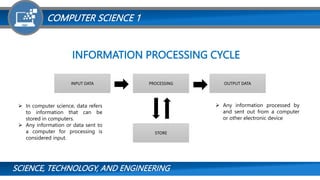
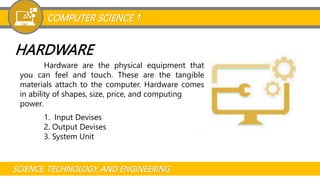
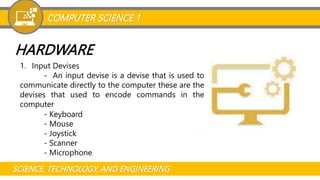
The document provides an overview of computer science and the basic elements of a computer system. It defines what a computer is and discusses different types of computers categorized by data management (analog, digital, hybrid) and processing power (personal computer, workstation, minicomputer, mainframe, supercomputer). It also explains the key elements that make up a computer system including hardware components like the CPU, memory, motherboard and I/O devices, as well as software components like operating systems, applications and programming languages. The document aims to introduce foundational concepts in computer science.