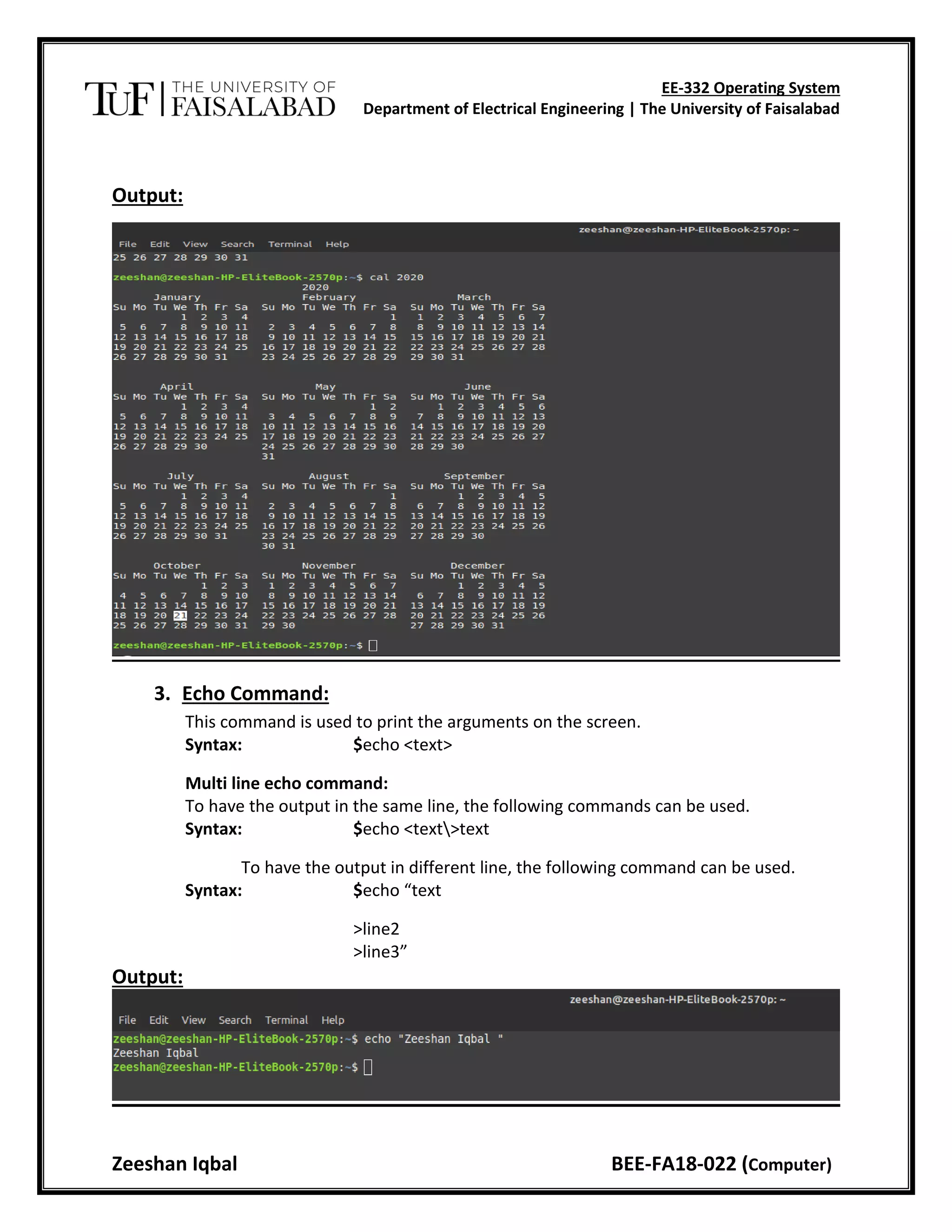
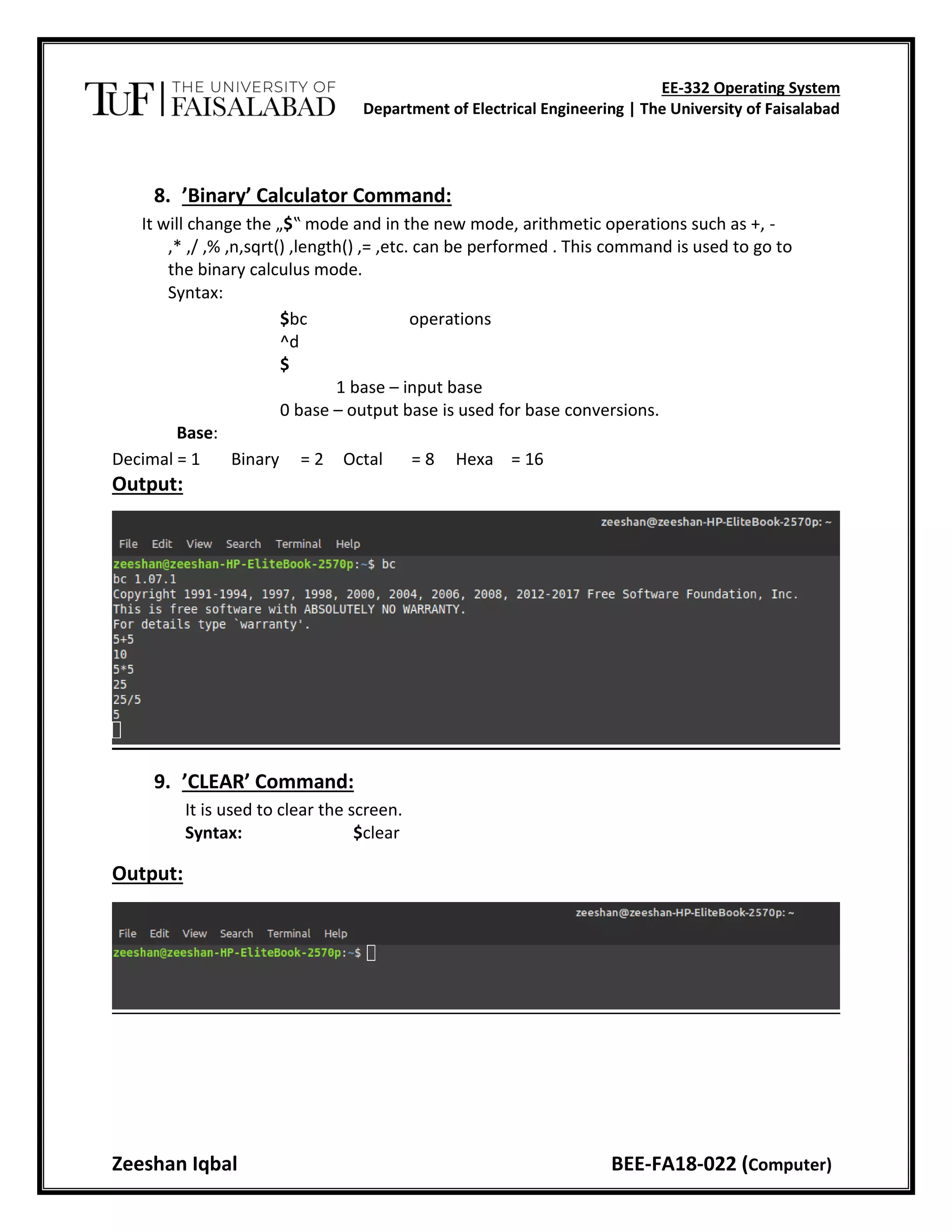
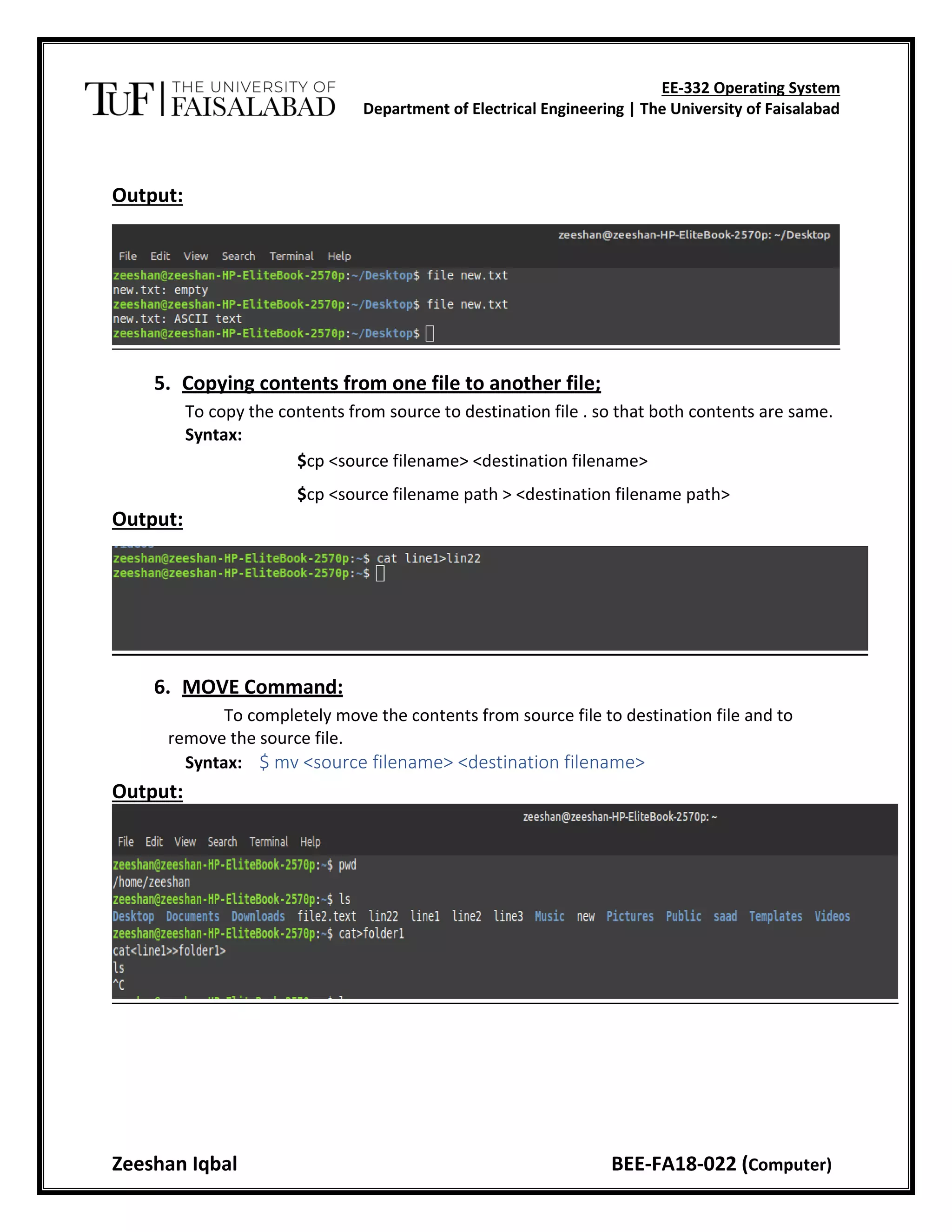
This document provides instructions for commands in Linux including commands to display the date and time, calendar, echo text, view who is logged in, change directories, manage files and directories, and more. It explains the syntax and use of commands like date, cal, echo, who, cd, ls, mkdir, rmdir, cat, cp, mv, rm, sort, and man. The objective is to study and execute basic commands in the Linux operating system.