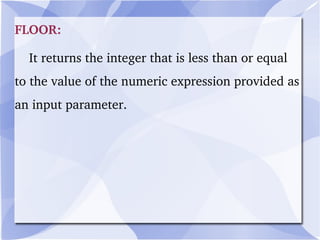
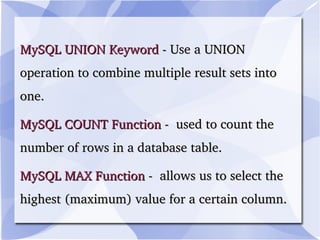
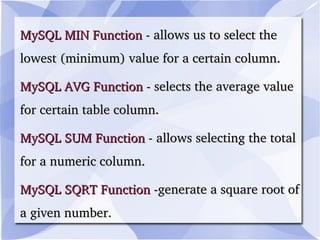
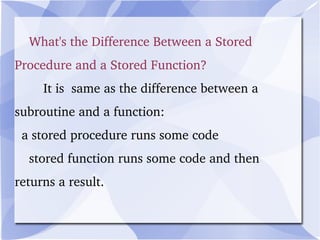
MySQL is an open-source relational database management system that runs on a server and allows for multi-user access to databases. It is commonly used with web applications and by popular websites. MySQL uses commands like SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE to retrieve, add, modify and remove data from databases. It also supports stored procedures and functions to organize more complex queries and calculations.