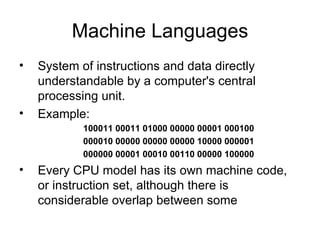
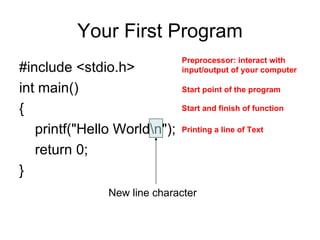
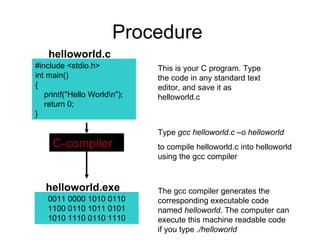
This document provides an overview and syllabus for a spring 2010 C programming language course. It introduces the goals of learning to read, write, compile, execute, and debug C programs. It outlines the course content which will cover C program structure, data types, control statements, functions, pointers, and more. Example C code for a simple "Hello World" program is provided and explained.