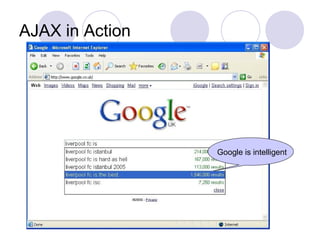
The document introduces Direct Web Remoting (DWR), an open-source Java library that facilitates interaction between Java server code and JavaScript in browsers, resembling a remote procedure call. It outlines the steps to create a DWR-enabled AJAX application, including configurations and client-side JavaScript implementation. Advantages of DWR include simplified code, elimination of URL mapping for services, and a built-in mechanism for handling asynchronous calls.