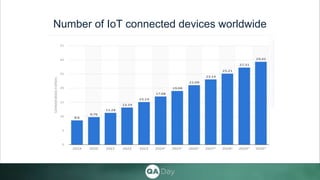
The document details an IoT testing manual presented by Bohdan Savchuk, aimed at various QA professionals, covering unique challenges and techniques in IoT testing. It outlines different approaches such as manual QA, cybersecurity, automation, and performance testing, along with their respective tasks, techniques, and benefits. The conclusion emphasizes the importance of integrating both manual and automated techniques for advancements in the IoT industry.