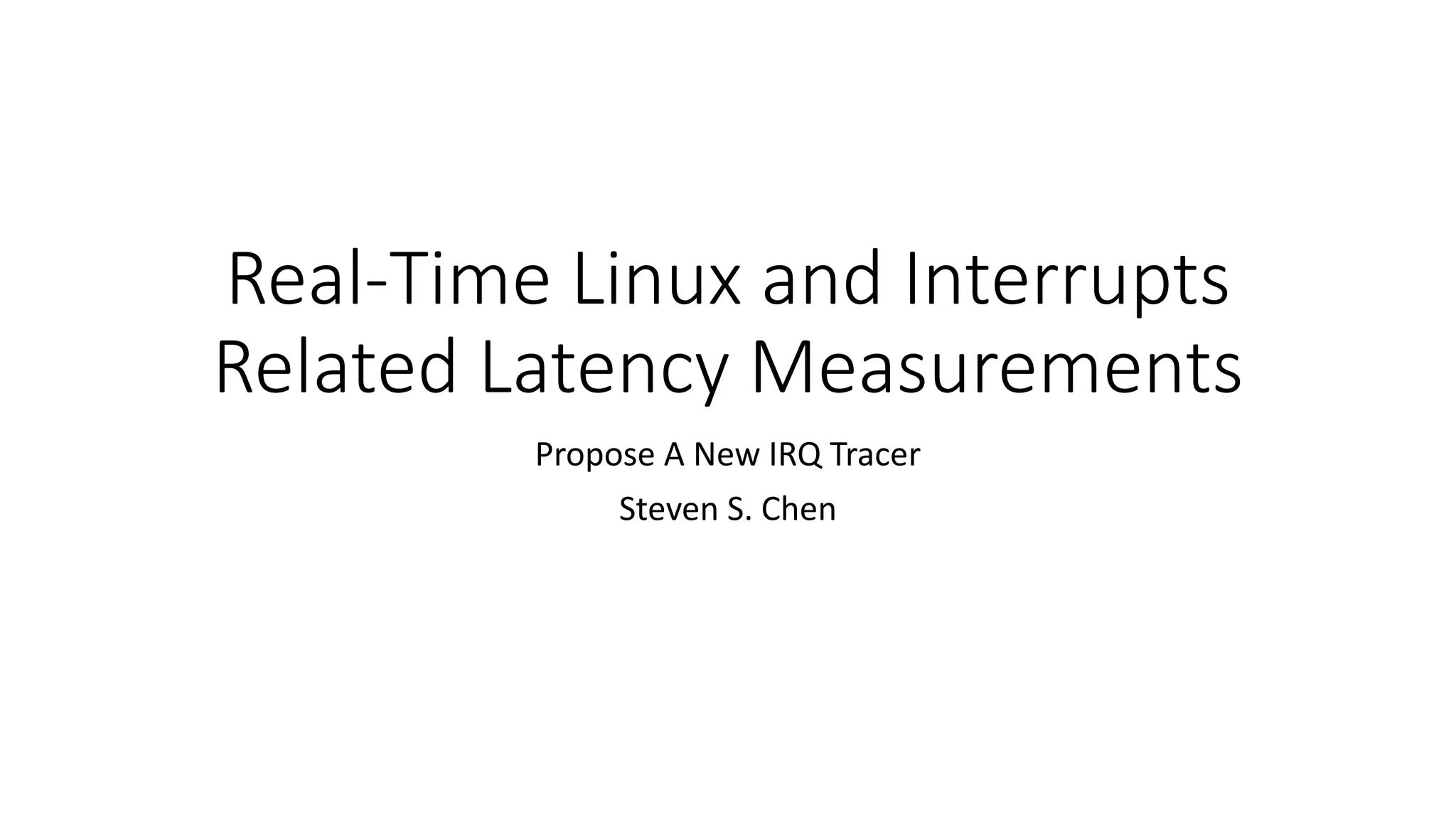
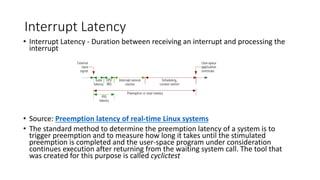
This document proposes a new IRQ tracer to measure interrupt latency in real-time Linux systems. The current methods are intrusive and not portable. The new tracer would combine features of existing tracers with less overhead as a standalone kernel module. It would measure all interrupts, not just simulated ones, and allow more customization and post-processing in user space.