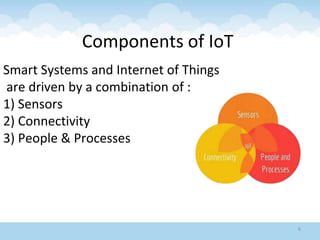
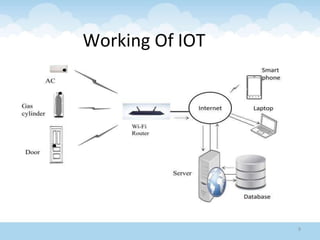
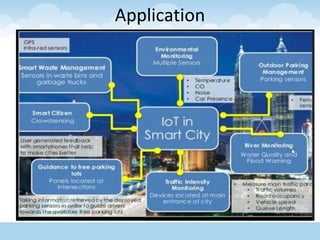
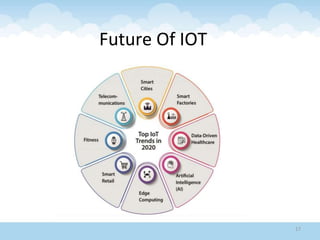
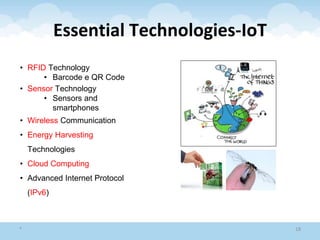
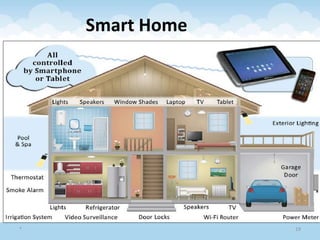
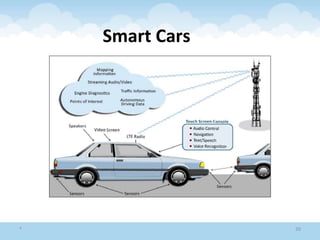
The document discusses the Internet of Things (IoT), highlighting its definition as an ecosystem of connected devices that communicate via the internet. It covers the history, importance, components, applications, advantages, challenges, and environmental impacts of IoT. The conclusion emphasizes the need for improved productivity and sustainability while addressing its challenges.