This document provides an introduction to biological classification, including:
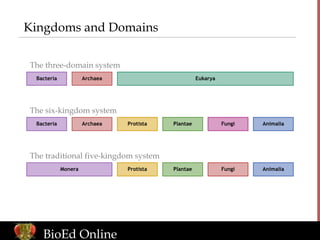
- Biologists classify organisms to represent evolutionary relationships and respond to new knowledge.
- Carolus Linnaeus established binomial nomenclature using genus and species names.
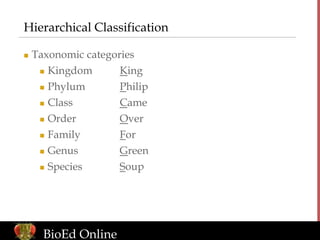
- Classification uses a hierarchical system of seven categories from kingdom to species.
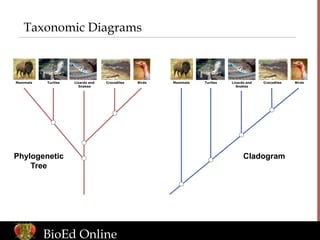
- Systematics studies evolution by combining evidence from fossils, anatomy, DNA, and other areas.
- Diagrams and dichotomous keys are used to classify and identify organisms.