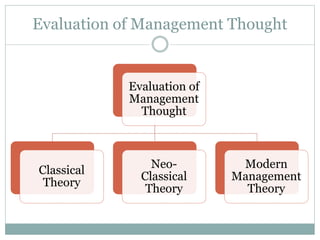
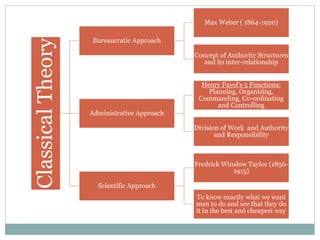
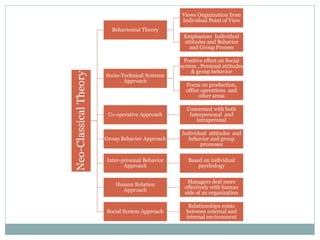
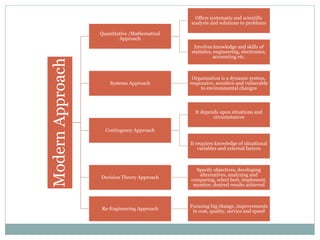
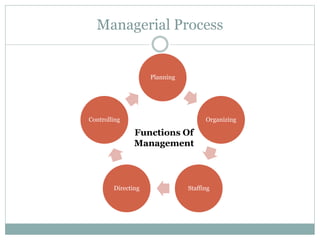
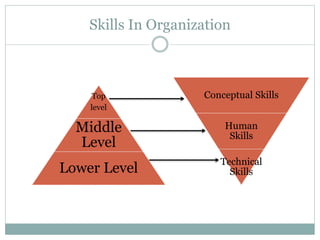
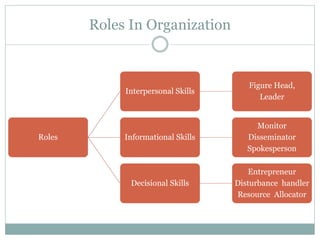
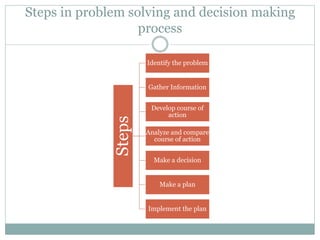
The document covers various aspects of the management process, including planning, organizing, staffing, directing, and controlling. It discusses the evolution of management theories such as classical, neo-classical, and modern approaches, emphasizing the roles and skills of managers at different organizational levels. Additionally, it outlines decision-making techniques, problem-solving processes, and group decision-making stages.