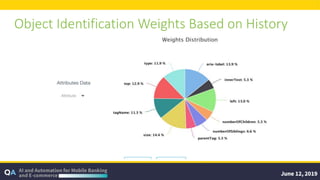
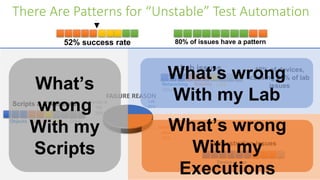
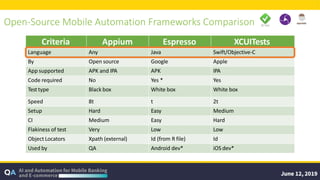
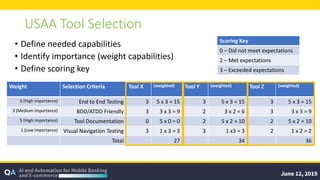
The document outlines guidelines for measuring the ROI of test automation, emphasizing the need for a business case, criteria for transitioning from manual to automated testing, and best practices for test selection. It discusses the use of AI and ML in test automation, techniques for assessing costs and efficiencies, and key metrics for productivity. Additionally, it provides a comparative analysis of different testing frameworks and selection criteria based on organizational needs.