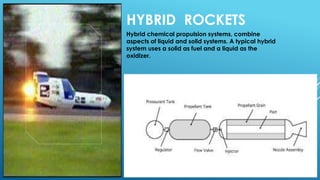
This document discusses rocket propulsion systems. It describes that rockets operate using conservation of momentum and Newton's third law of motion. Propulsion systems are classified by the type of energy transferred to propellant, including thermodynamic and electrodynamic propulsion. Thermodynamic systems transfer heat and pressure to propellant and expel it through a nozzle. Examples discussed include cold gas thrusters, liquid and solid chemical rockets, and hybrid rockets which use aspects of both liquid and solid fuel systems. The document also briefly mentions solar electric rockets and nuclear thermal rockets as future propulsion methods.