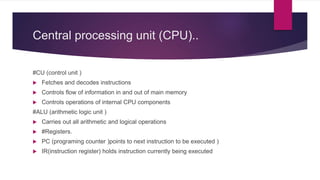
The document outlines the basics of computers and programming, covering essential concepts such as hardware components (CPU, memory, storage), software types (operating systems, application software), and programming languages (machine, assembly, high-level). It explains the process of programming, including problem-solving techniques and steps to compile and execute code. Additionally, it provides a historical context for algorithms and the evolution of programming languages.