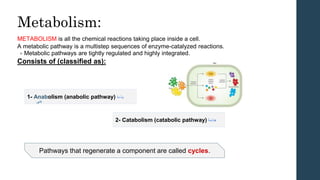
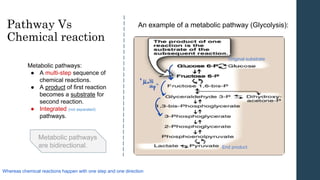
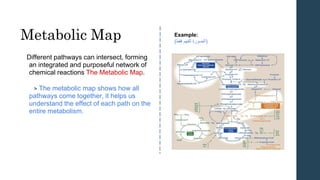
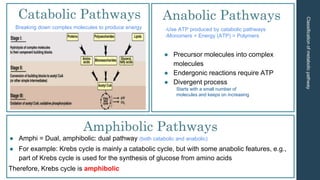
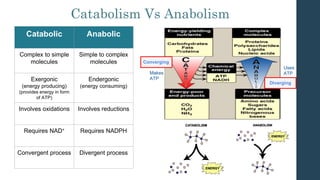
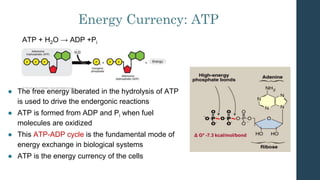
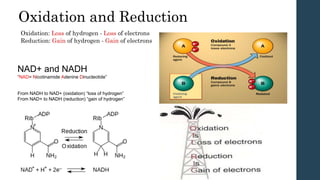
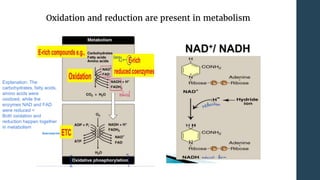
This document discusses metabolism and metabolic pathways. It defines metabolism as all the chemical reactions that take place inside a cell. Metabolic pathways are multi-step sequences of enzyme-catalyzed reactions that are tightly regulated and integrated. There are two main types of pathways: anabolic pathways that build complex molecules, and catabolic pathways that break down molecules to release energy. ATP is produced through catabolism and used to fuel endergonic anabolic reactions. Metabolism involves both oxidation and reduction reactions, with NAD+ and NADH acting as electron carriers. Metabolism is regulated through substrate availability, product inhibition, and allosteric effectors. The major metabolic fuels are carbohydrates, lipids, and