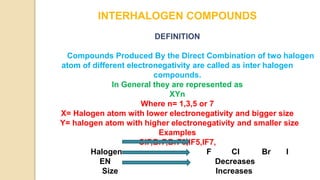
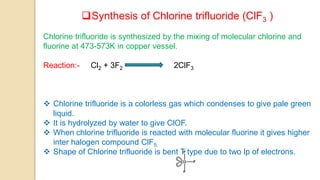
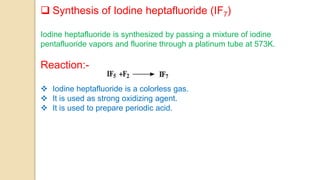
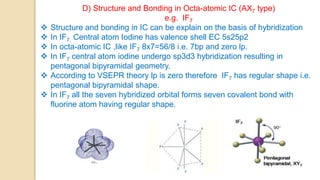
Interhalogen compounds are formed by the direct combination of two halogen atoms with differing electronegativities, represented as XyN, where X has lower electronegativity. They can be synthesized through direct combination or by reacting lower interhalogen compounds with higher ones. These compounds have diverse applications, including as non-aqueous solvents, catalysts, and fluorinating agents, with varied structures and bonding based on hybridization principles.