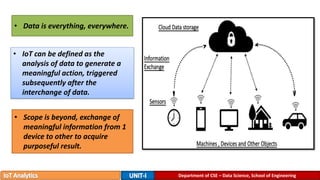
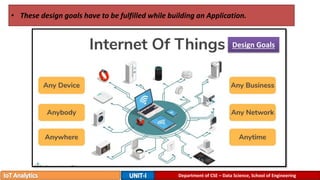
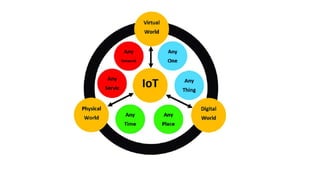
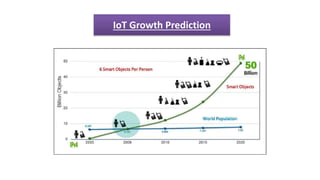
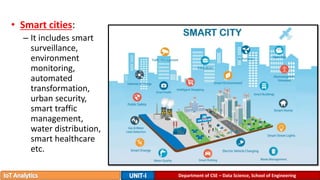
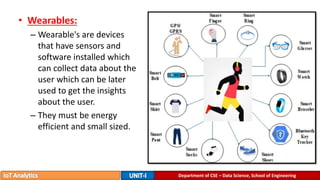
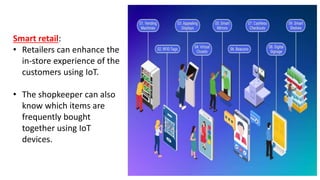
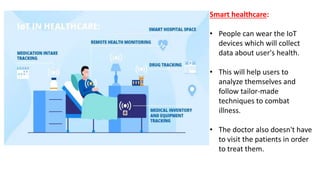
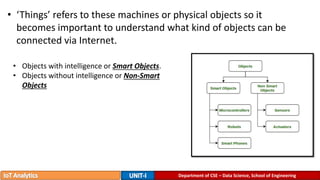
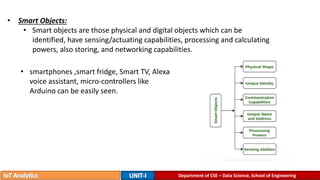
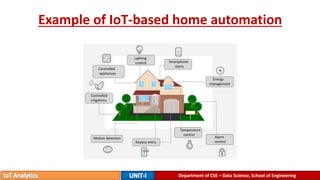
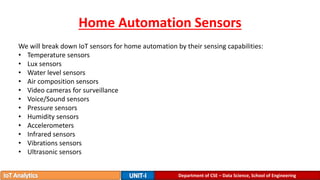
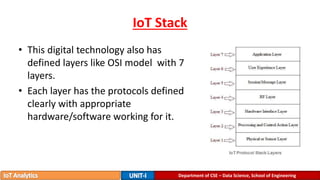
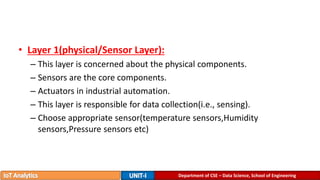
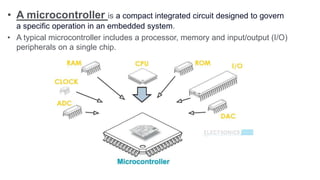
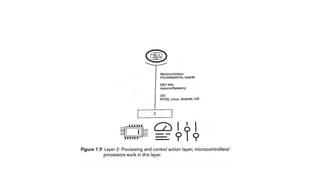
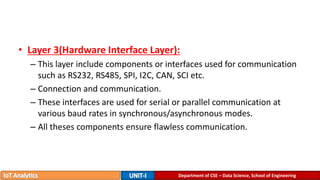
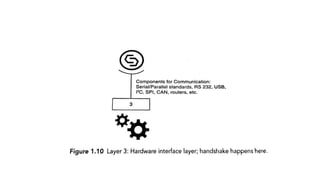
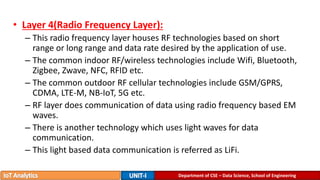
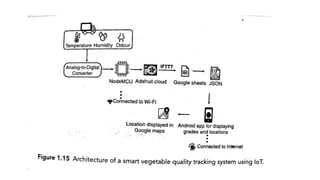
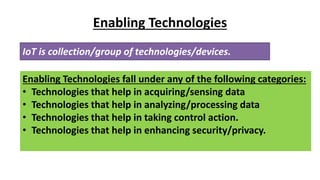
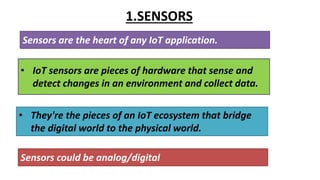
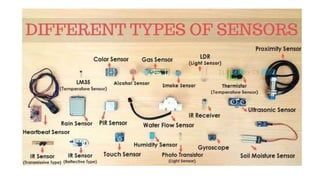
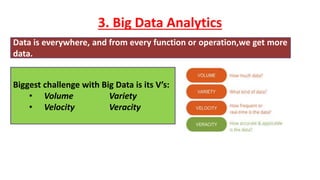
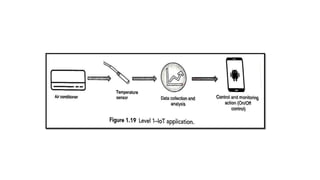
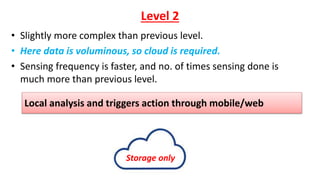
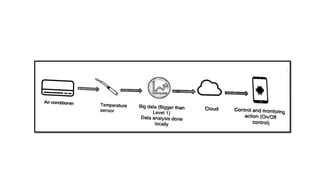
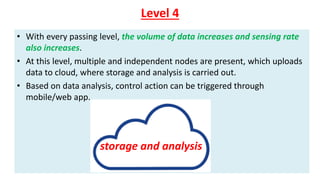
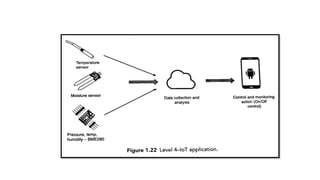
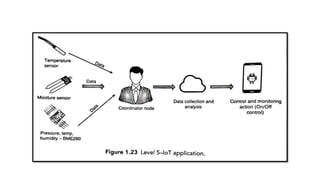
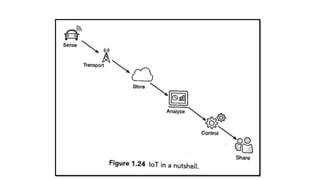
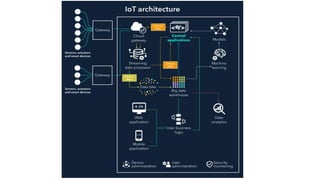
The document provides an introduction to the Internet of Things (IoT), detailing its definition as a network of interconnected devices that can collect and exchange data, and highlights its application areas, including smart homes, cities, healthcare, and wearables. It addresses key characteristics of IoT, such as connectivity, intelligence, scalability, and safety, while also outlining various components, layers, and protocols involved in IoT technology. Additionally, it explores challenges and future growth predictions for IoT as a transformative technology.