The document provides a comprehensive overview of data mining, detailing its processes, life cycle, methods, applications, challenges, and future scope. It outlines the stages of data mining, such as data cleaning, integration, selection, transformation, mining, evaluation, and representation, and discusses the various algorithms and techniques employed across different fields. The conclusion emphasizes the significance of data mining in extracting knowledge from vast databases and its applications in various domains, signaling its ongoing relevance and evolving methodologies.

![ABSTRACT
Data Mining is an approach to discover or extract
knowledge from Databases.
Generally to store databases, enterprises make data
warehouses and data marts.
Data warehouses and data marts contain large
mountains of data.
The mountains represent valuable resource to the
enterprise.
Due to extracting knowledge from large data
warehouses or depositories, data mining plays great
role in various fields of machine learning.
Data mining is used in education, medical, scientific,
business fields. Various algorithms and programs are
2
used for data mining approach.[1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/areviewondatamining-130415093951-phpapp01/85/A-review-on-data-mining-2-320.jpg)
![INTRODUCTION
Now the world of information technology, all things are
become automated.
Information technology is used in every field of human
life such as business, engineering, medical,
mathematical, scientific.
All these fields of human life have lead to the large
volume of data storage in various formats such as
records, files, documents, images, sounds, recordings,
videos and many new data.
Collection of related data is also known as database. To
extract correct data from large databases, the proper
mechanism is used, that mechanism is also known as
DATA MINING. It is a knowledge discovery technique
(KDD).[2] 3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/areviewondatamining-130415093951-phpapp01/85/A-review-on-data-mining-3-320.jpg)
![PROCESS
(1) Selection
(2) Pre-processing
(3) Transformation
(4) Data Mining
(5) Interpretation/Evaluation.[2,3]
4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/areviewondatamining-130415093951-phpapp01/85/A-review-on-data-mining-4-320.jpg)
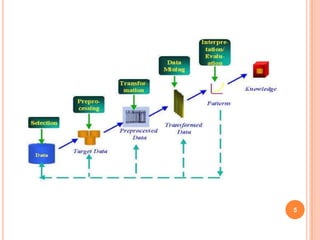

![CONTD…….
5. Data mining: It is the crucial step in which clever
techniques are applied to extract potentially useful patterns.
6. Pattern evaluation: In this step, interesting patterns
representing knowledge are identified based on given
measures.
7. Knowledge representation: It is the final phase in
which the discovered knowledge is visually presented to
the user. This essential step uses visualization
techniques to help users understand and interpret the
data mining results.[4,2]
7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/areviewondatamining-130415093951-phpapp01/85/A-review-on-data-mining-7-320.jpg)
![DATA MINING LIFE CYCLE
The Cross Industry Standard Process for Data
Mining (CRISP-DM) which defines six phases:
(1) Business Understanding
(2) Data Understanding
(3) Data Preparation
(4) Modeling
(5) Evaluation
(6) Deployment.[6]
8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/areviewondatamining-130415093951-phpapp01/85/A-review-on-data-mining-8-320.jpg)

![CONTD……
4. Modeling: In this phase, various modeling techniques
are selected and applied and their parameters are
calibrated to optimal values.
5. Evaluation: In this stage the model is thoroughly
evaluated and reviewed. The steps executed to
construct the model to be certain it properly achieves
the business objectives.
6. Deployment: The purpose of the model is to increase
knowledge of the data, the knowledge gained will need
to be organized and presented in a way that the
10
customer can use it.[6,8]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/areviewondatamining-130415093951-phpapp01/85/A-review-on-data-mining-10-320.jpg)

![CONTD……
Classification of data mining systems according to
mining techniques used: This classification is
according to the data analysis approach used such as
machine learning, Neural networks, genetic algorithms,
statistics, visualization, database oriented or data
warehouse-oriented, etc.[5,2]
12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/areviewondatamining-130415093951-phpapp01/85/A-review-on-data-mining-12-320.jpg)
![DATA MINING METHODS
On-Line Analytical Factor analysis
Processing (OLAP) Neural Networks
Classification Regression analysis
Association Rule Mining Structured data analysis
Temporal Data Mining Sequence mining
Time Series Analysis Text mining
Spatial Mining, Drug Discovery
Anomaly/outlier/change Exploratory data analysis
detection
Predictive analytics
Association rule learning
Web Mining
Cluster analysis
Data analysis etc.[1,8] 13
Decision trees](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/areviewondatamining-130415093951-phpapp01/85/A-review-on-data-mining-13-320.jpg)
![DATA MINING APPLICATIONS
Games
Business
Science and Engineering
Human rights
Spatial data mining.[5]
14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/areviewondatamining-130415093951-phpapp01/85/A-review-on-data-mining-14-320.jpg)
![CHALLENGES
Sensor data mining
Pattern mining
Visual data mining
Subject based data mining
Music data mining
The Digital Library retrieves.[1,2,5]
15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/areviewondatamining-130415093951-phpapp01/85/A-review-on-data-mining-15-320.jpg)
![CONCLUSION
In this paper I briefly reviewed data mining, background
of data mining, methods, life cycle model, and types of
data mining, application of it.
This review will be helpful to you to easily understand
what data mining is, previously used data mining
techniques.
Now days use data mining techniques and also process
of data mining.
In this I completely, explain applications and types of
data mining. [1,2,4,5]
16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/areviewondatamining-130415093951-phpapp01/85/A-review-on-data-mining-16-320.jpg)
![FUTURE SCOPE
Data mining is a very wide concept. It contains many
concepts such as various algorithms to extract
knowledge from large databases.
Soft Computing techniques like Fuzzy logic, Neural
Networks and Genetic Programming which contains
Complex data objects Includes high dimensional, high
speed data streams, sequence, noise in the time series,
graph, Multi instance objects, Multi represented objects
and temporal data etc.
These are used in Business, Web, Medical diagnosis,
Scientific and Research analysis fields (bio, remote
sensing etc…), Social networking etc.[1,7]
17](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/areviewondatamining-130415093951-phpapp01/85/A-review-on-data-mining-17-320.jpg)