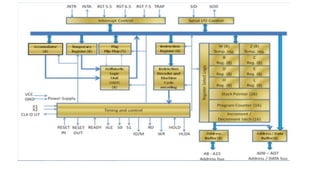
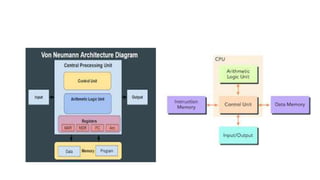
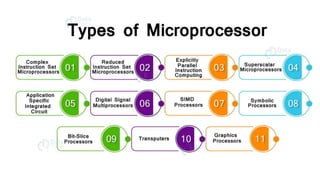
A microprocessor is an integrated circuit that functions as the central processing unit of a computer, executing instructions and performing calculations. The document outlines the evolution of microprocessors, detailing key milestones and the fetch-decode-execute cycle, as well as the architectural differences between von Neumann and Harvard architectures. Applications of microprocessors include personal computing devices, embedded systems, and various consumer electronics.