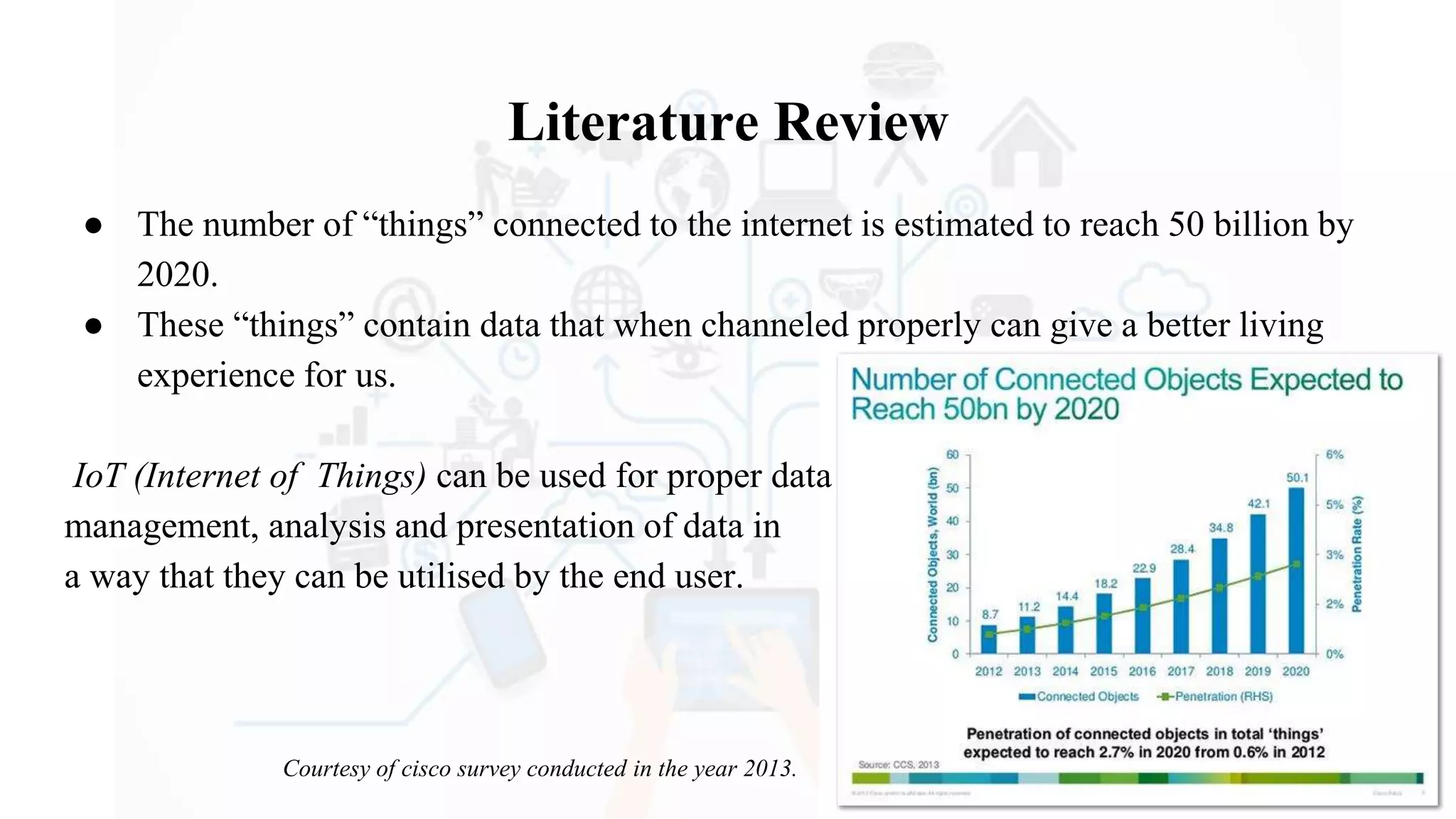
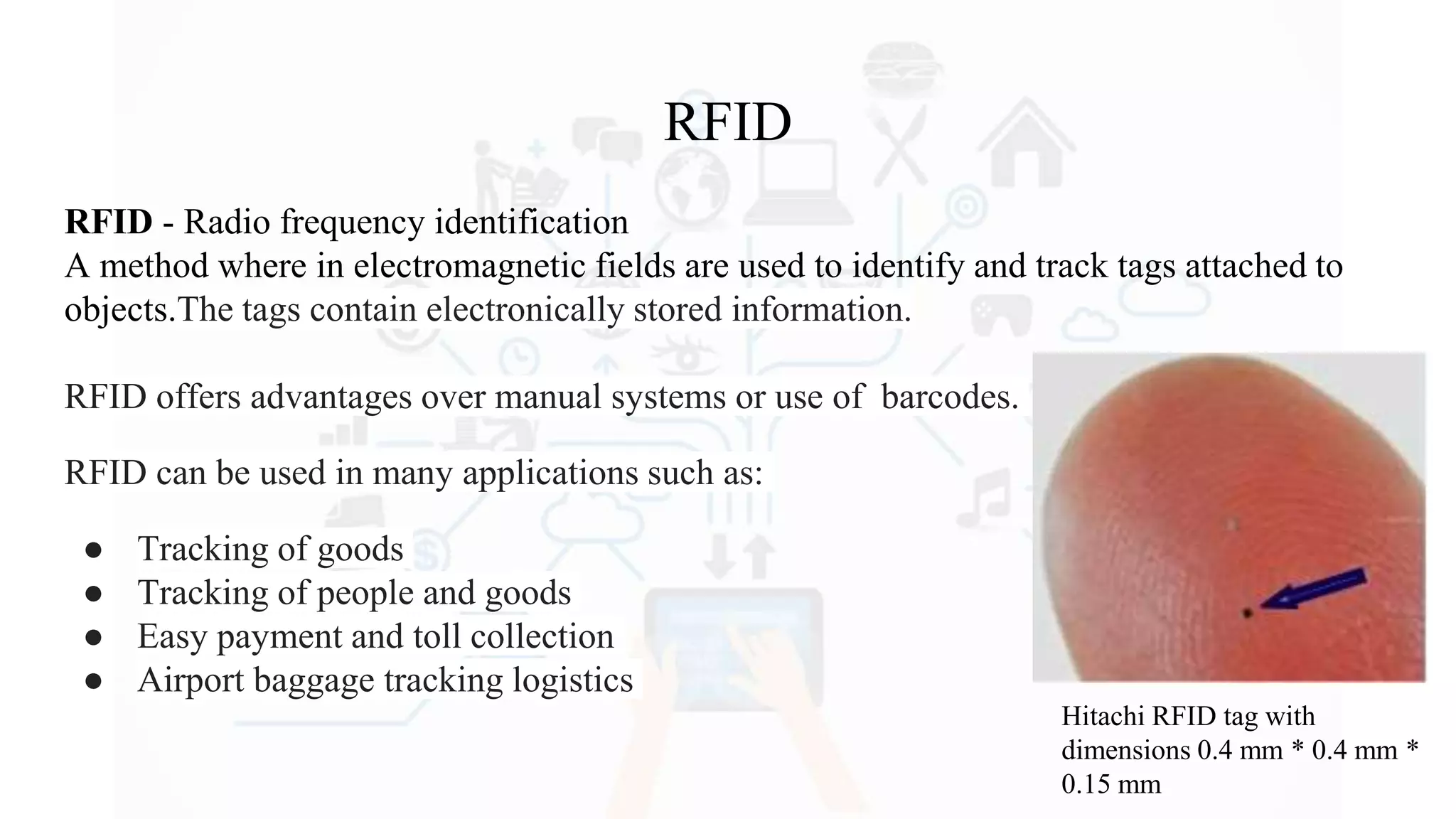
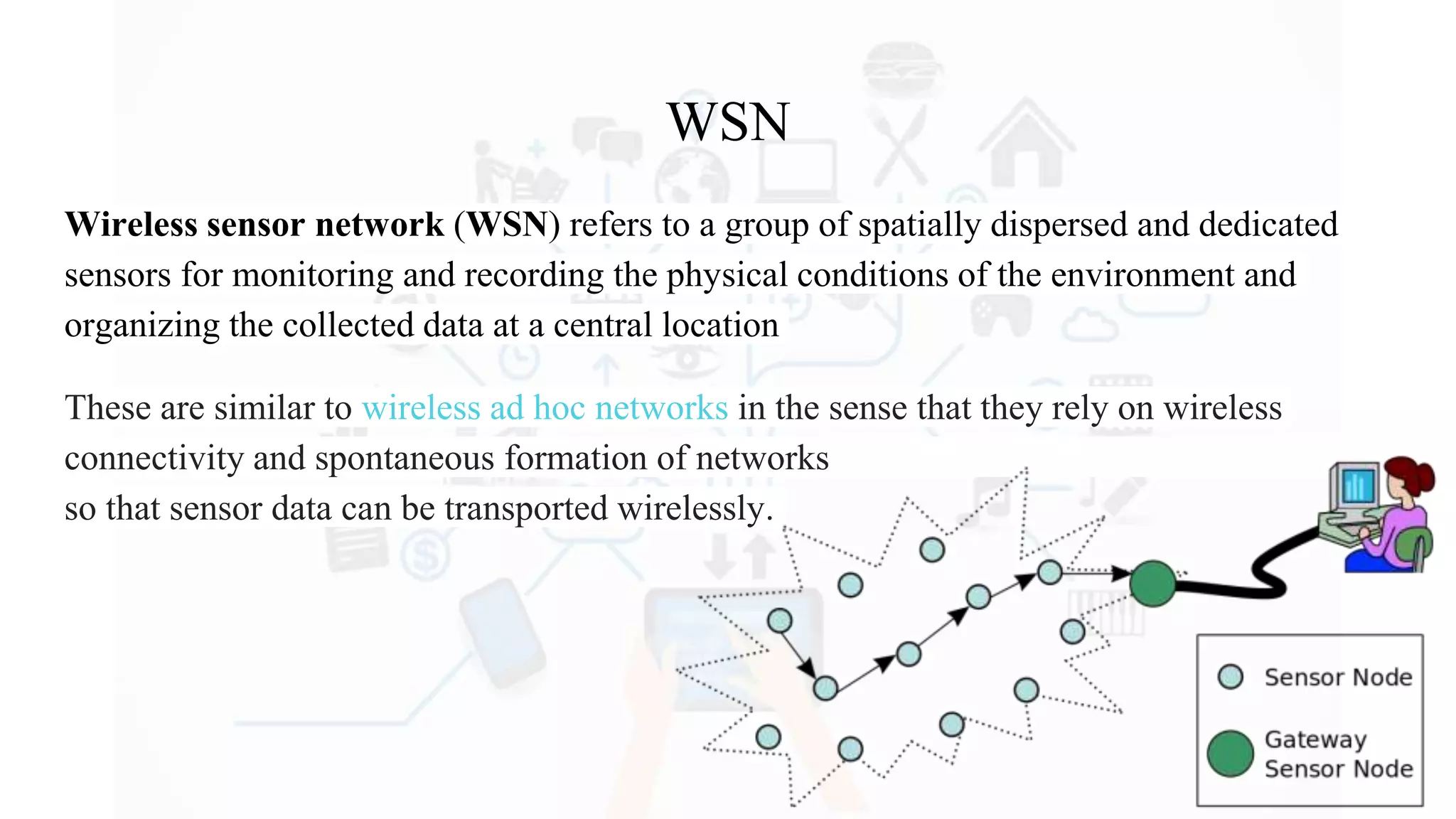
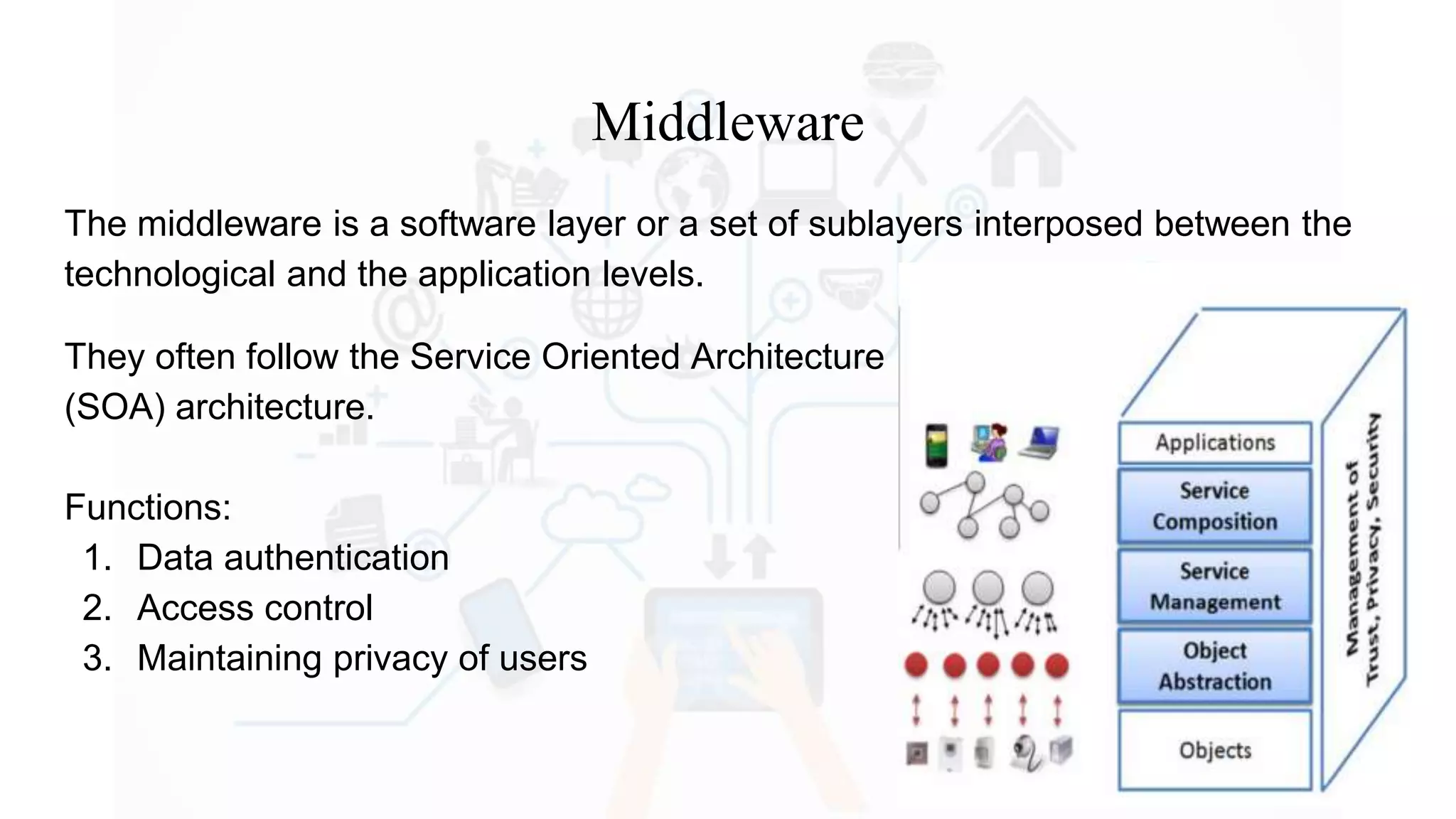
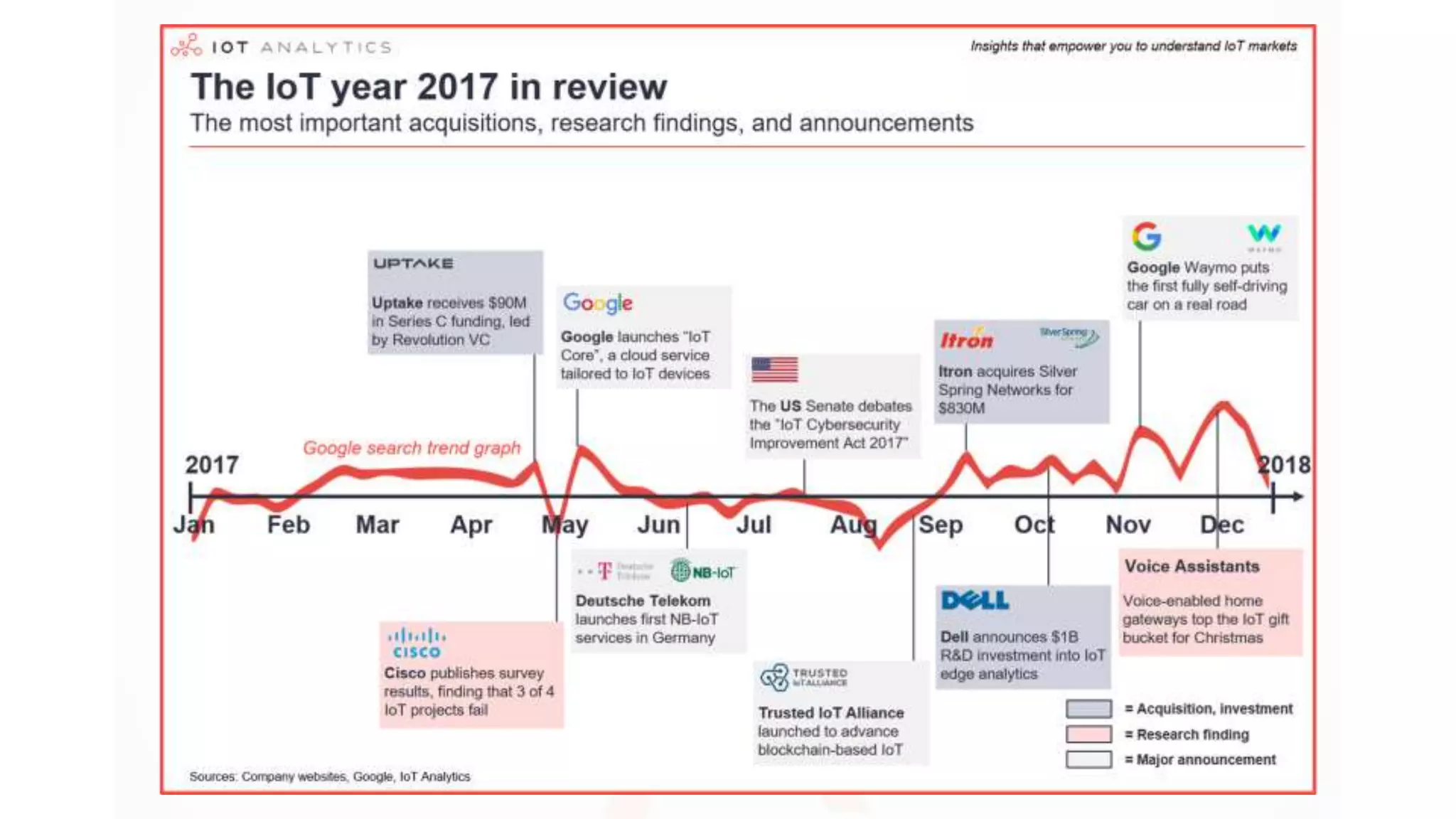
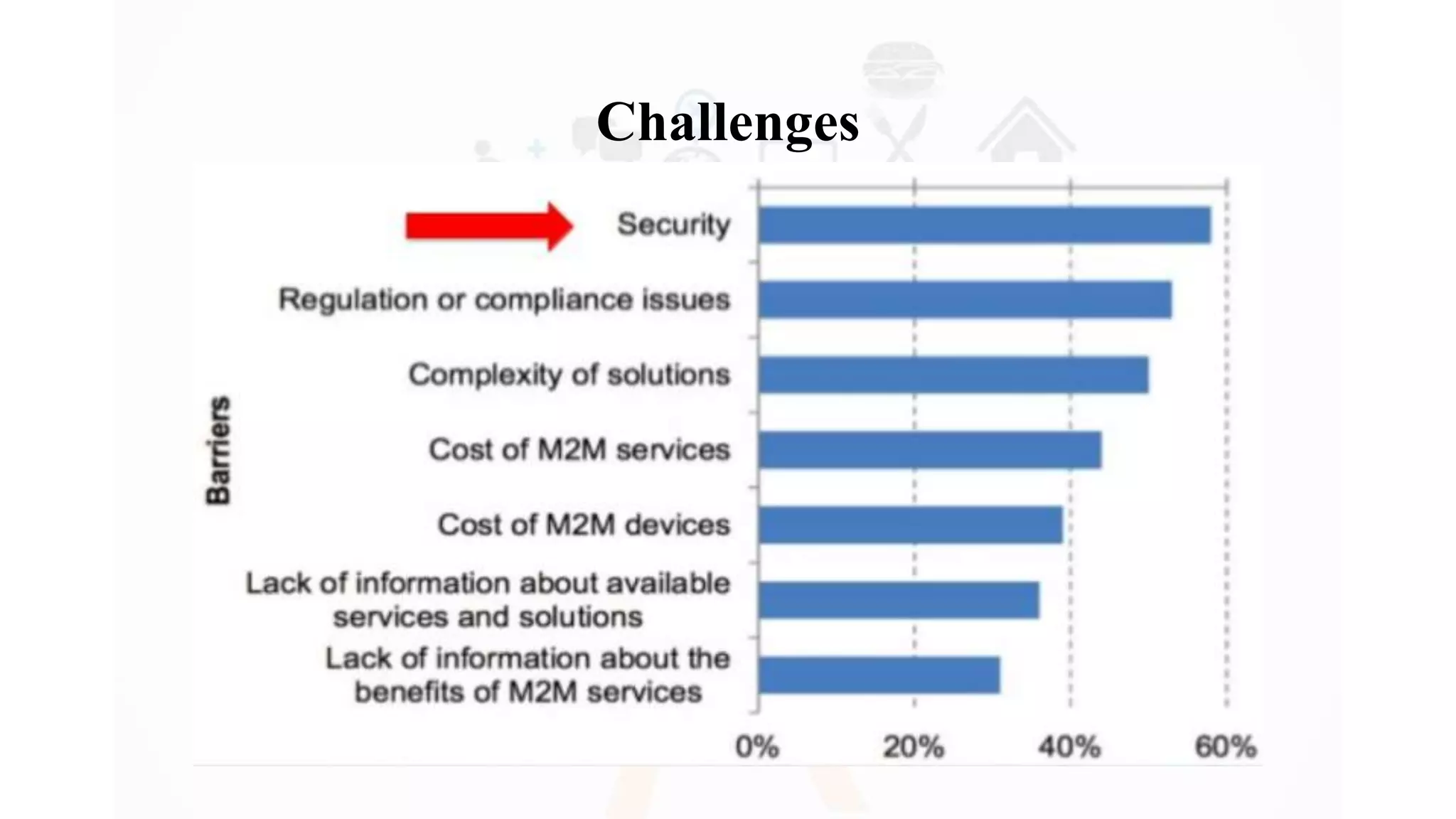
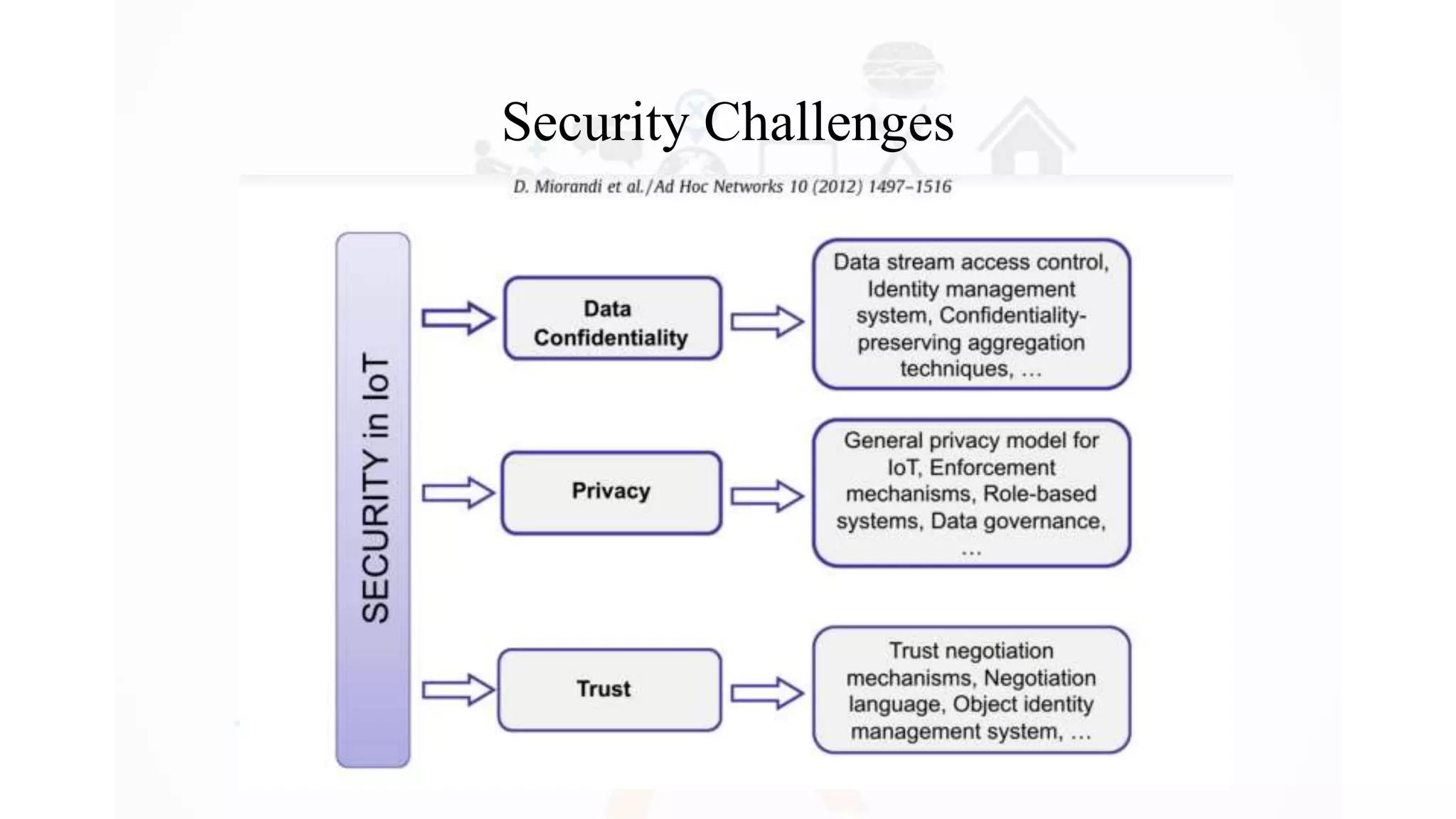
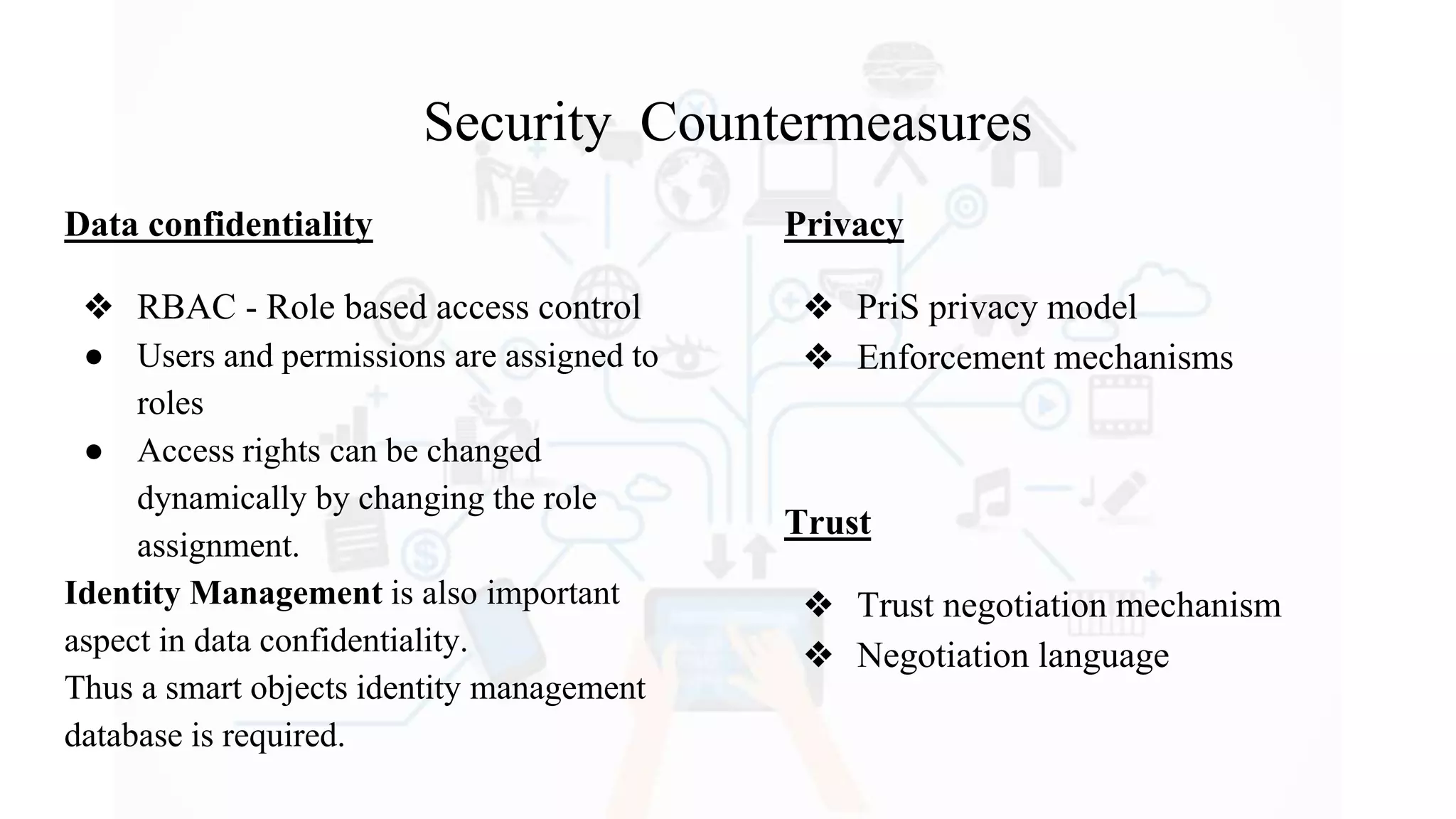
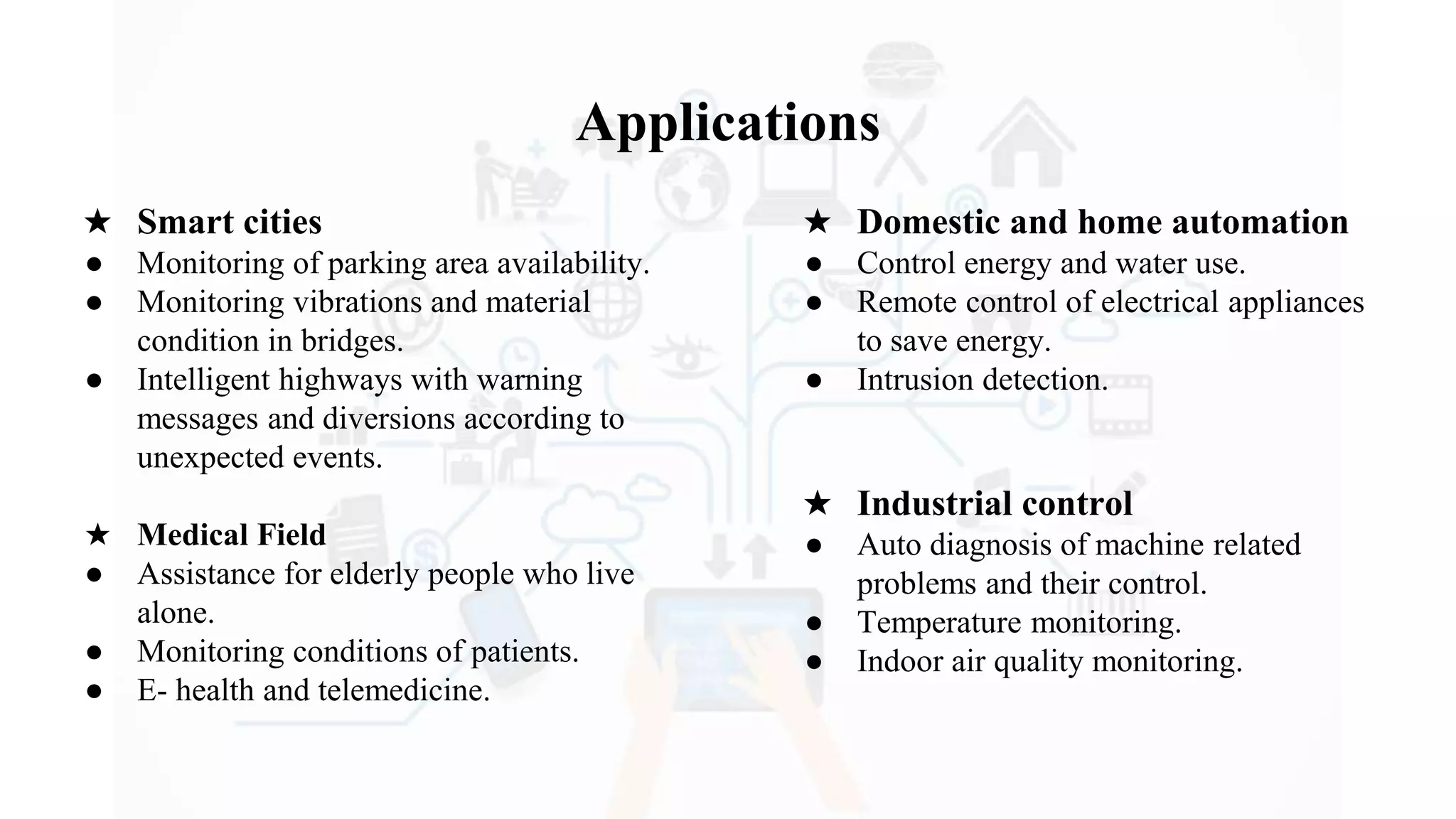
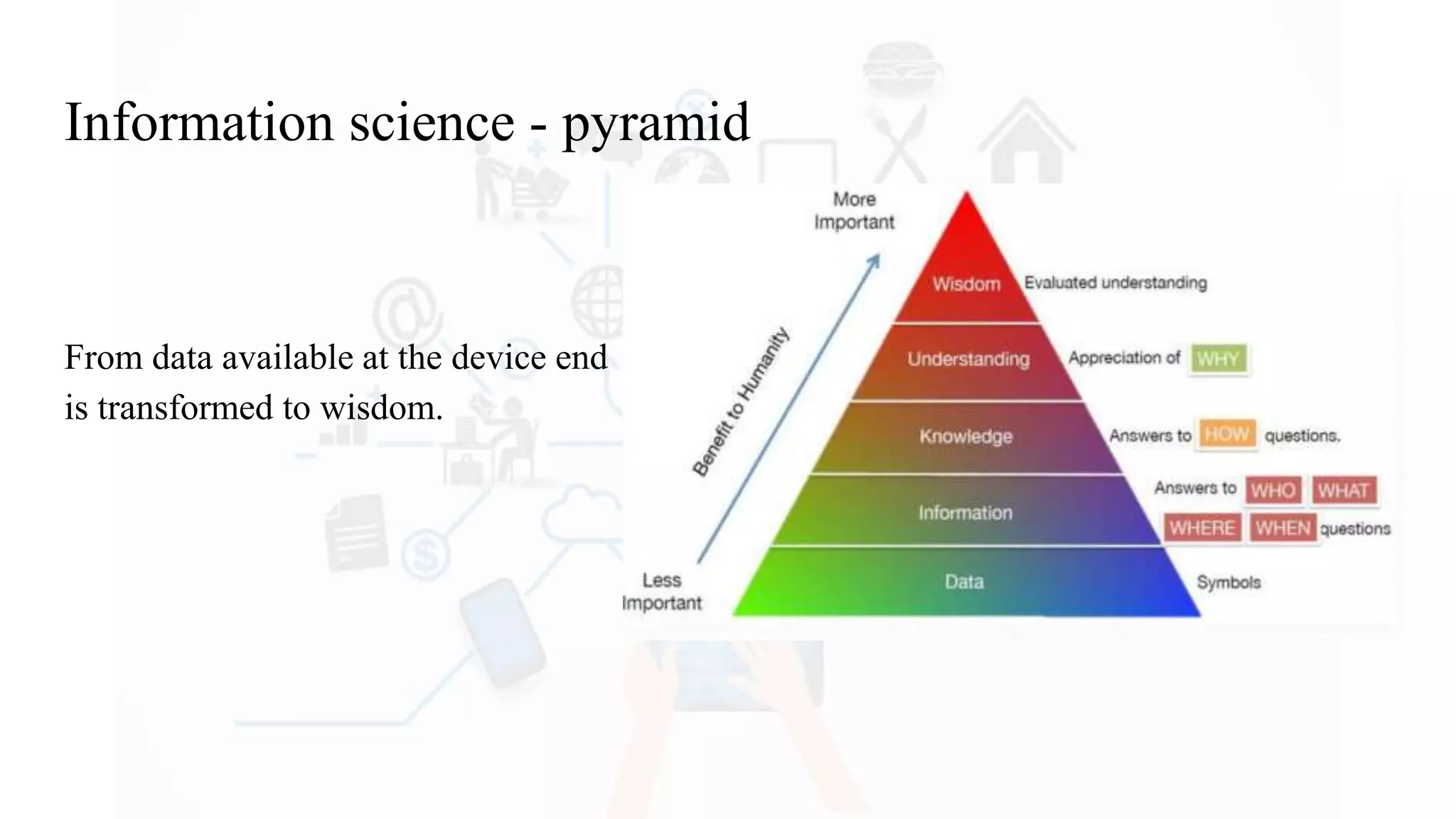
The document discusses Internet of Things (IoT), providing an introduction and overview. It defines IoT as the network of physical devices embedded with sensors and connectivity that allows them to exchange data via the internet. The document outlines some key enabling technologies for IoT like RFID, wireless sensor networks, middleware, and presentation tools. It also discusses some common challenges for IoT like security and privacy issues. Examples of major IoT applications are given in areas like smart cities, healthcare, home automation, and industrial control. In conclusion, the document states that IoT has the potential to enhance services across many sectors and will likely become widespread in the coming decade as the necessary technologies continue to develop.