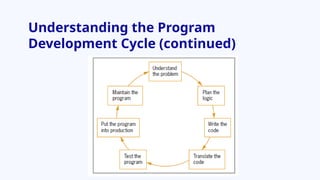
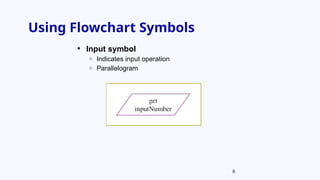
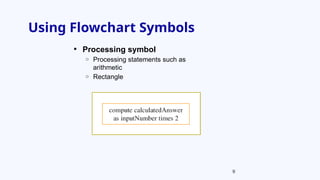
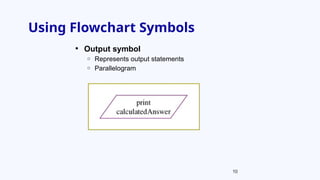
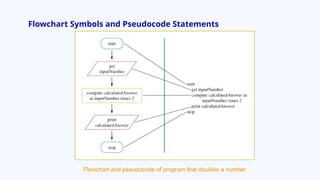
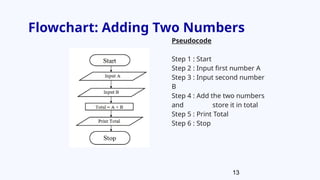
The document provides an overview of program development, including the use of pseudocode and flowcharts to represent logical steps in solving programming problems. It outlines the program development cycle, which encompasses understanding problems, logic planning, coding, and execution. The document further demonstrates how to write pseudocode and draw flowcharts with specific examples like doubling a number and calculating areas.






![14
Flowchart: Calculating area of a square
Pseudocode
Step 1 : Start
Step 2 : Read value for a (side)
Step 3 : [Compute] Area = A * A
Step 4 : Output Area
Step 5 : Stop
Complete the flowchart.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introtoprogramminglec-02-241015030419-056bdcac/85/Introduction-to-Programming-Lecture-Material-2-14-320.jpg)
