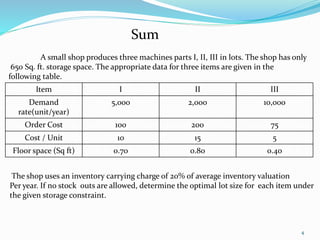
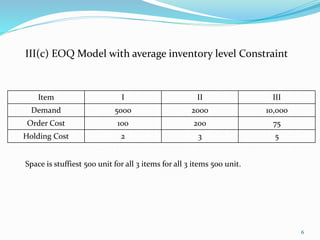
The document discusses multi-item inventory models that account for constraints like limited warehouse capacity, total investment, or number of orders. It presents assumptions and notations for developing inventory models under various constraints. As an example, it provides data on the demand, costs, and space requirements for three machine parts and calculates the optimal lot size for each under the given storage constraint of 650 square feet.