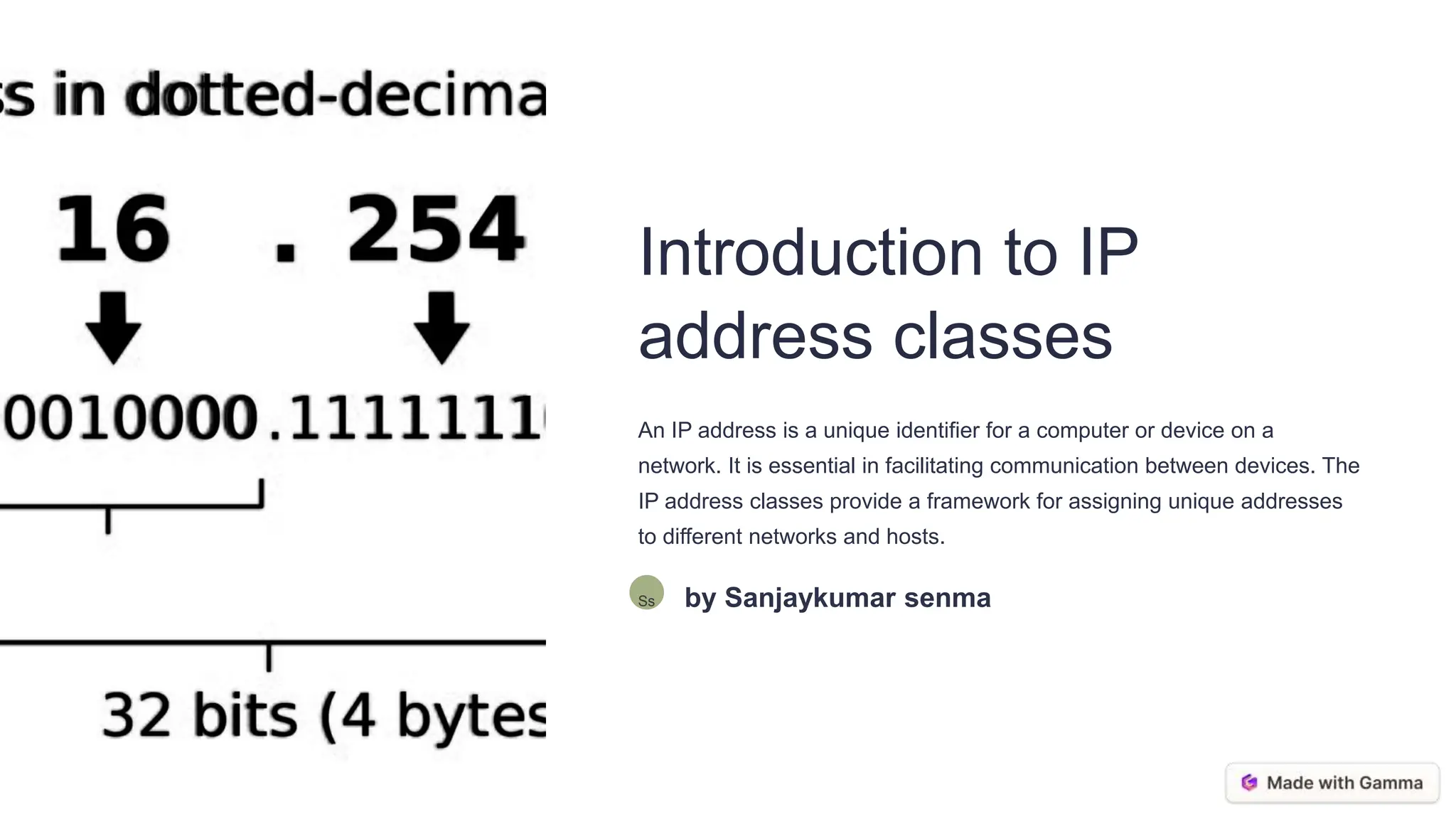
IP addresses are assigned using address classes that divide them into network and host portions. Class A uses 1 octet for network with up to 126 networks but many hosts each. Class B uses 2 octets for network with 65,000 networks and fewer hosts each. Class C uses 3 octets for network with over 2 million networks but very few hosts each. Subnetting further divides large networks into smaller subnetworks for more efficient management and addressing. It improves performance, scalability and security.