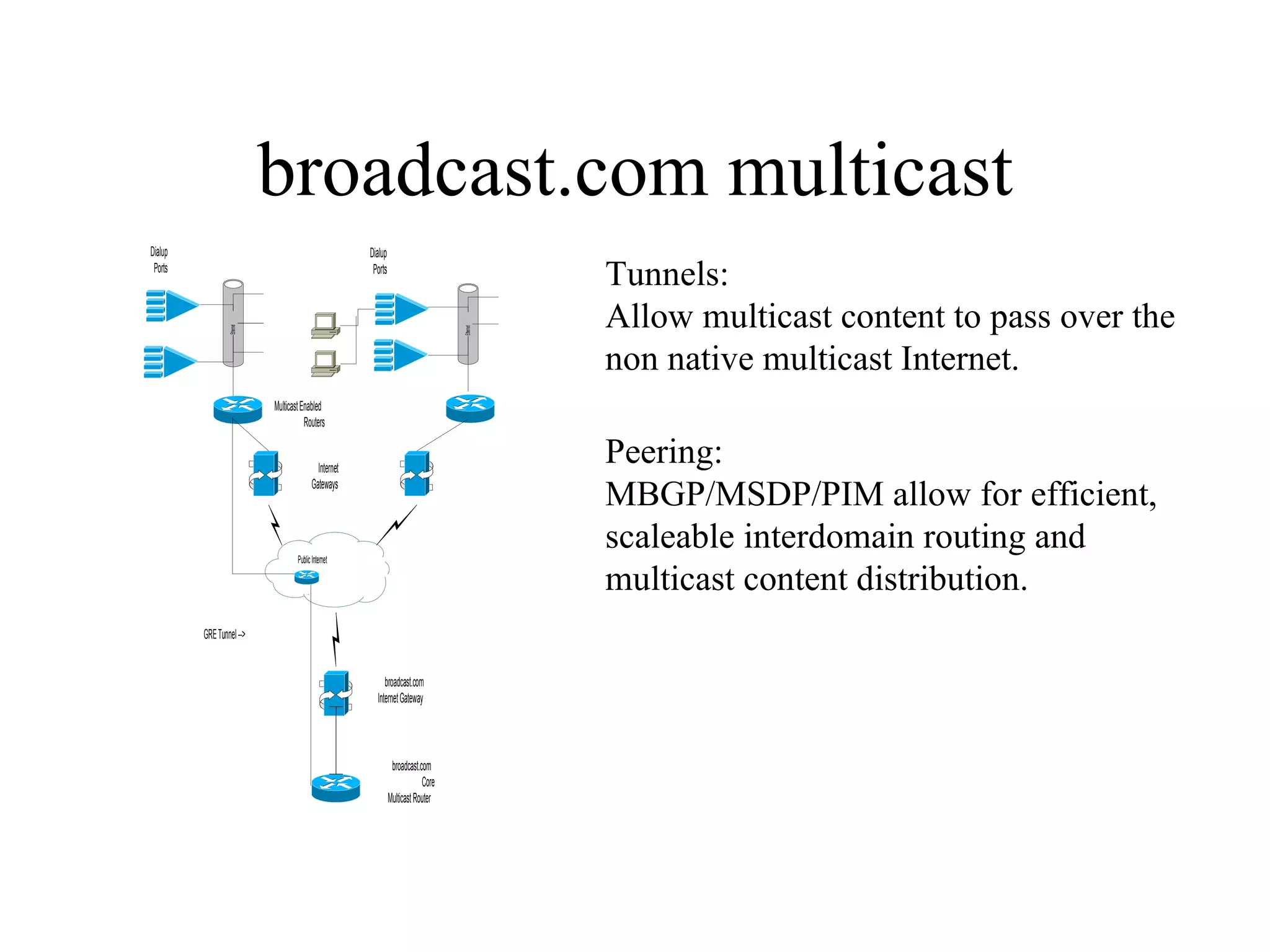
The document discusses multicast networking using broadcast.com as an example. It describes using multicast connections and tunnels to distribute content between networks like UUNet and Sprint. It also notes pitfalls like lack of vendor support and challenges of large-scale deployment. It advocates for protocols like MBGP, MSDP and PIM for more efficient inter-domain routing compared to older protocols. It predicts larger enterprise deployments of multicast in 1999 with improvements in quality of service, management, applications and broadband infrastructure.