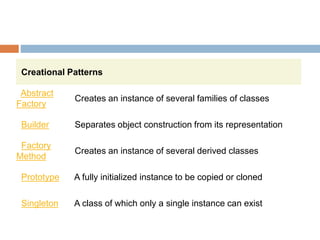
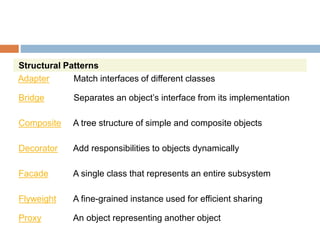
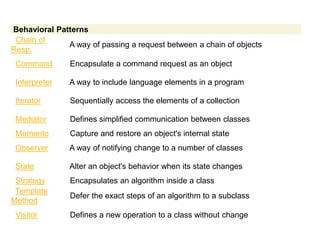
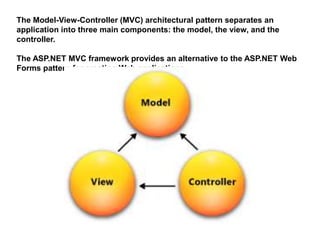
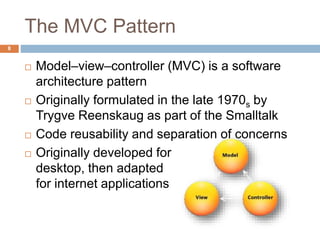
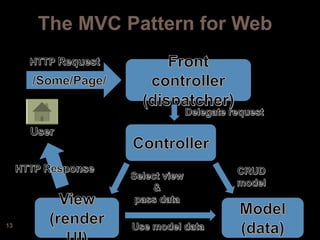
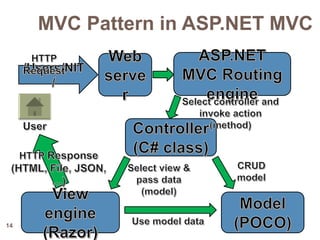
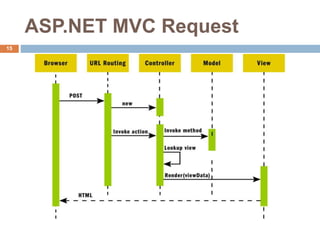
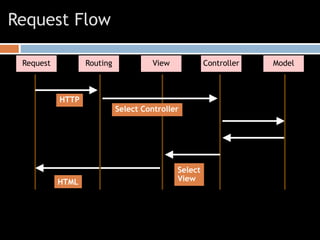
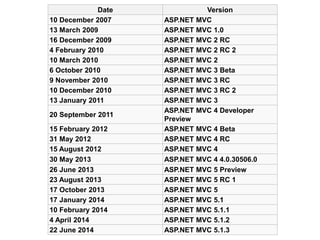
The document discusses design patterns and the Model-View-Controller (MVC) architectural pattern. It describes the 23 Gang of Four design patterns categorized into creational, structural, and behavioral patterns. It then explains the MVC pattern, how it separates an application into the model, view, and controller components, and the typical request flow from request to response. Finally, it provides a brief history of ASP.NET MVC and the technologies used in ASP.NET MVC development.