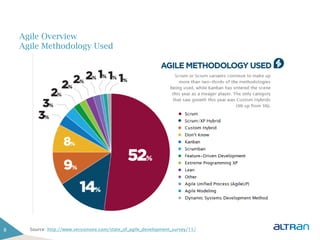
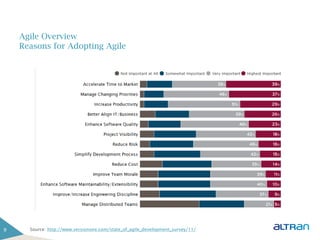
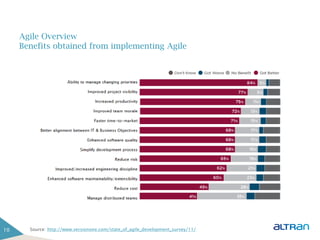
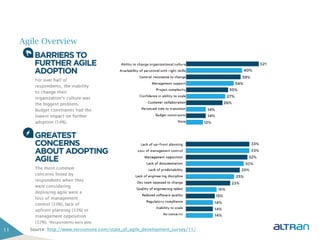
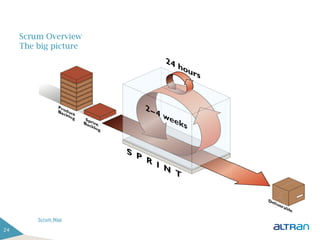
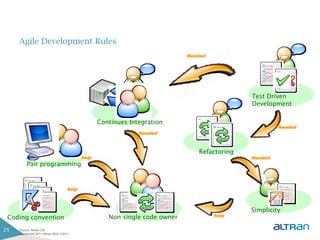
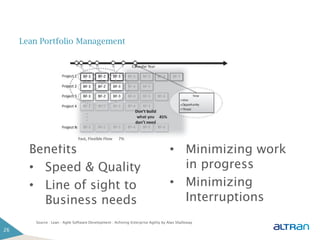
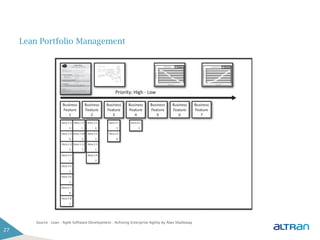
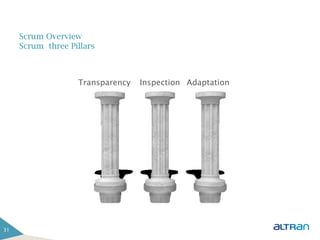
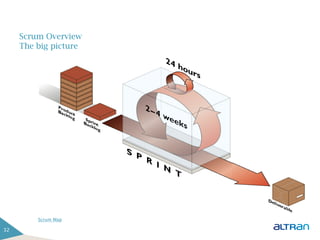
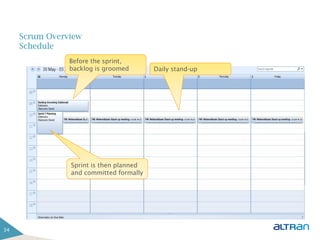
The document provides an introduction to agile methodologies and Scrum, outlining key concepts like iterative development, self-organizing teams, and delivering working software frequently. It also describes Scrum practices such as sprint planning, daily stand-ups, sprint reviews and retrospectives. The goal of the document is to educate people about agile and Scrum principles and processes through presentations and exercises.