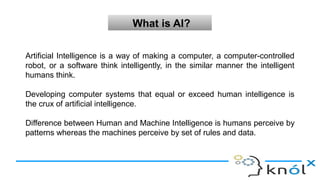
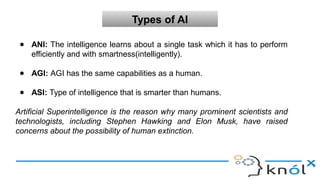
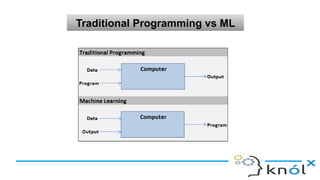
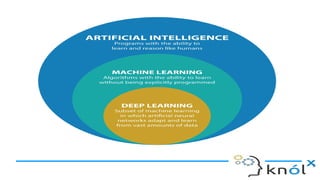
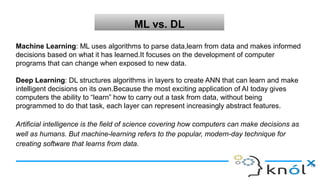
The document introduces artificial intelligence (AI) and its goals, emphasizing its aim to replicate human-like intelligent behavior through various disciplines such as psychology and linguistics. It distinguishes between types of AI, including artificial narrow intelligence, general intelligence, and artificial superintelligence, while also contrasting traditional programming with machine learning and deep learning techniques. Additionally, the document covers Prolog, a logic programming language used in AI, explaining its structure, including facts, rules, and queries.




![List in Prolog
● Prolog also has a special facility to split the first part of the list (called the
head) away from the rest of the list (known as the tail).
Example:
● [a,b,c] unifies with [Head|Tail] resulting in Head=a and Tail=[b,c].
● p([a], X, Y). x=[a],y=[]
15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontoaiusingprolog-190117071444/85/Introduction-To-AI-Using-Prolog-15-320.jpg)

