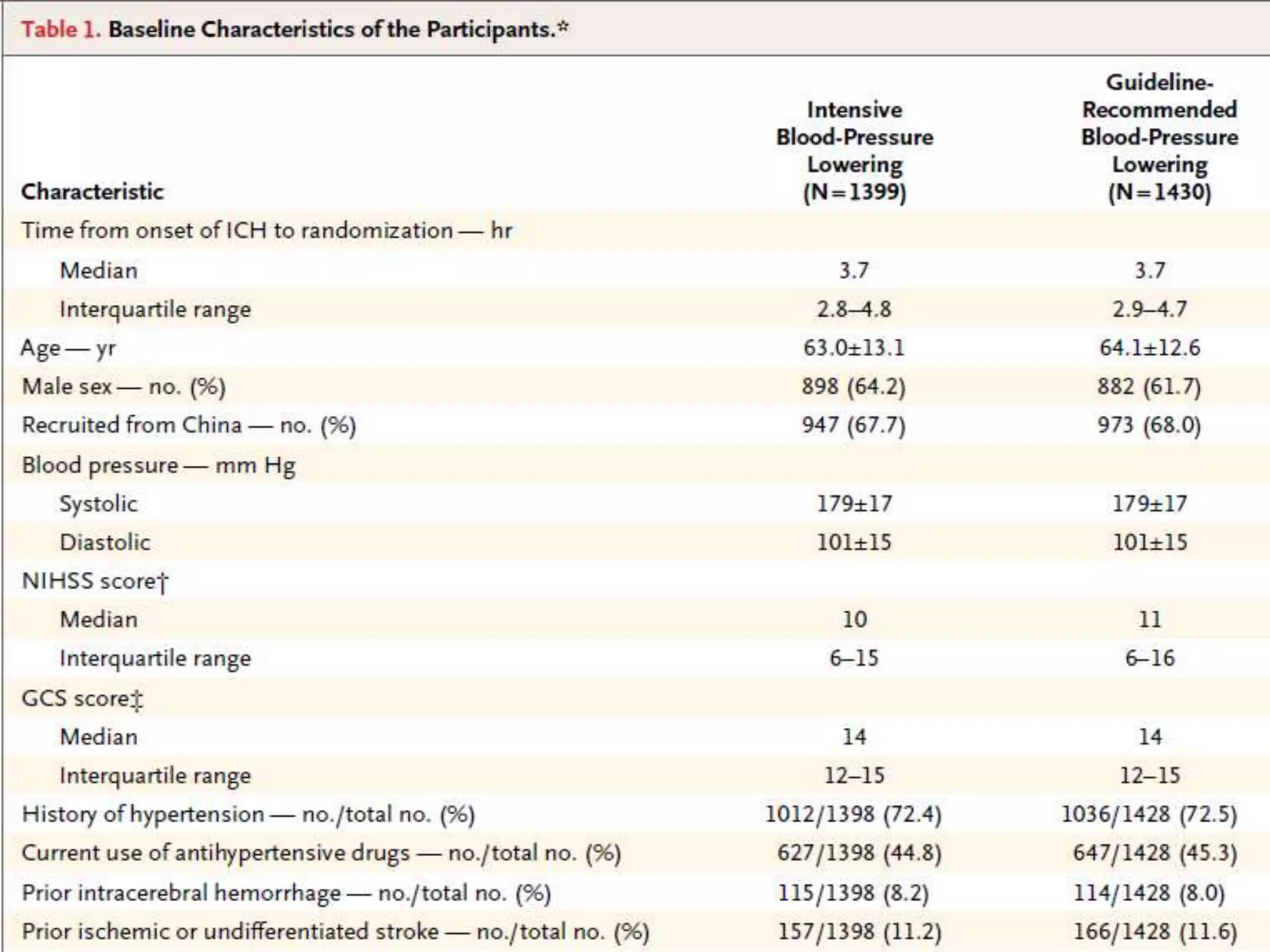
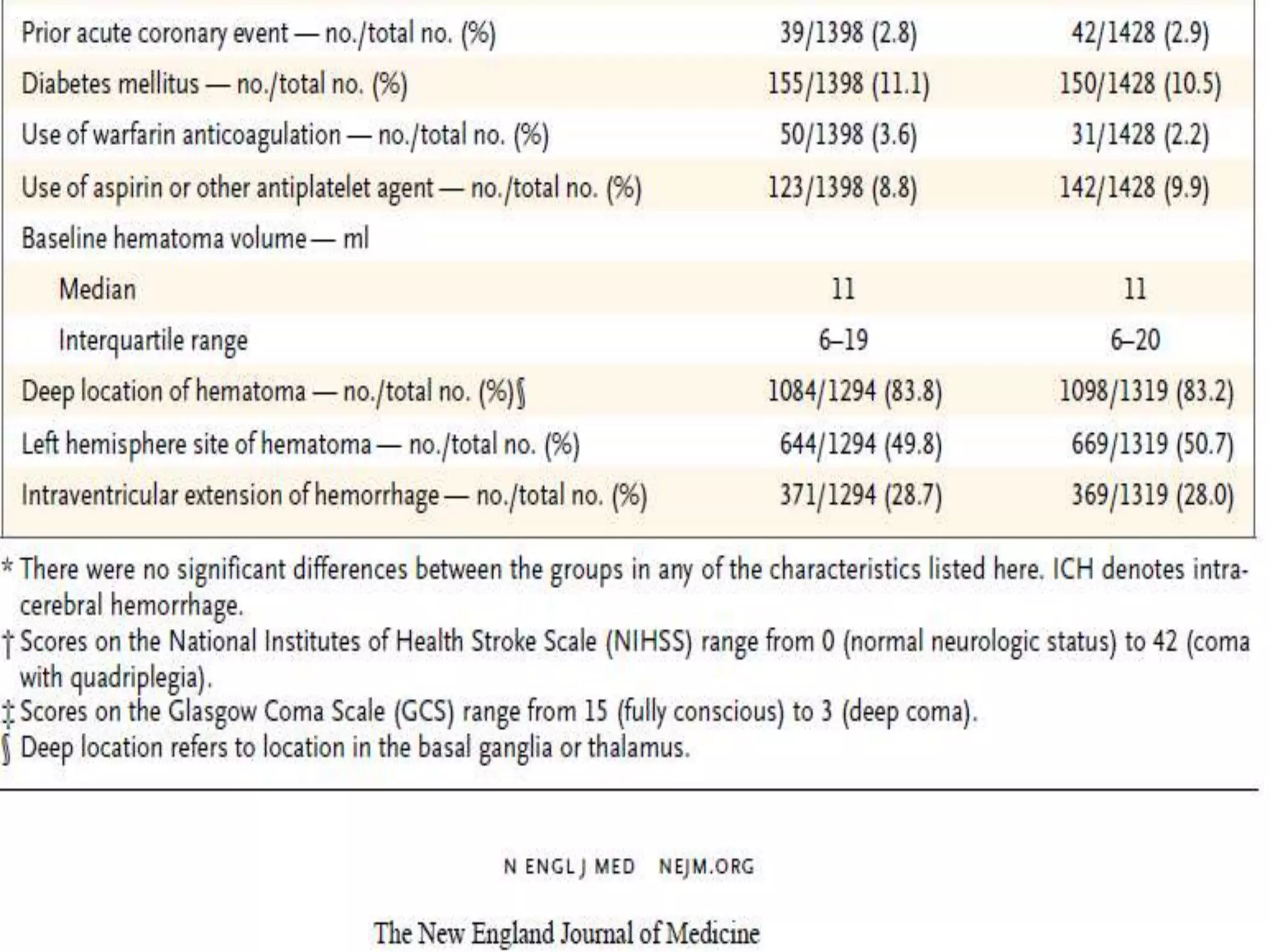
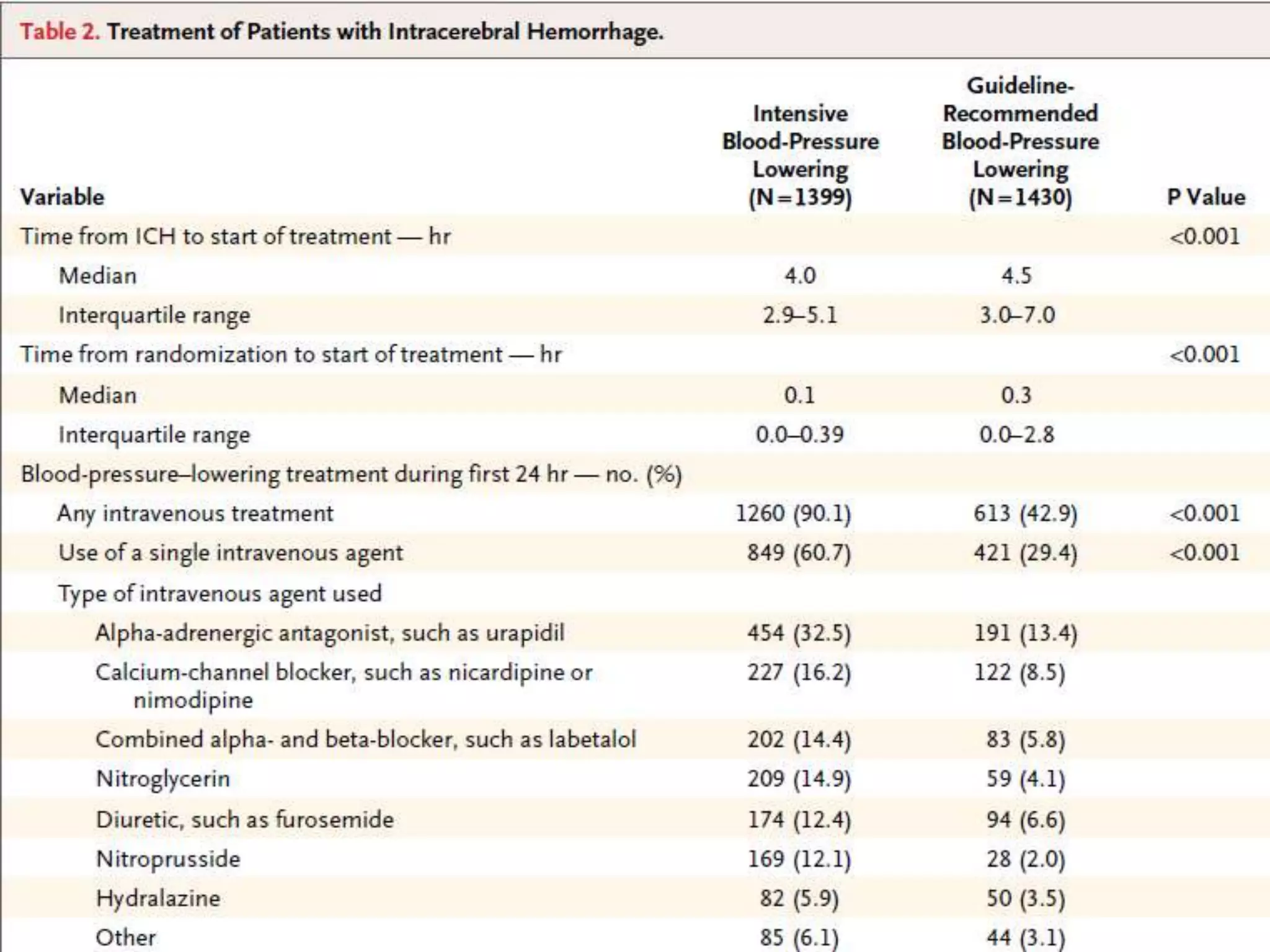
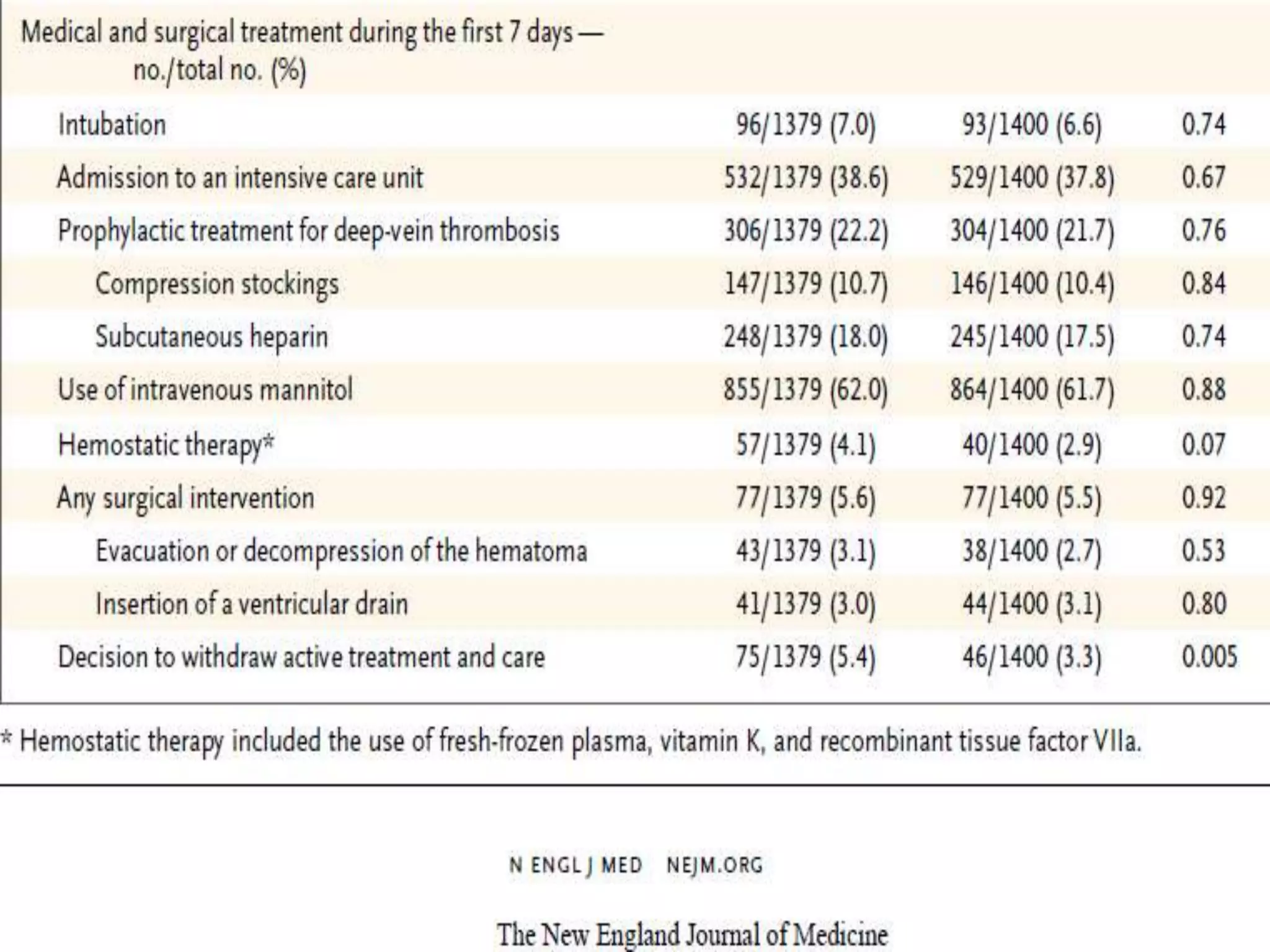
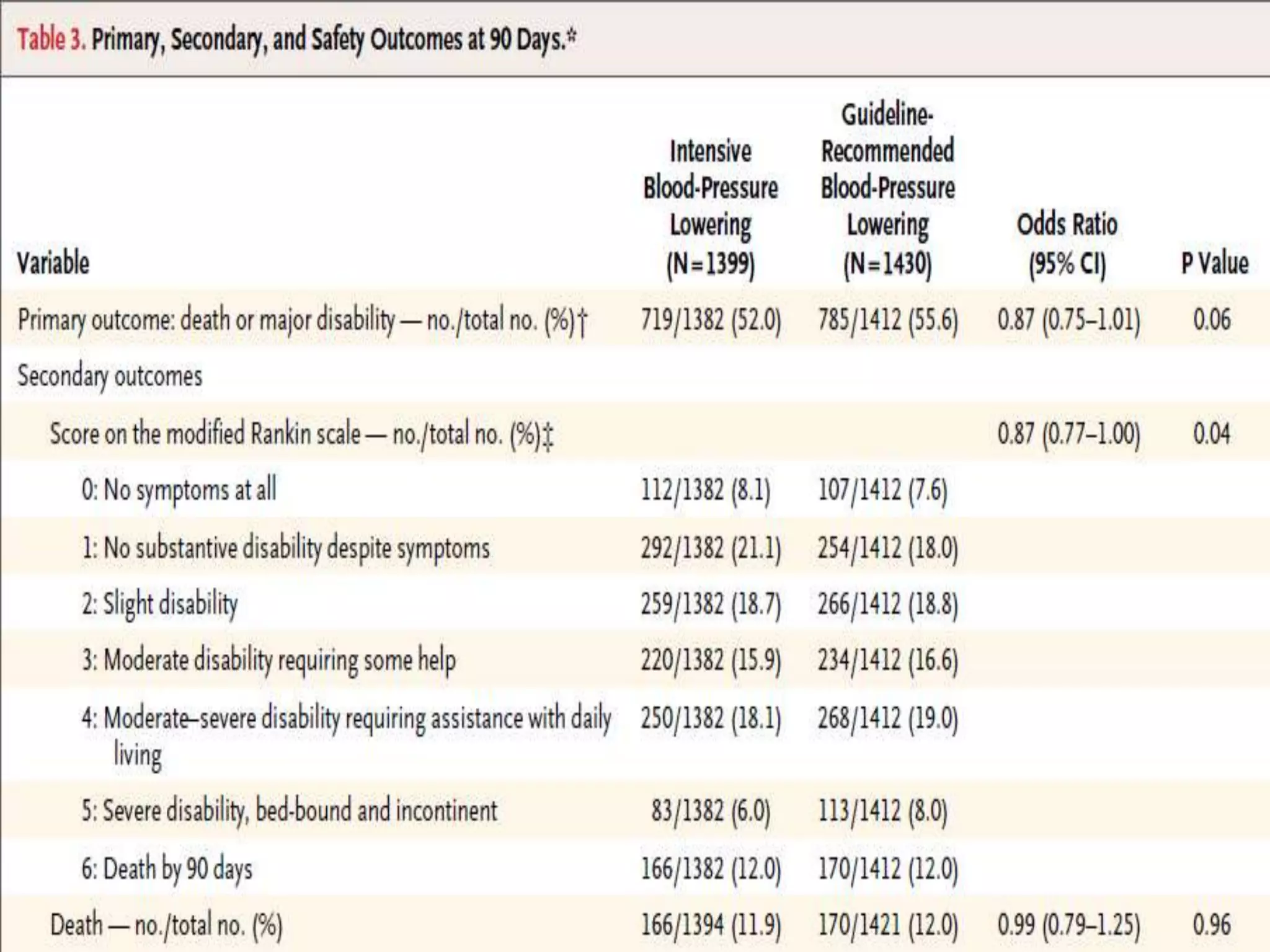
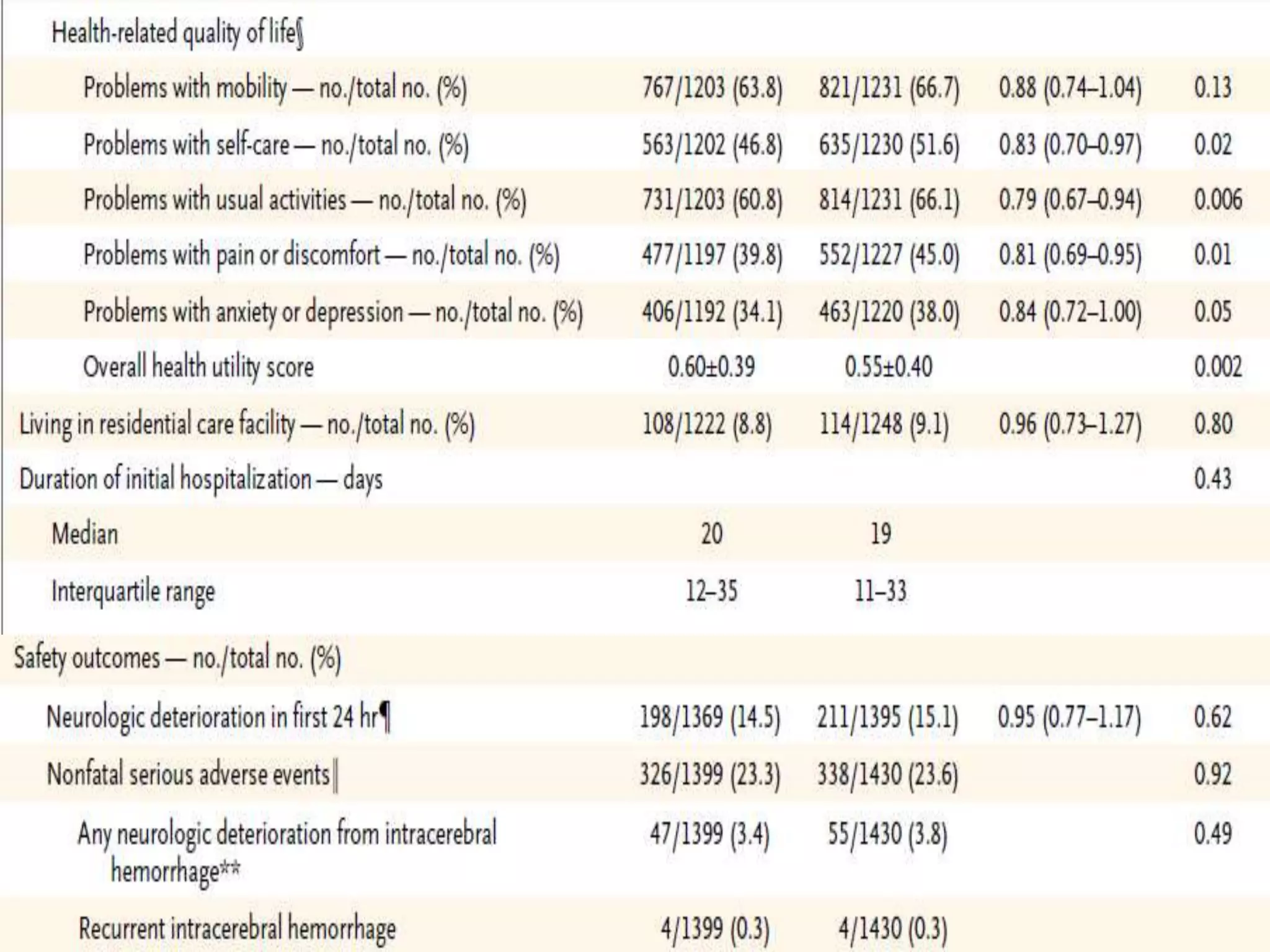
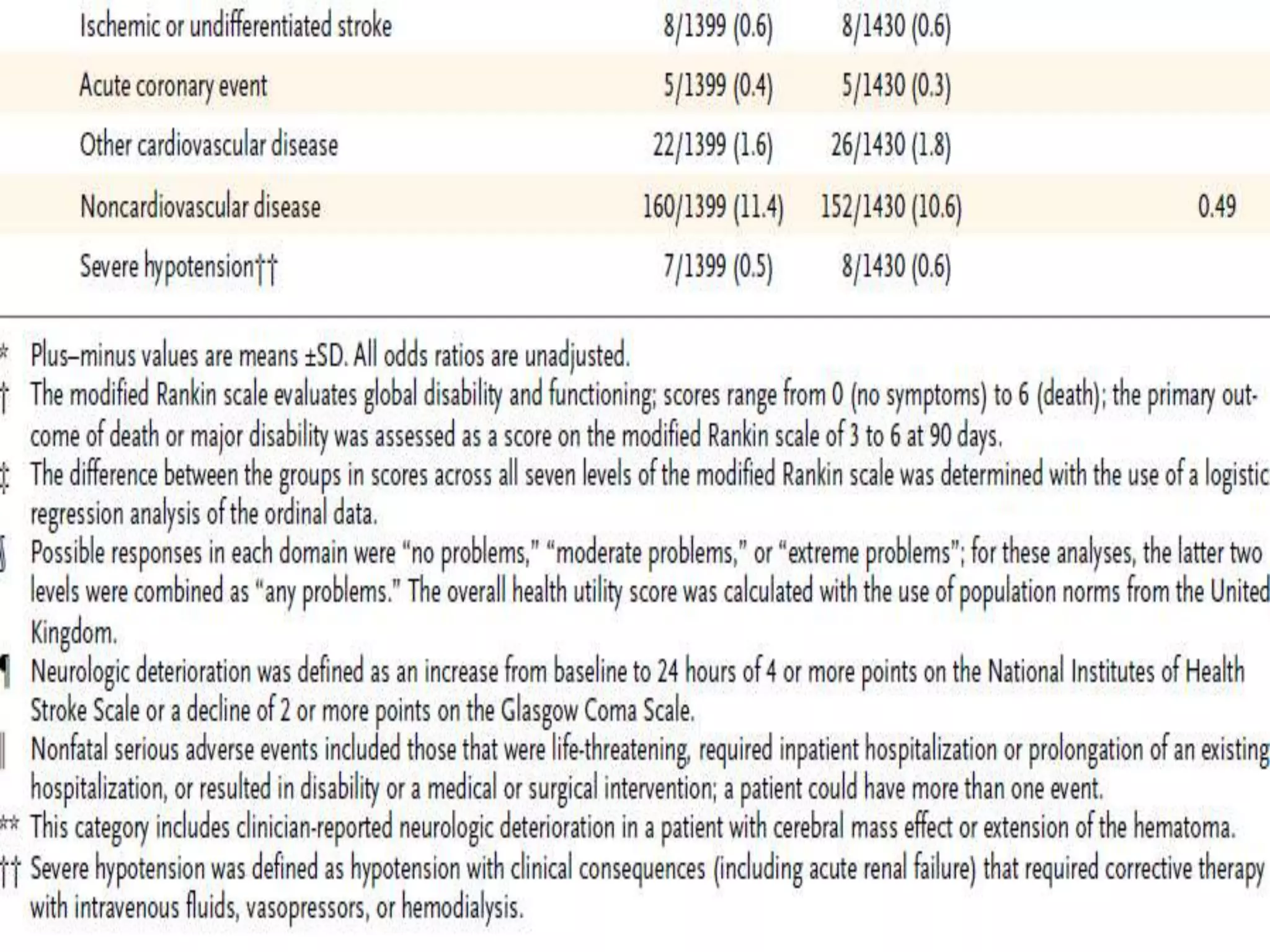
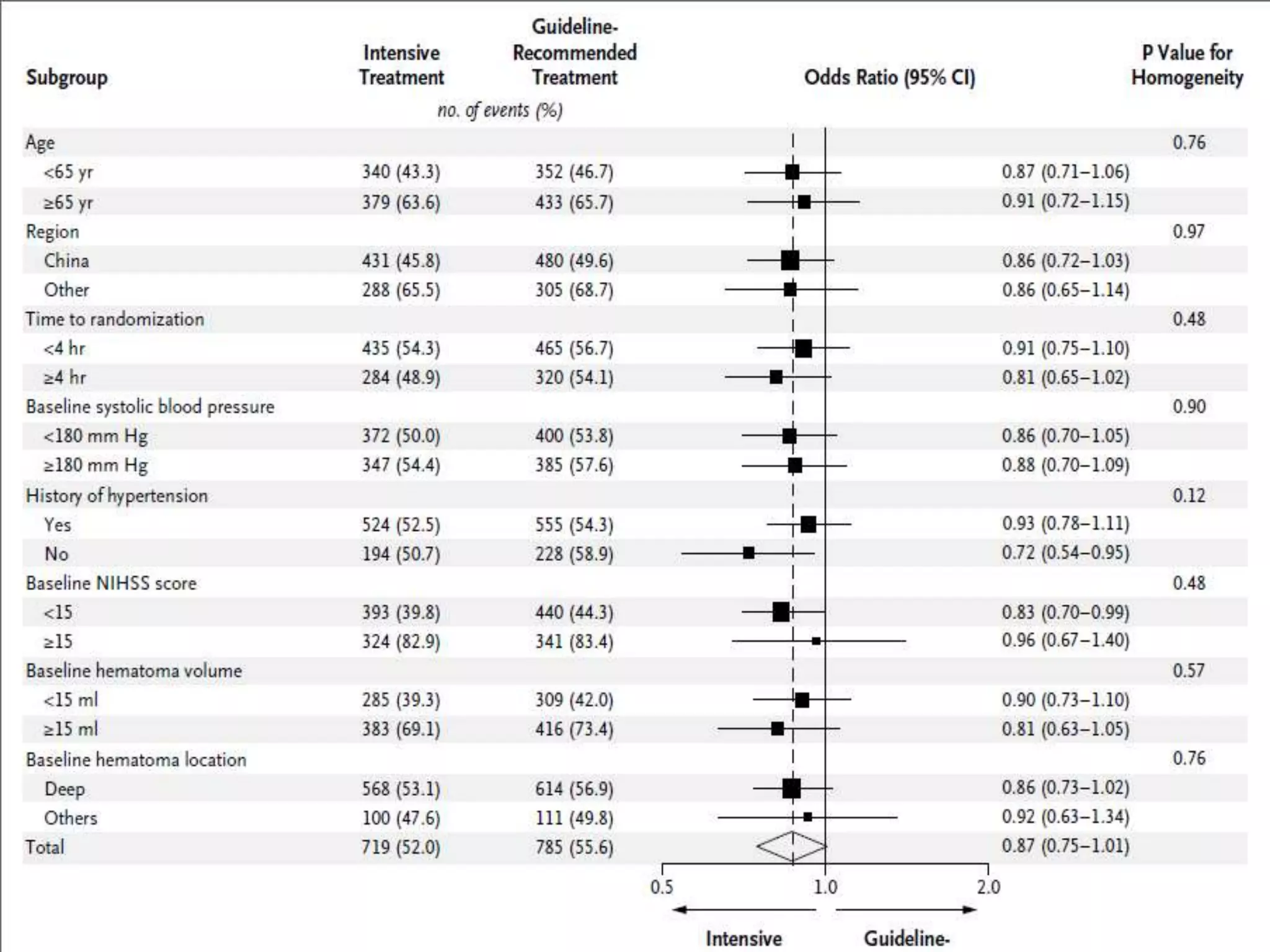
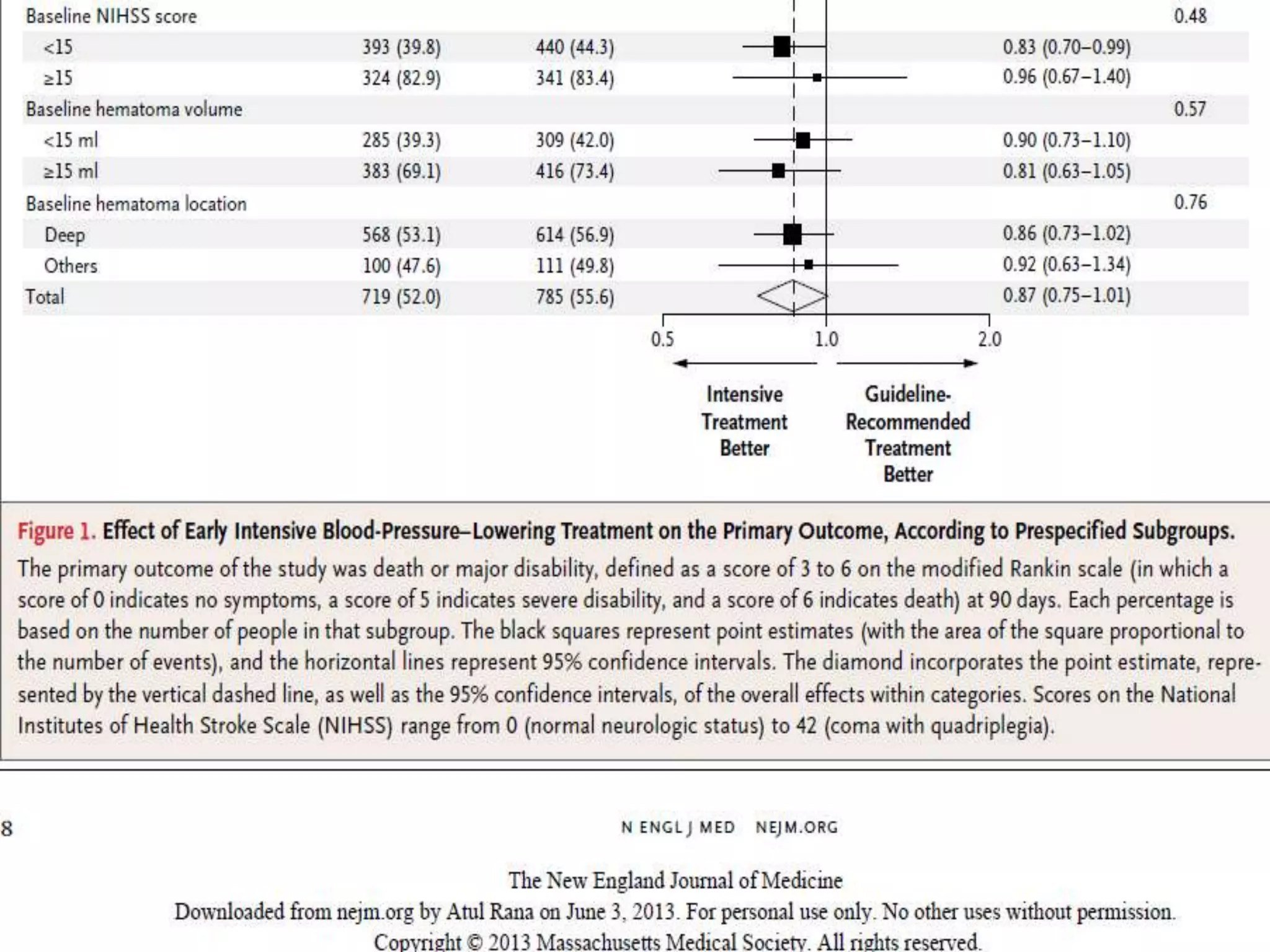
This document summarizes the INTERACT2 trial which studied the effects of early intensive blood pressure lowering in patients with intracerebral hemorrhage. The trial involved over 2800 patients across 21 countries who were randomized to either receive intensive treatment to lower their blood pressure below 140 mmHg within 1 hour or guideline-recommended treatment with no lower target. The primary outcome was death or major disability at 90 days. While intensive treatment did not significantly reduce the primary outcome, ordinal analysis showed better functional outcomes. Intensive treatment also improved quality of life scores and was not associated with higher death or adverse event rates.


![• The diagnosis of intracranial hemorrhage was confirmed by
means of computed tomography (CT) or magnetic
resonance imaging (MRI).
• Patients were excluded:-
1. if there was a structural cerebral cause for the
intracerebral hemorrhage,
2 .if they were in a deep coma (defined as a score of 3 to 5
on the Glasgow Coma Scale [GCS], in which scores range
from 3 to 15, with lowerscores indicating reduced levels of
consciousness)
3 .if they had a massive hematoma with a poor prognosis,
4. if early surgery to evacuate the hematoma was
planned](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/interact2trail-130902145800-phpapp01/75/Interact-2-trail-4-2048.jpg)