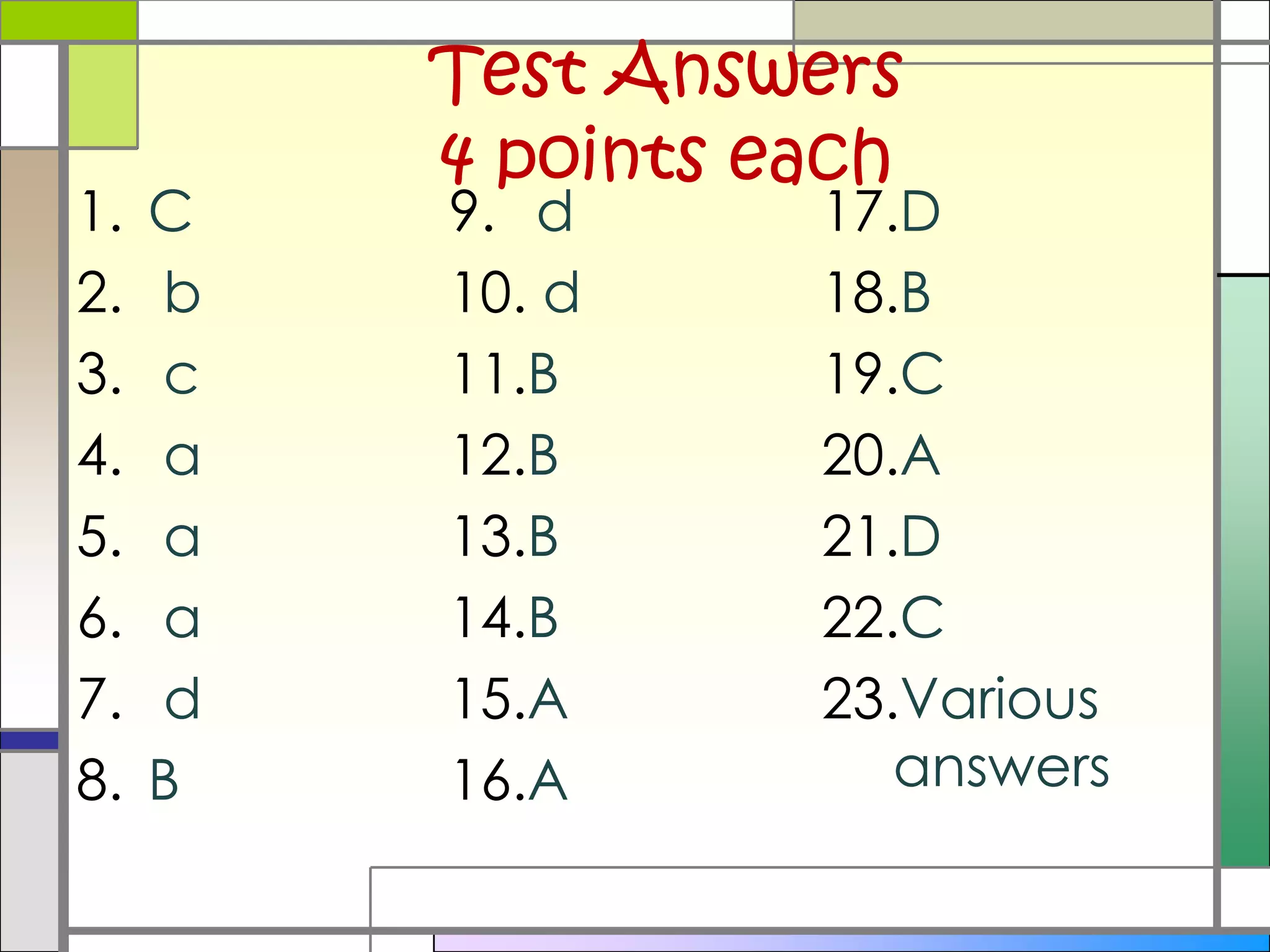
The document provides information for a science class unit on paleontology. It includes instructions for students to hand in late work, notes that midterm grades will be sent home on Friday, and provides test answers. It also outlines the unit, describes upcoming projects on fossils and tiers, and defines key terms like observation, inference and conclusion. Homework assigned is to complete Tier 1.