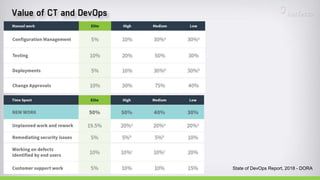
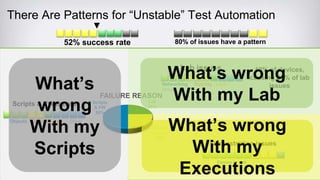
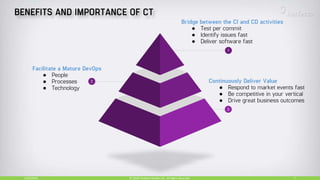
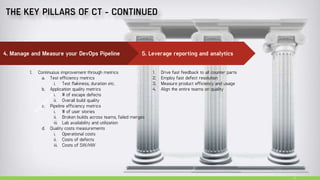
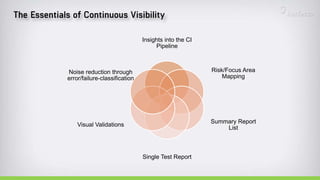
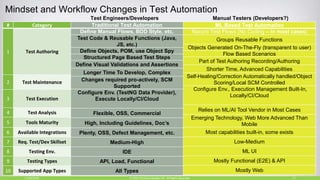
The document discusses continuous testing as a means to automate tests in the software delivery pipeline for fast feedback on business risks. It highlights common issues in test automation, such as instability and failure patterns, and emphasizes the need for a risk-based approach to improve testing efficiency. Additionally, it outlines the role of machine learning in test automation, including use cases for recognizing objects and making quality-related decisions based on data.