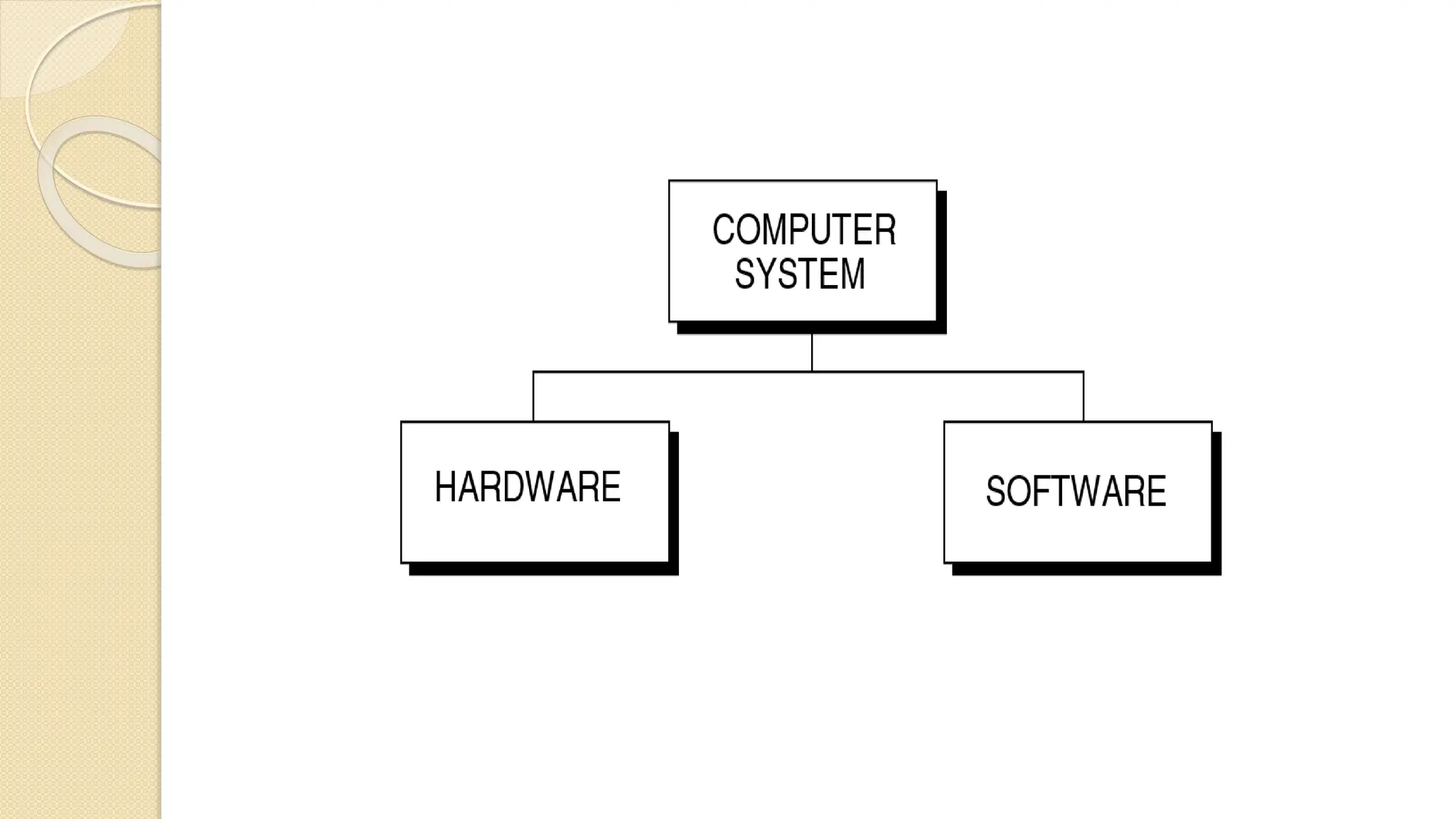
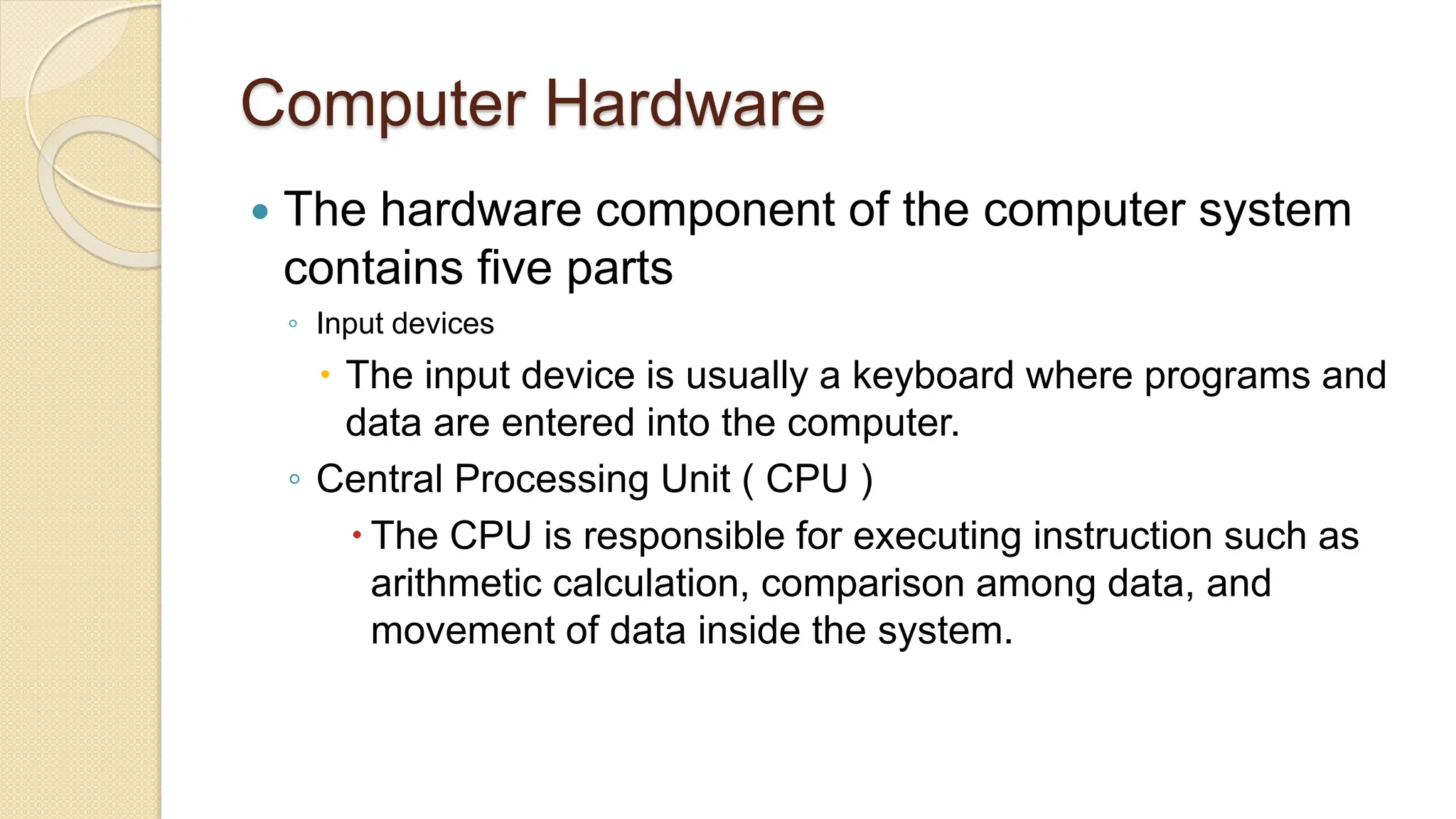
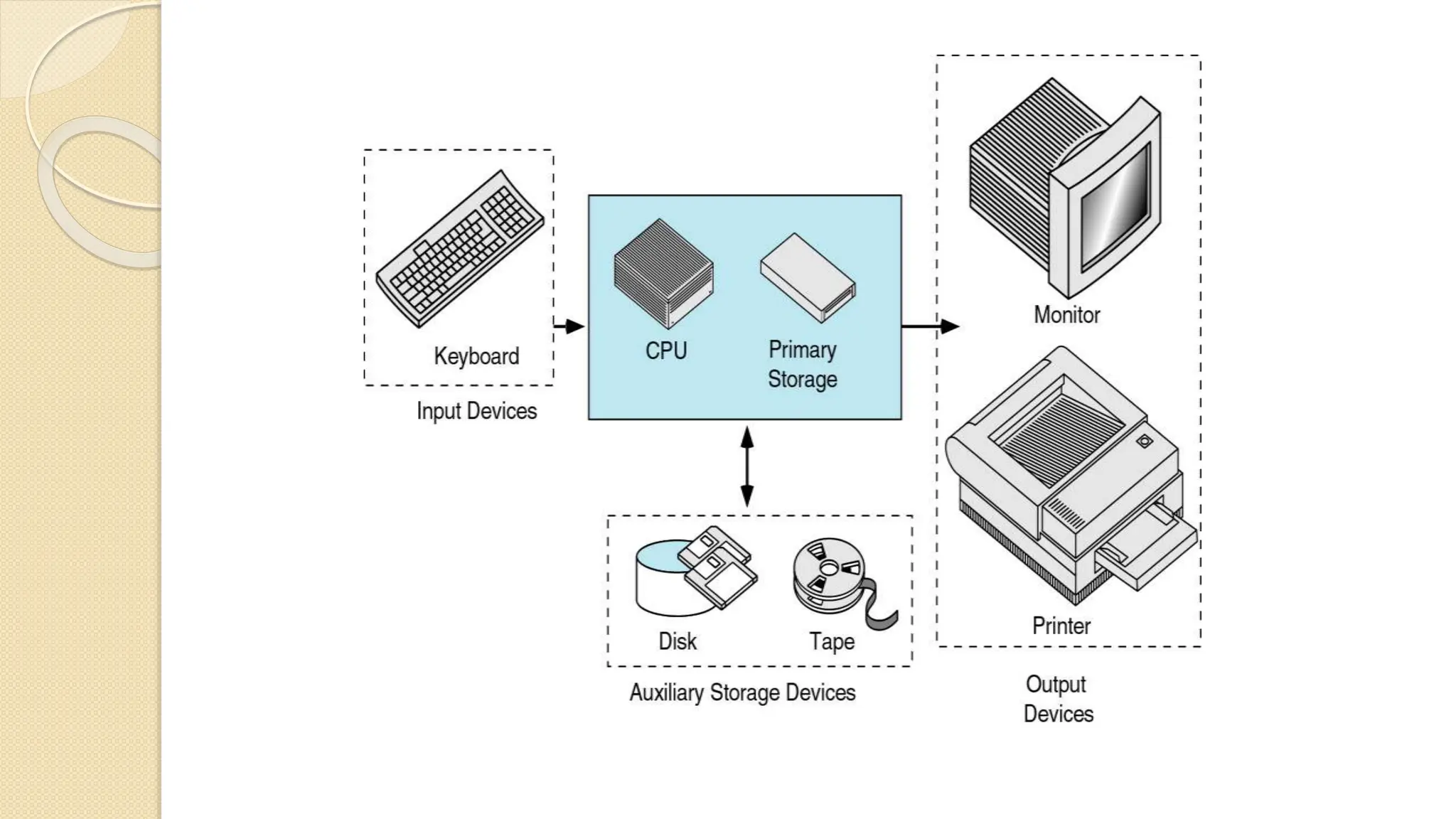
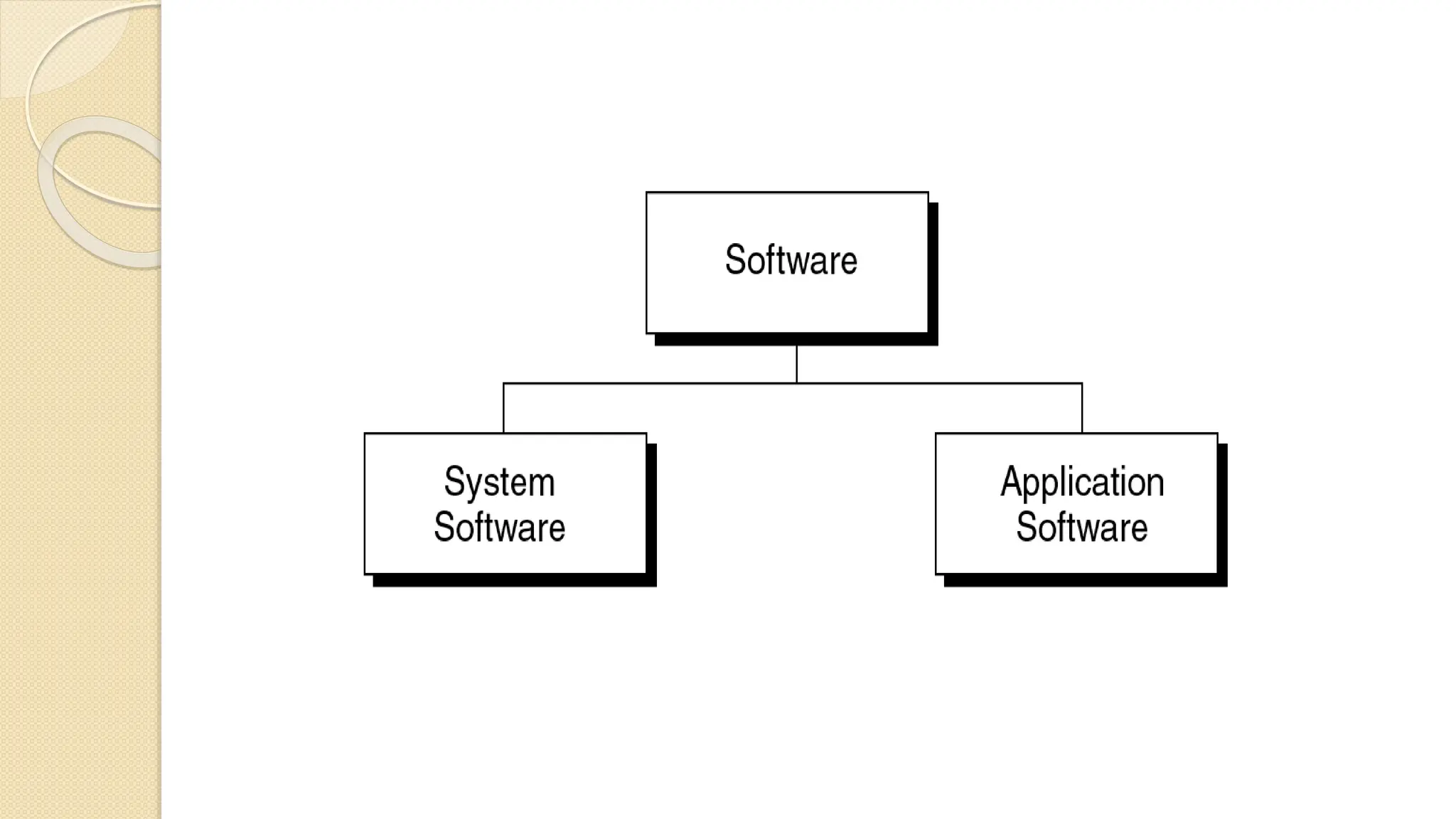
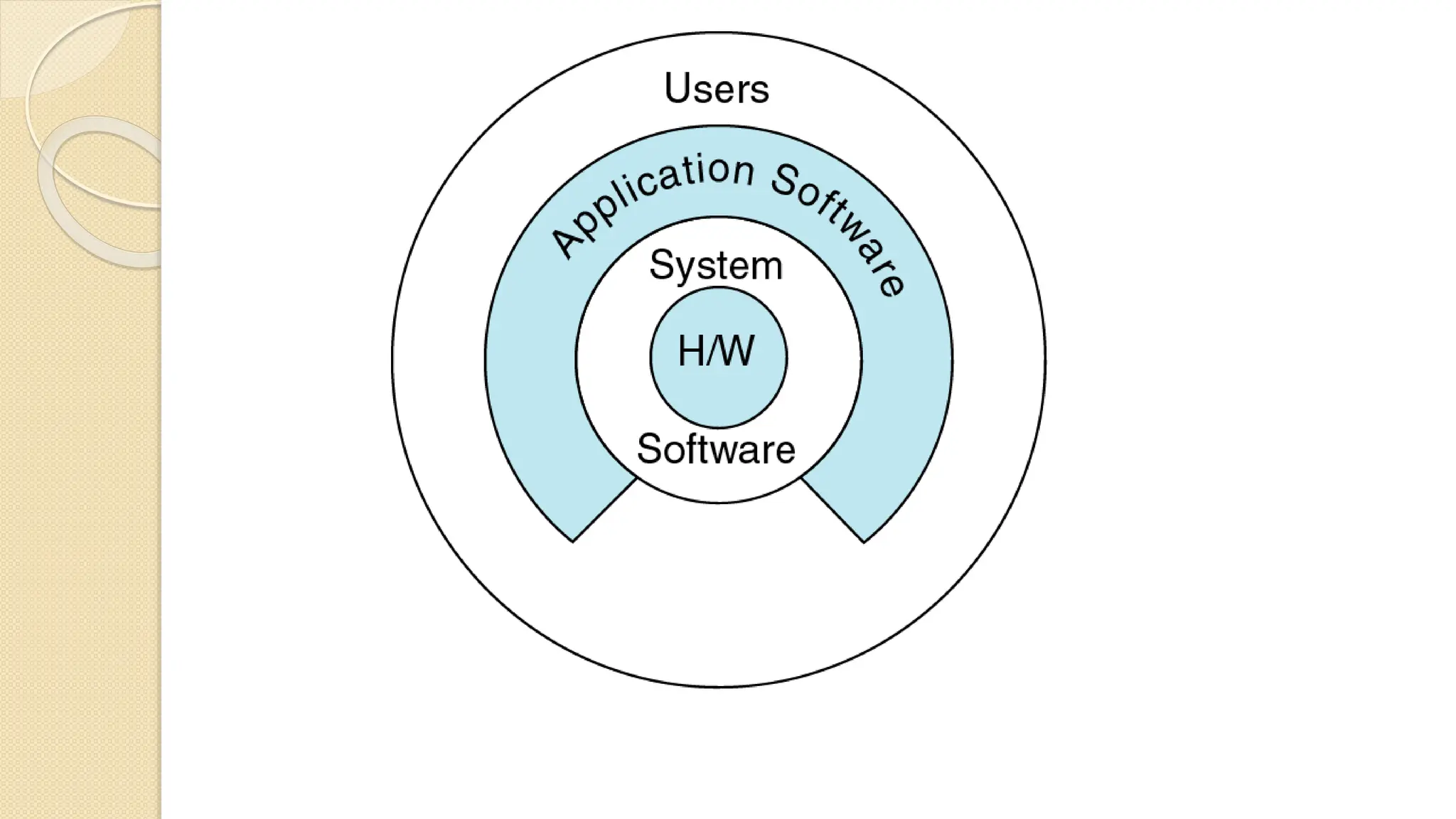
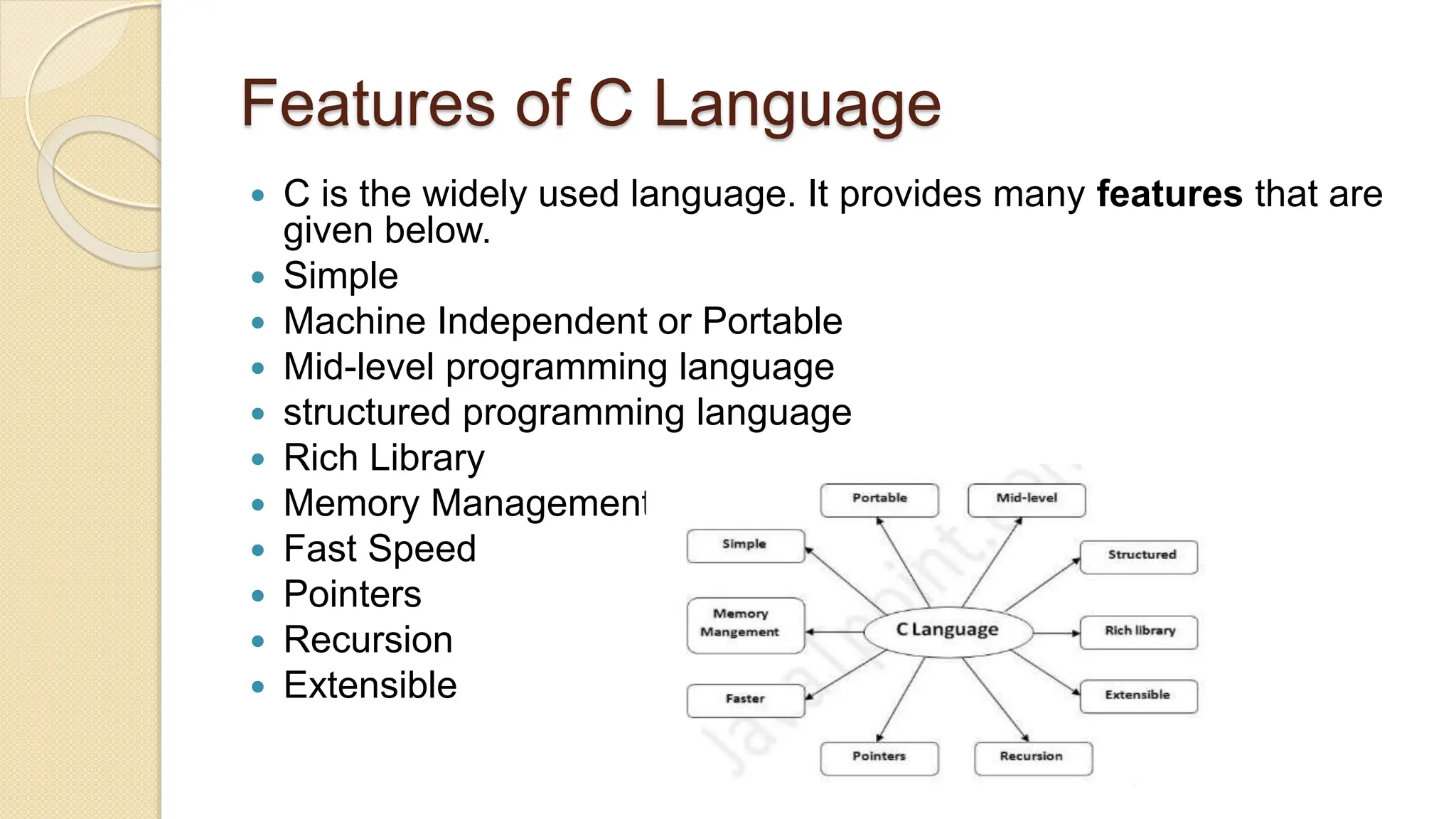
The document provides an introduction to computer systems and the C programming language, including its history, features, and structure. It explains the components of computer hardware and software, as well as the basics of writing and compiling C programs. Key aspects of C include its machine independence, procedural orientation, and dynamic memory management.