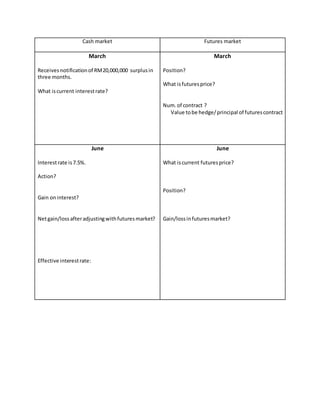
The document discusses KLIBOR futures contracts, which are based on 3-month Kuala Lumpur interbank deposits. The futures price is quoted as an index calculated as 100 minus the interest rate. For example, a 7.5% deposit rate in the cash market corresponds to a 92.50 index price in the futures market. Buying a futures contract at 93.75 locks in a 6.25% borrowing rate, while selling at 92.50 locks in a 7.5% lending rate. The document provides an example of a company using KLIBOR futures to hedge interest rate risk on a RM20 million investment in 3 months.