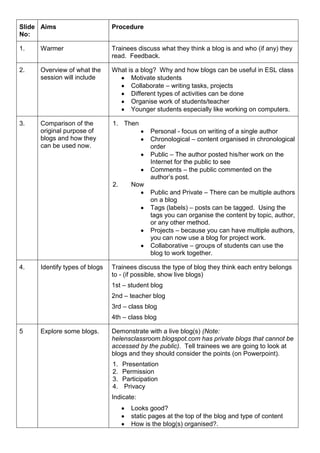
This document provides guidance for using blogs in ESL classrooms. It begins by discussing the original purpose of blogs and how they are now used. Types of blogs are identified as public, private, teacher, student, and class blogs. Live blogs are demonstrated and criteria for evaluating them are provided. Teachers are encouraged to use blogs to share resources, homework, projects, and information. Motivating ongoing blog use is discussed. Factors to consider when planning a blog are outlined. The document concludes by providing guidance on setting up blogs with Blogger and including useful websites for learning more features.