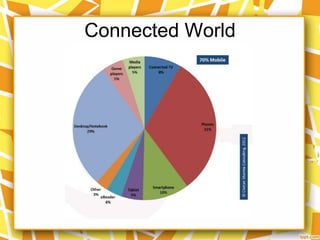
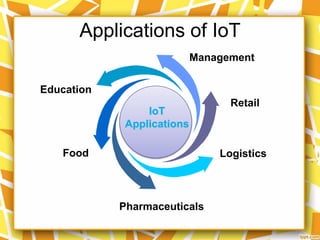
The document discusses the Internet of Things (IoT), which refers to a global network that allows both people and devices to communicate electronically. It provides definitions of IoT from different sources, noting it allows household appliances and "things" to have identities and communicate within various contexts. The document outlines some applications of IoT in various industries and also discusses challenges including issues around privacy, efficiency, standards, and developing sustainable energy sources for billions of connected devices.