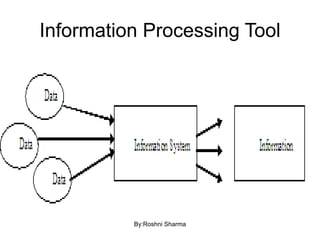
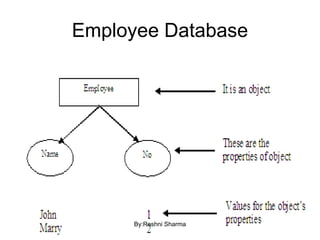
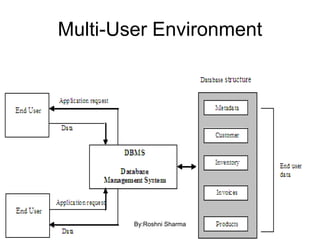
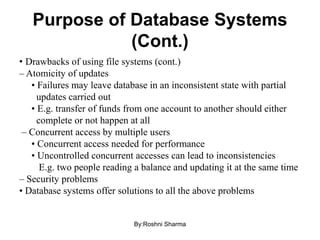
This document defines key concepts in databases including data, information, database, database management system (DBMS), and database system. It states that data are raw facts that become information after processing. A database is a collection of related data that represents some aspect of the real world. A DBMS is a collection of programs used to access and manage a database. The purpose of database systems is to solve issues with using file systems to store data, such as data redundancy, difficulty of access, lack of integrity, and not supporting concurrent access by multiple users. Characteristics of database approaches include being self-describing through a data dictionary, insulating programs from data, supporting multiple views, and enabling sharing and transaction processing of data among multiple