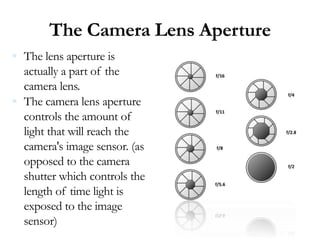
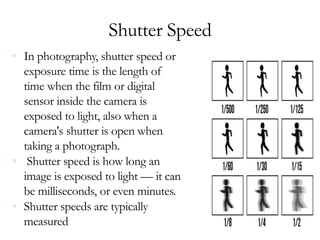
This document discusses the major parts and functions of a camera. It explains that a camera contains a lens to focus light and a shutter to control exposure time. It also includes a mirror, viewfinder, flash, buttons to control focus, ISO, shutter speed, and more. The document provides details on how each component works and its role in capturing and processing an image.