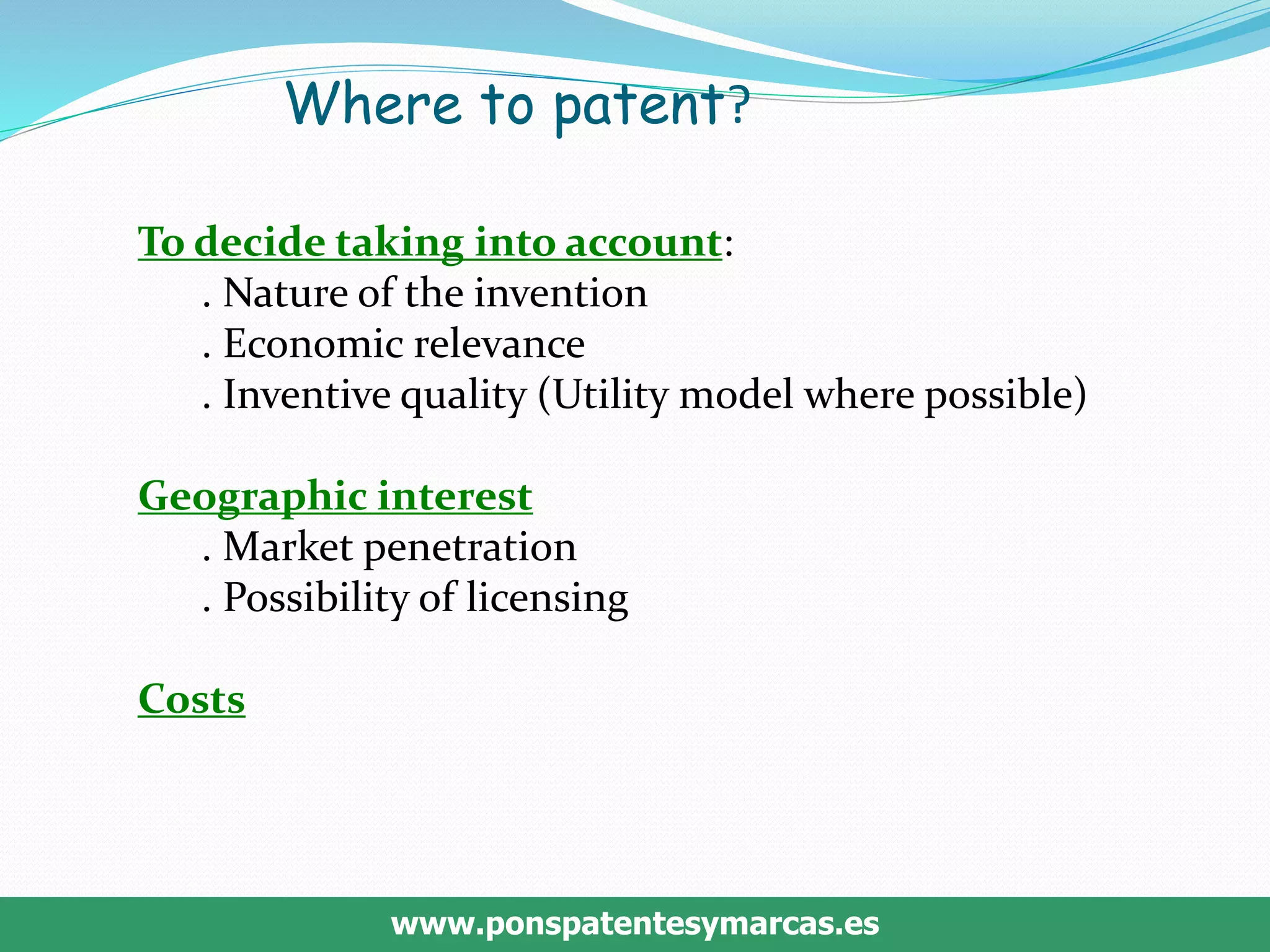
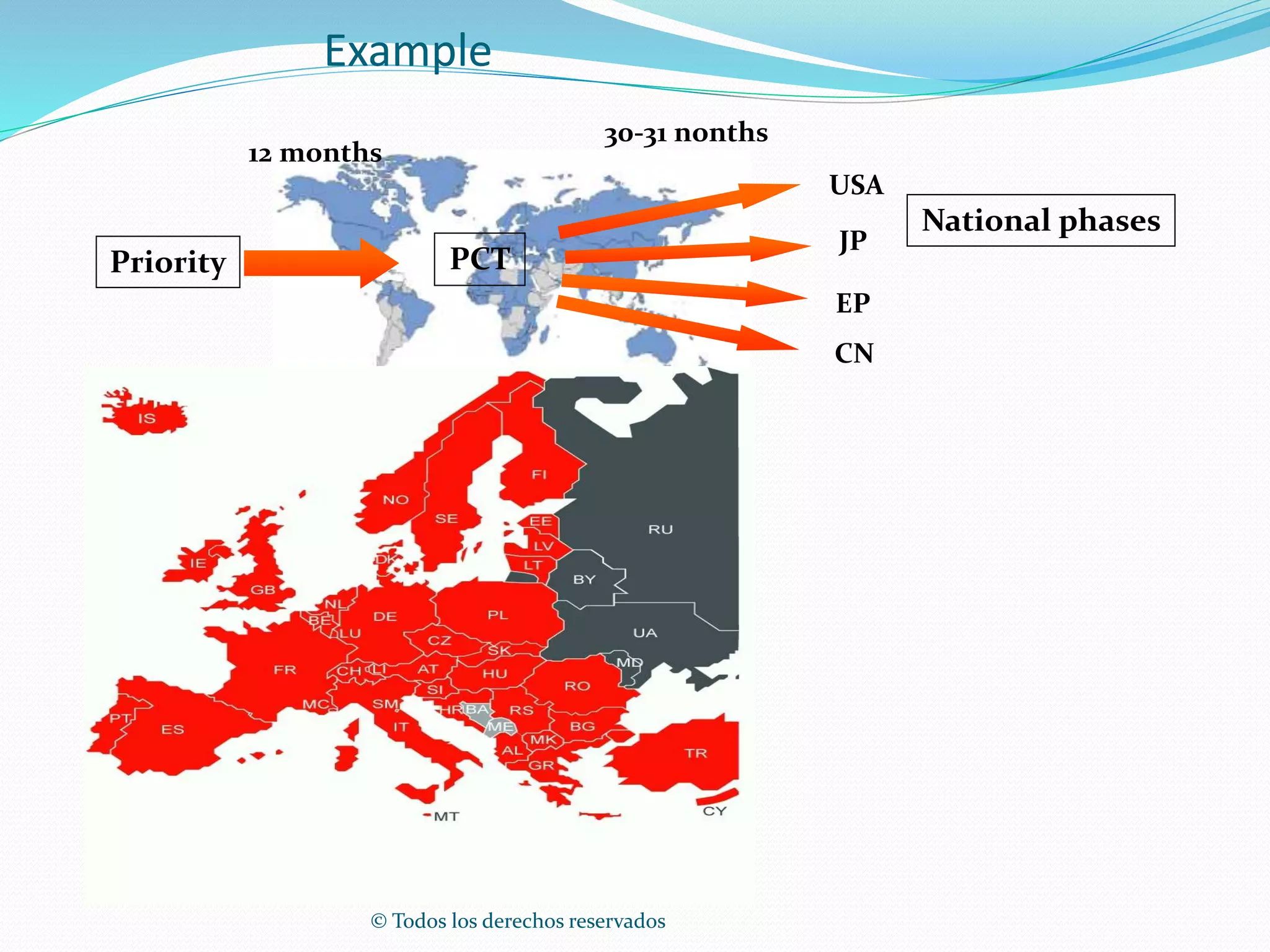
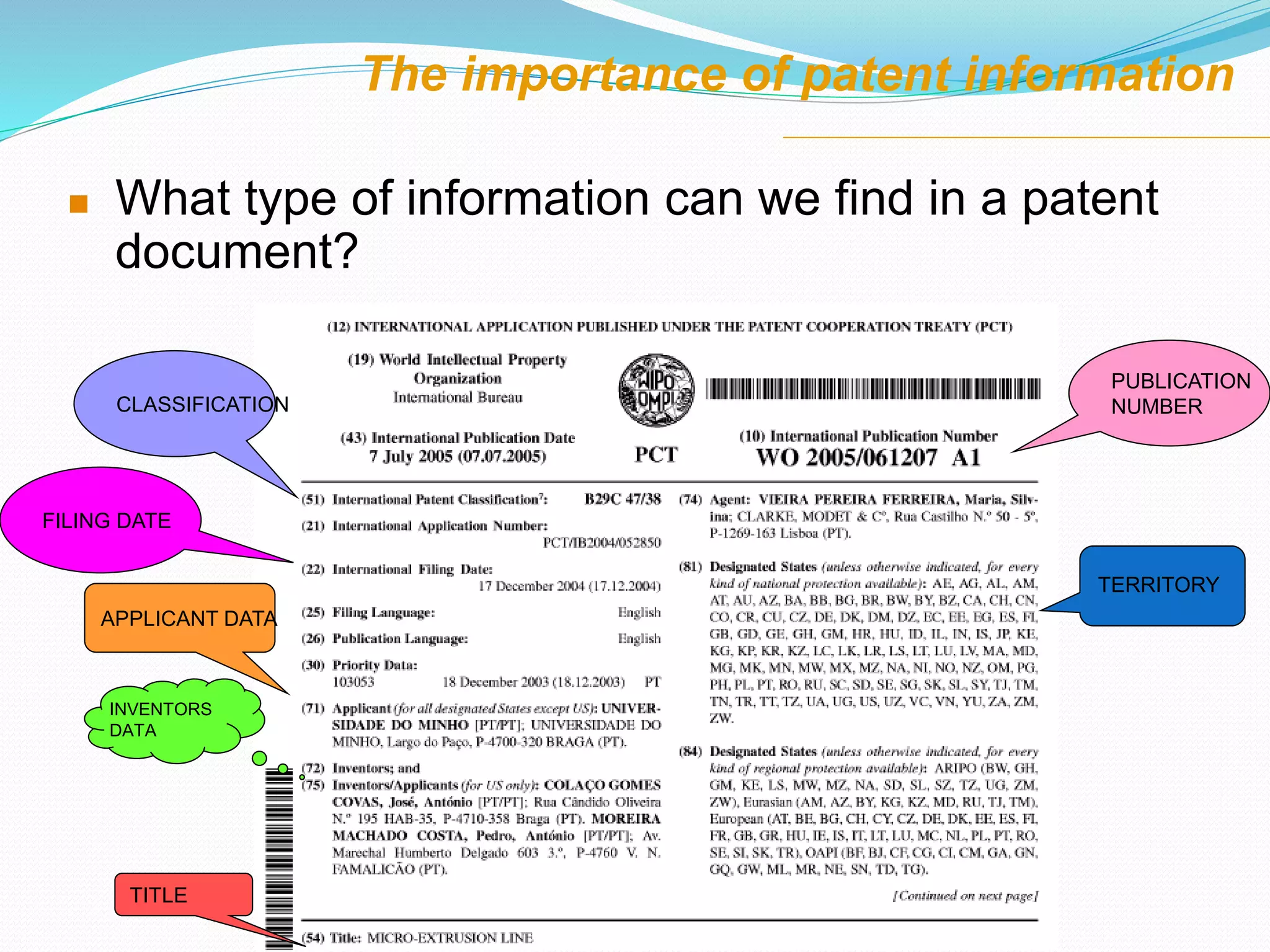
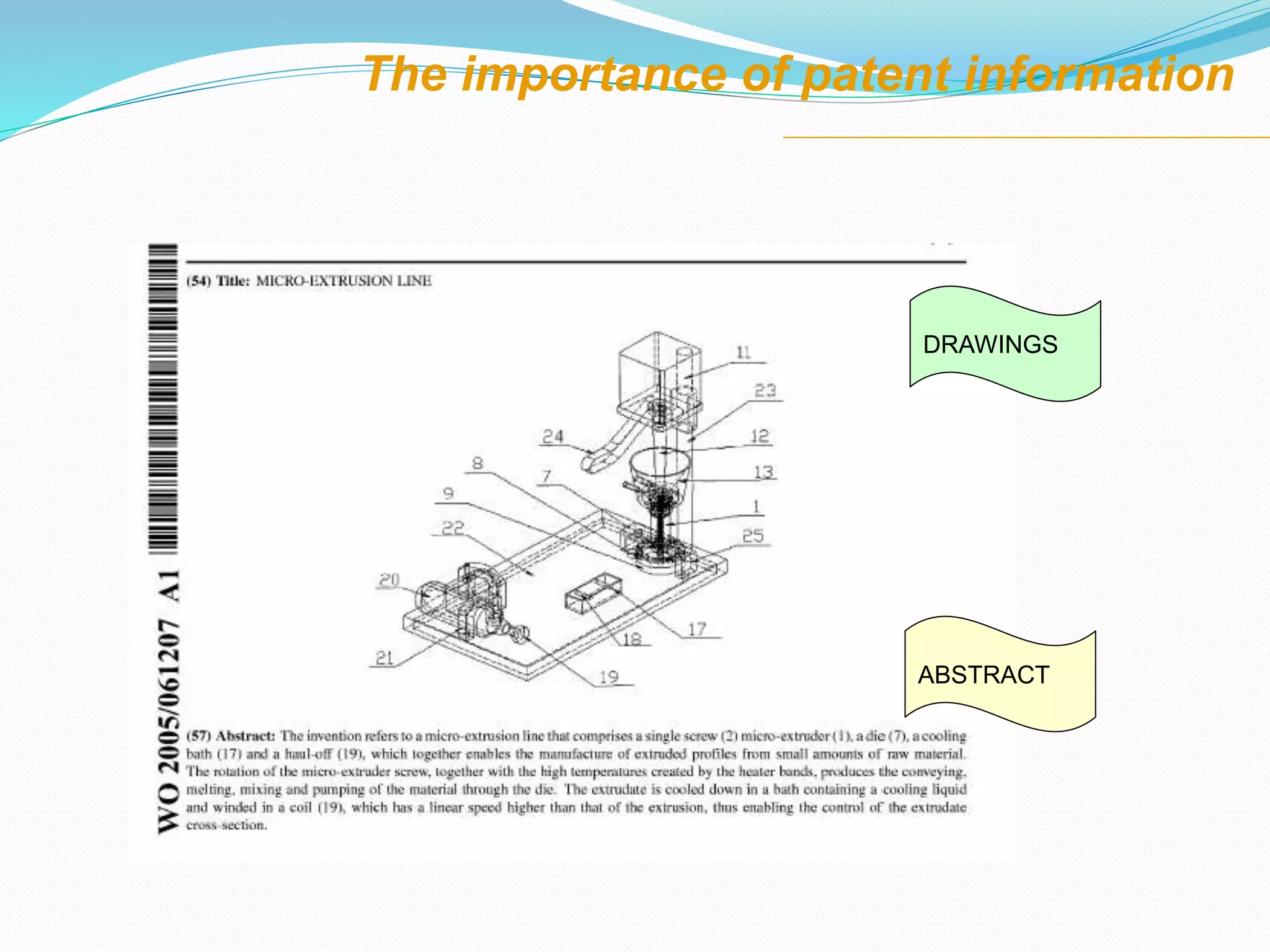
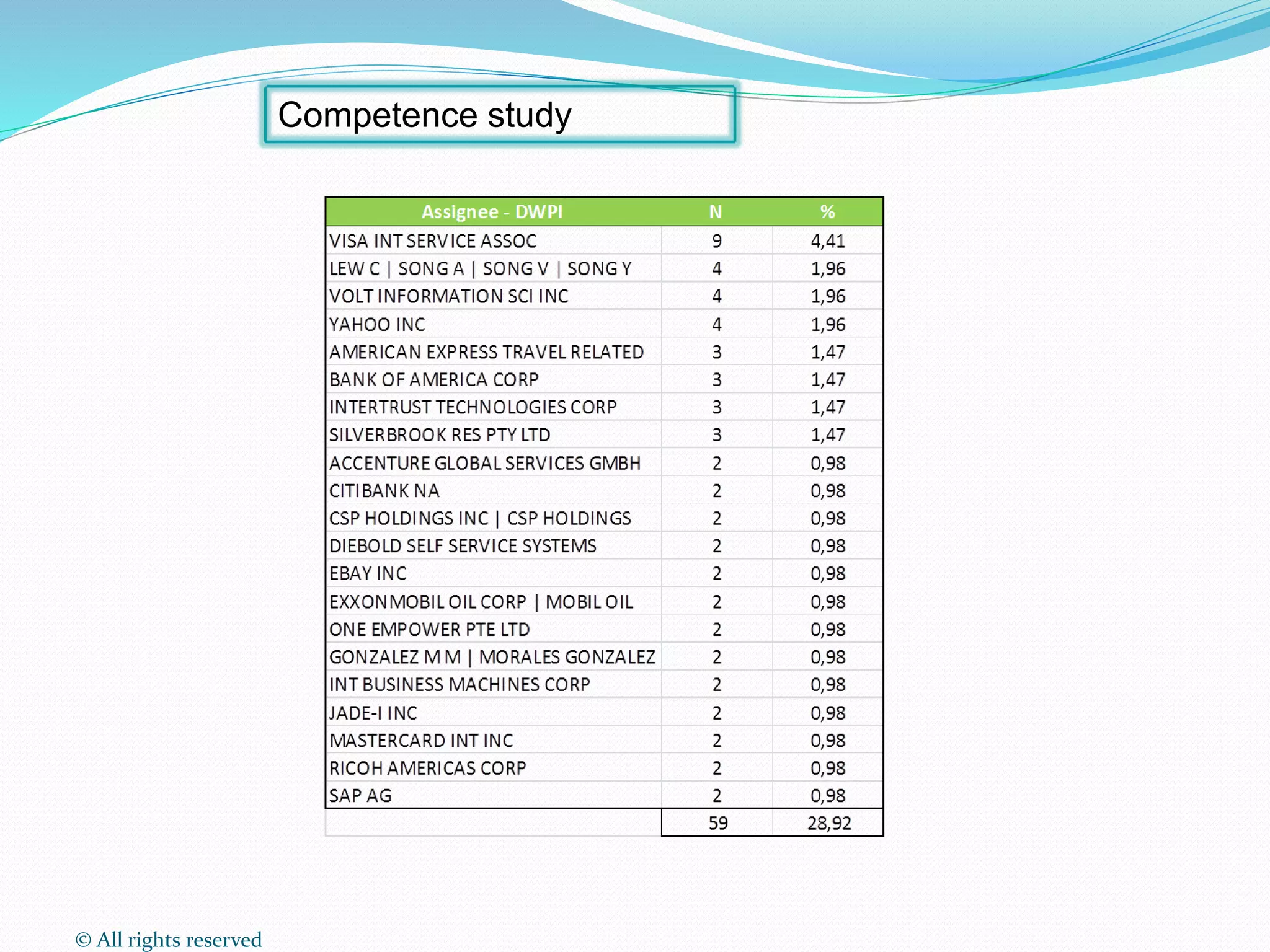
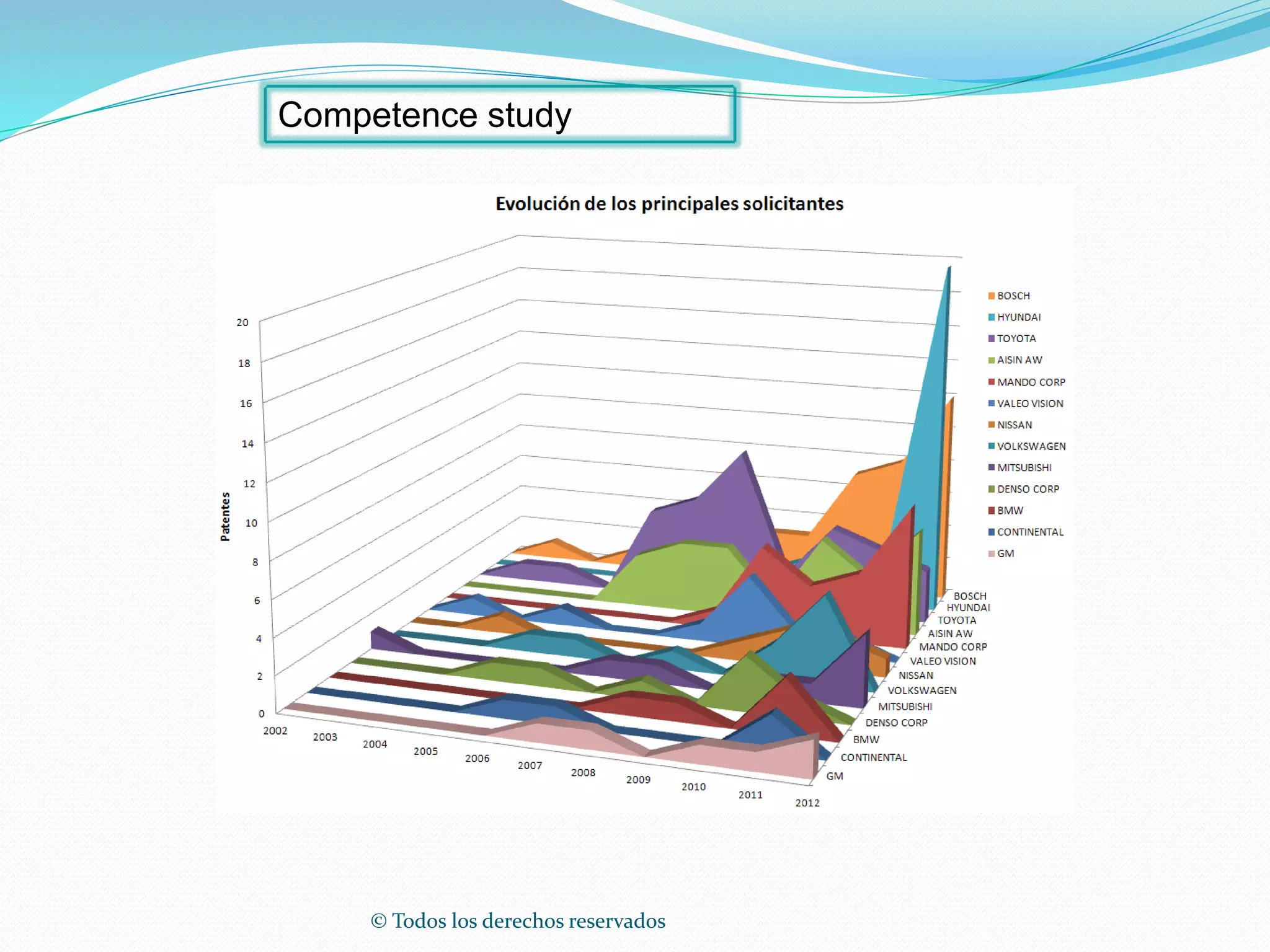
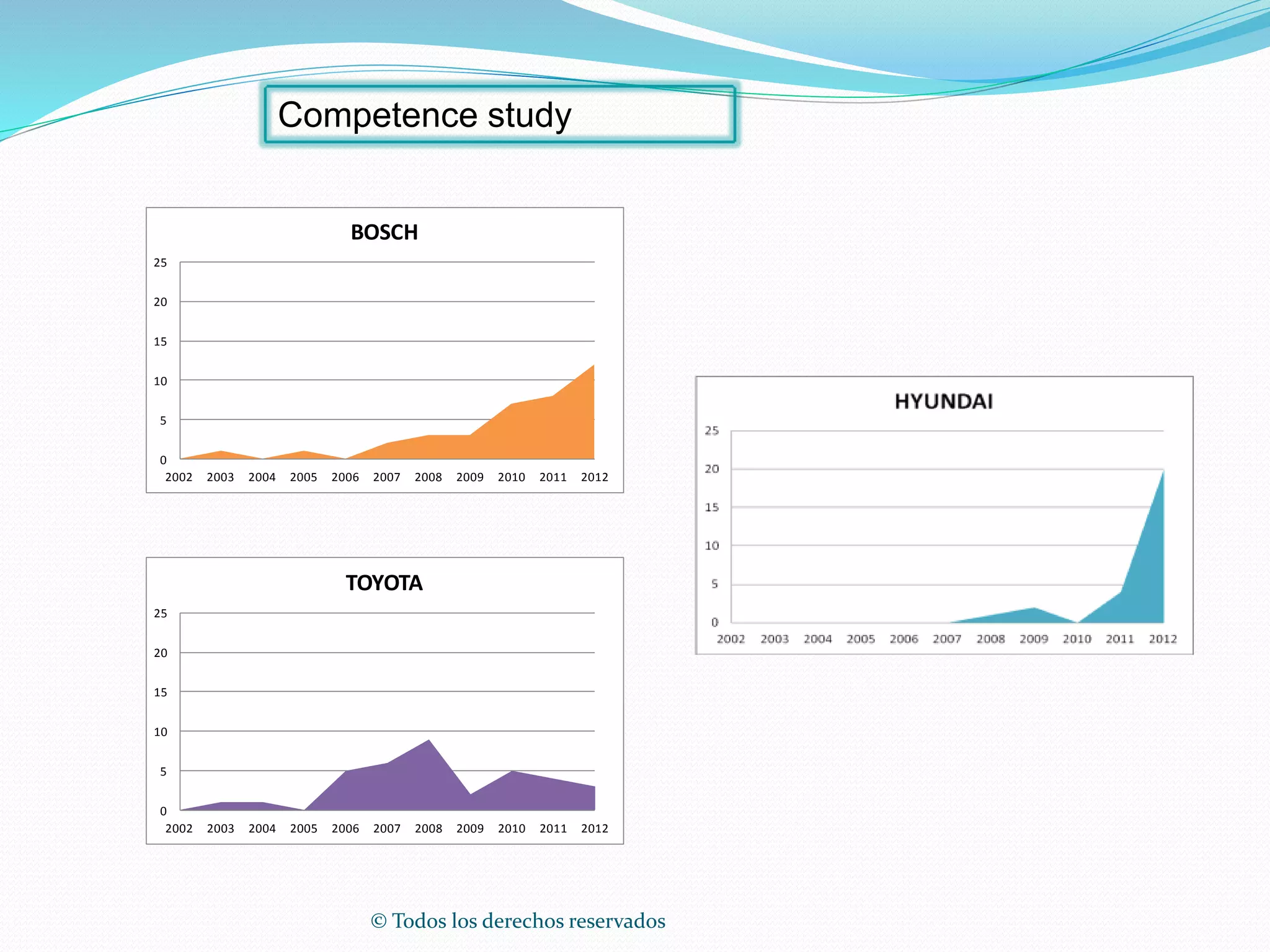
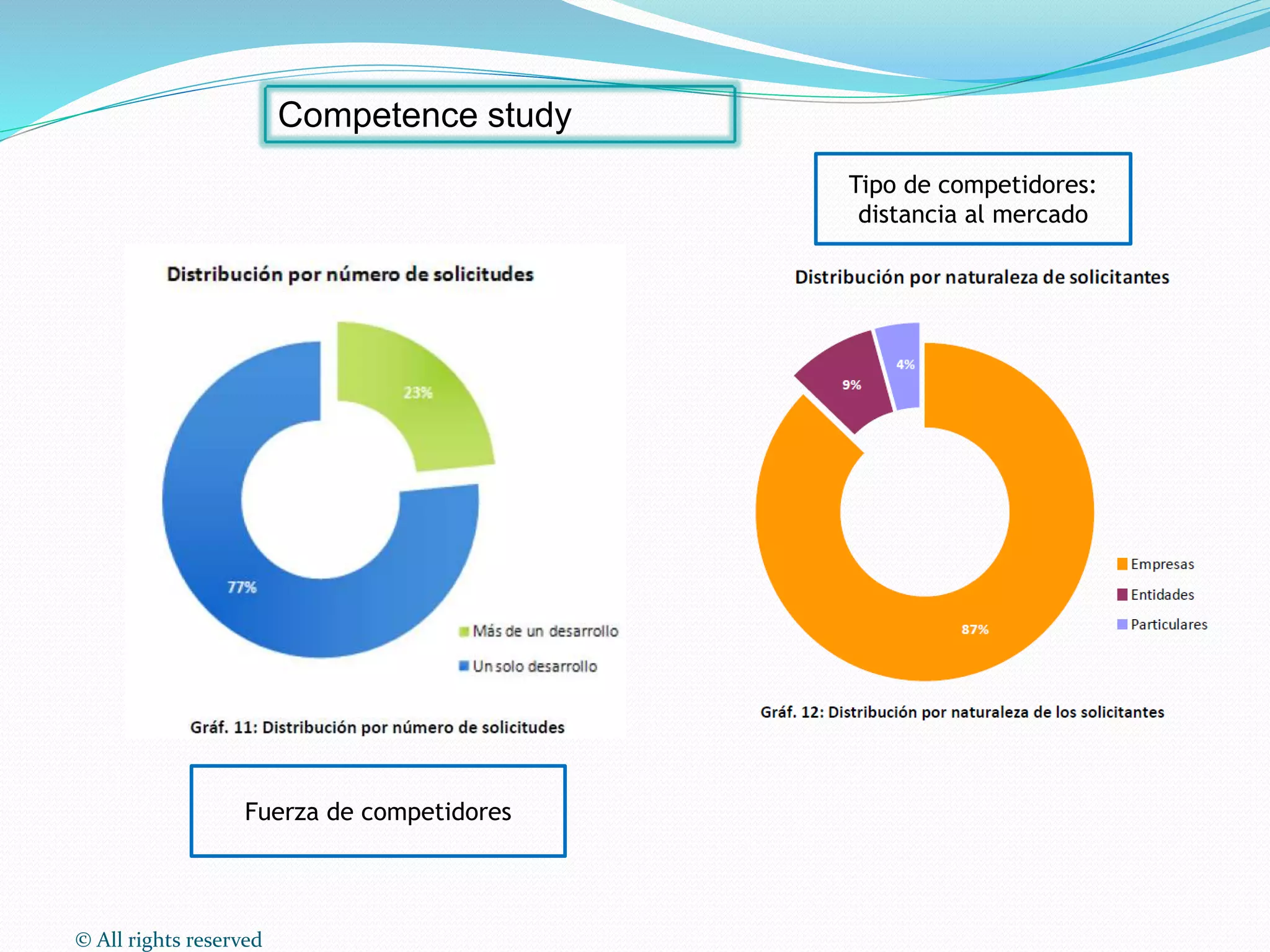
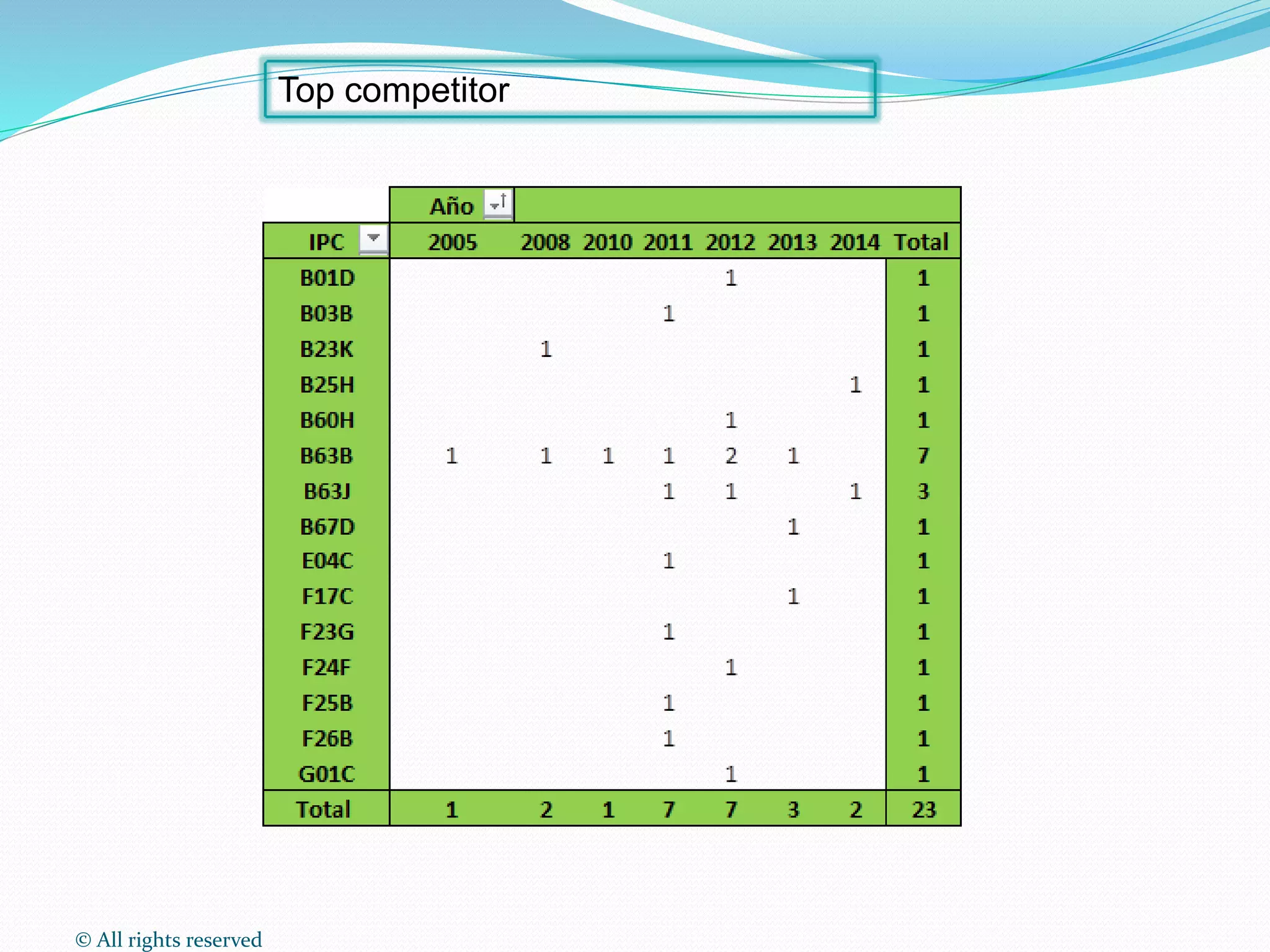
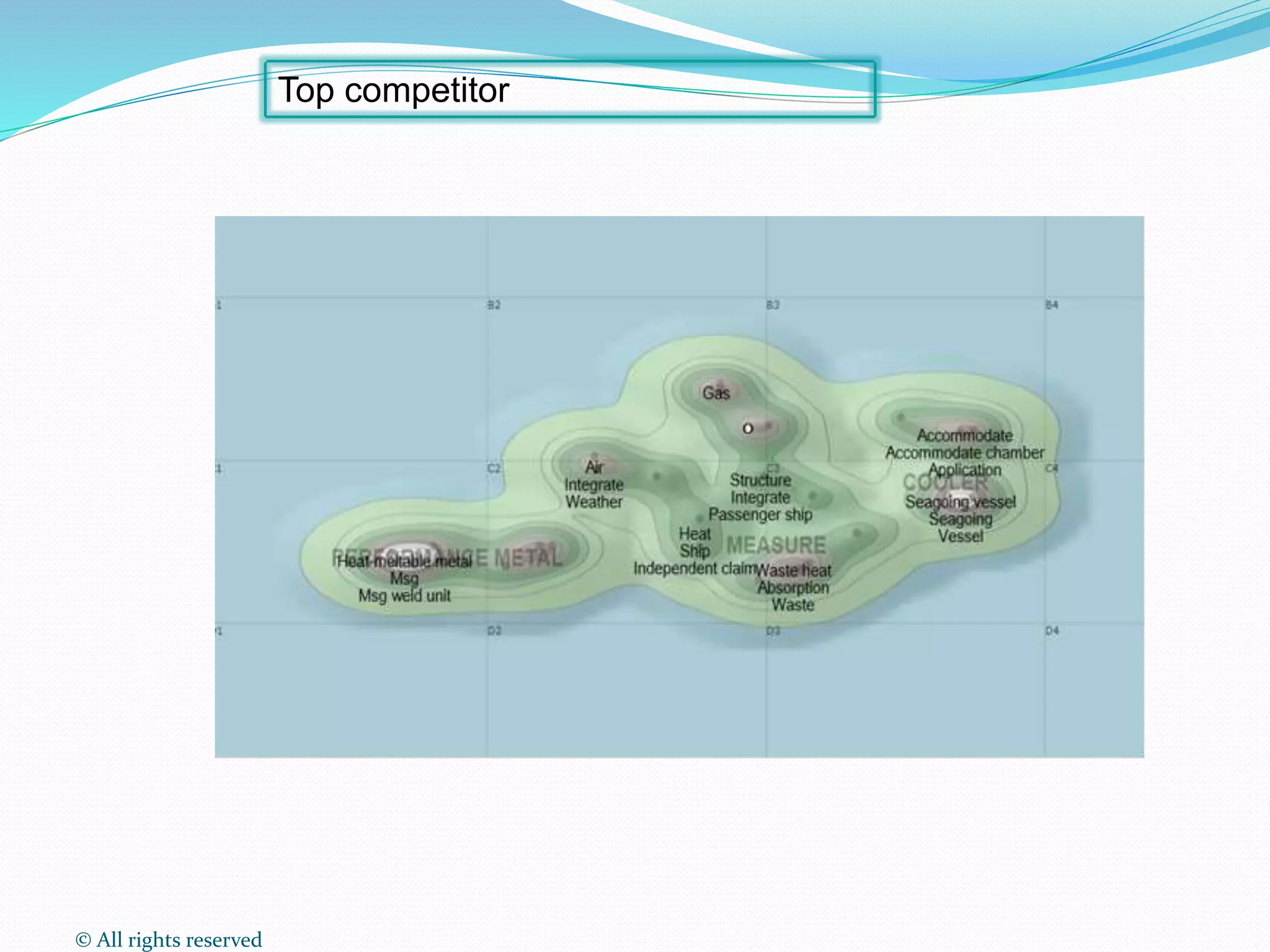
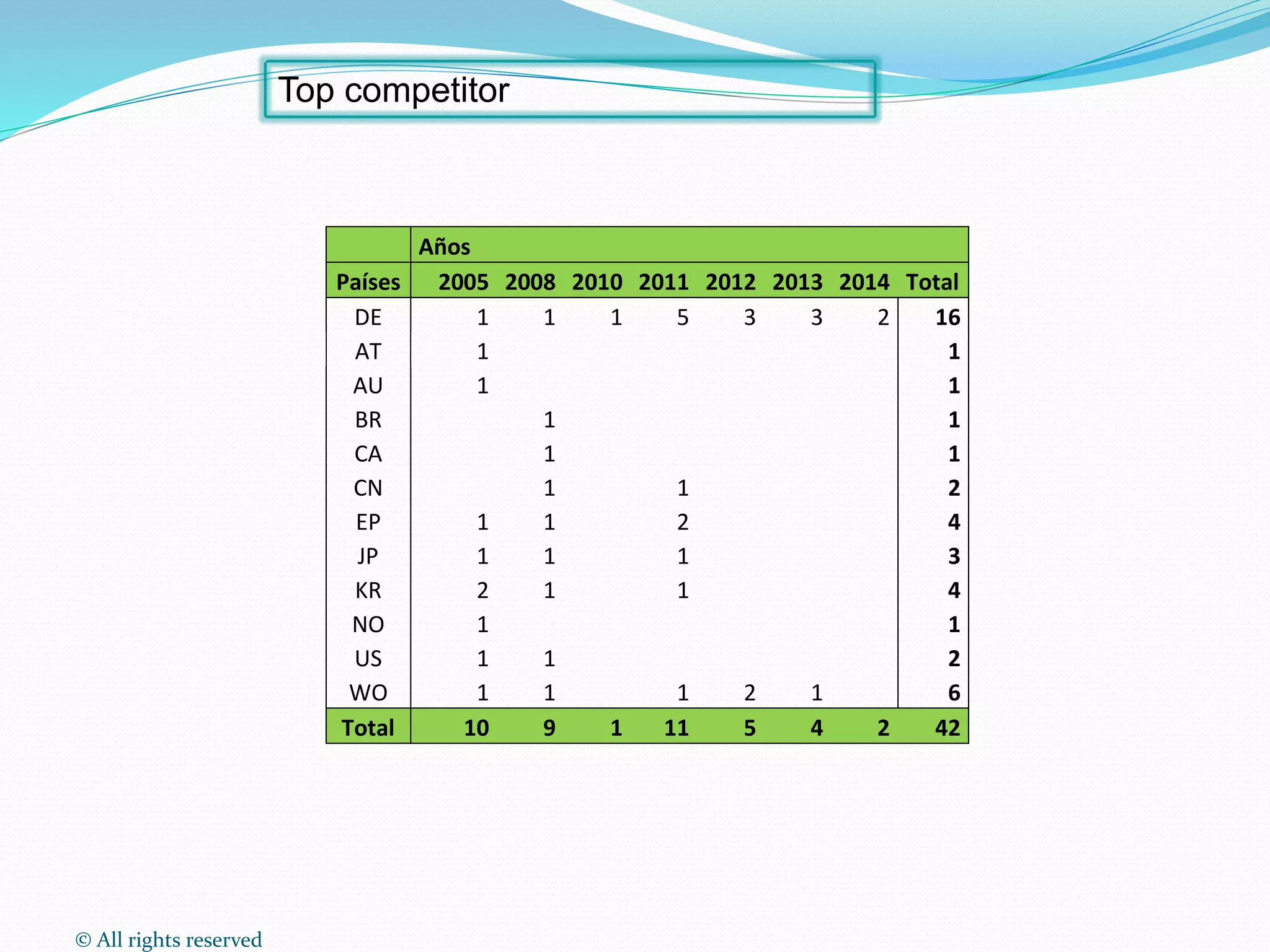
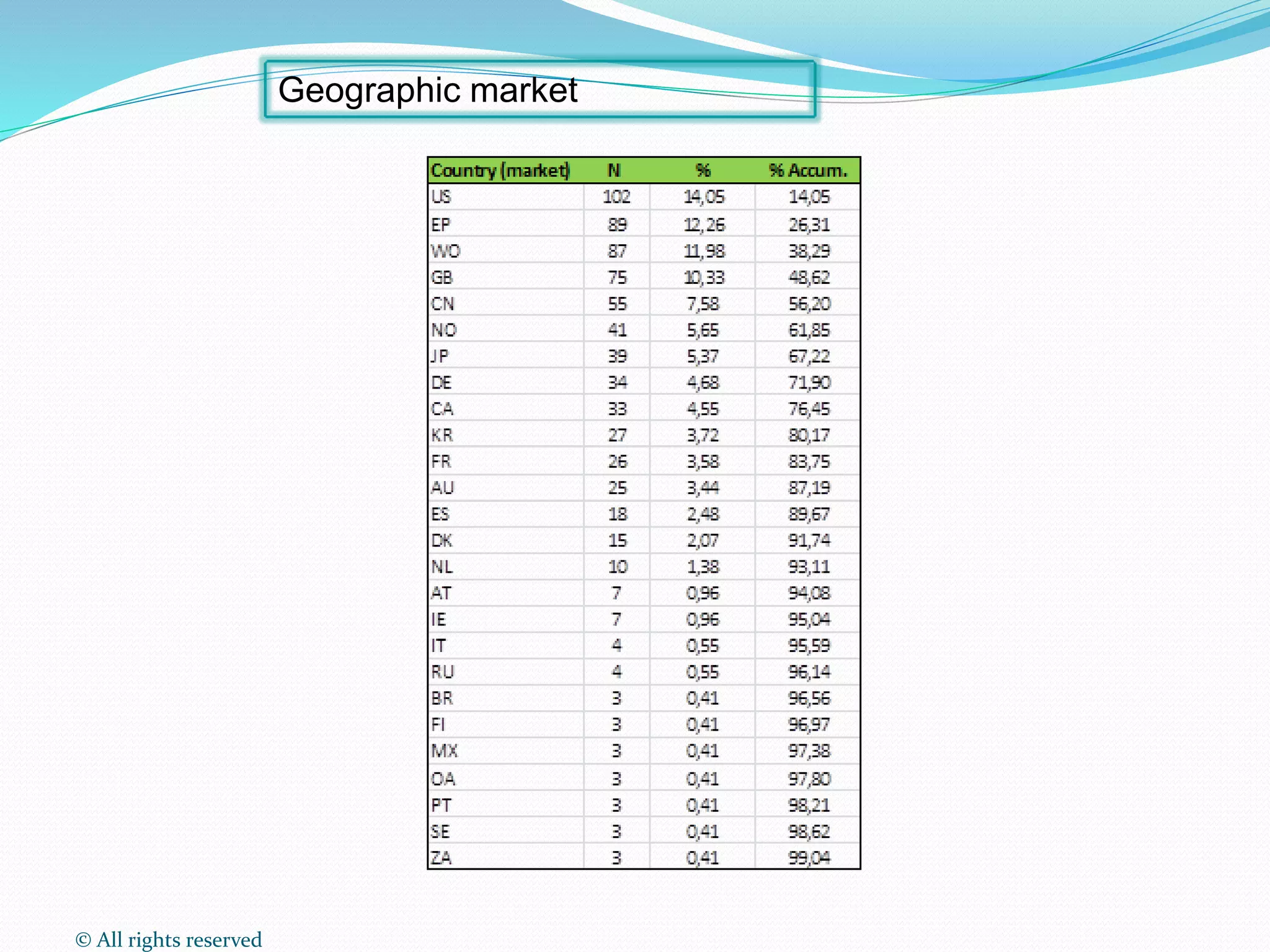
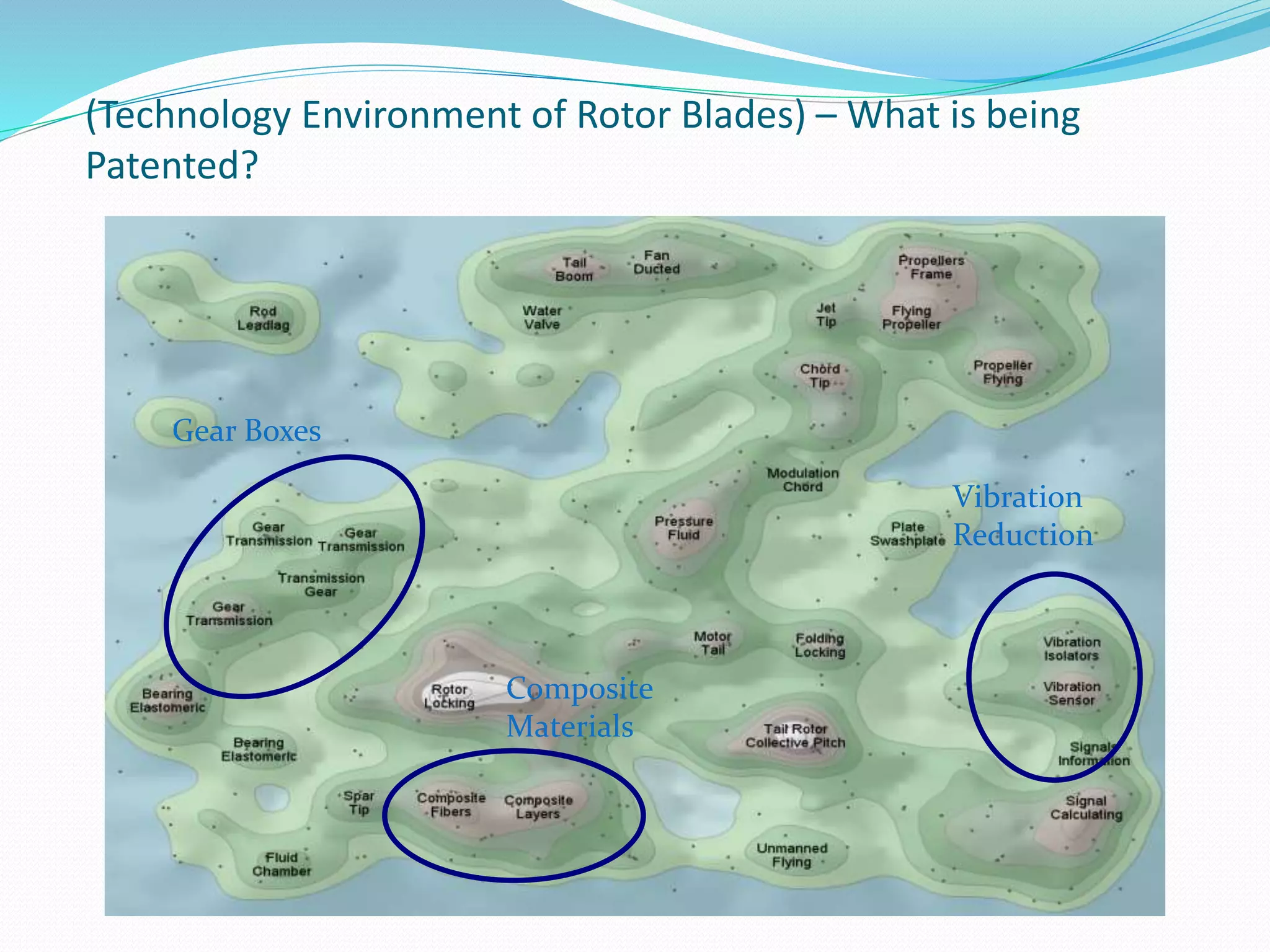
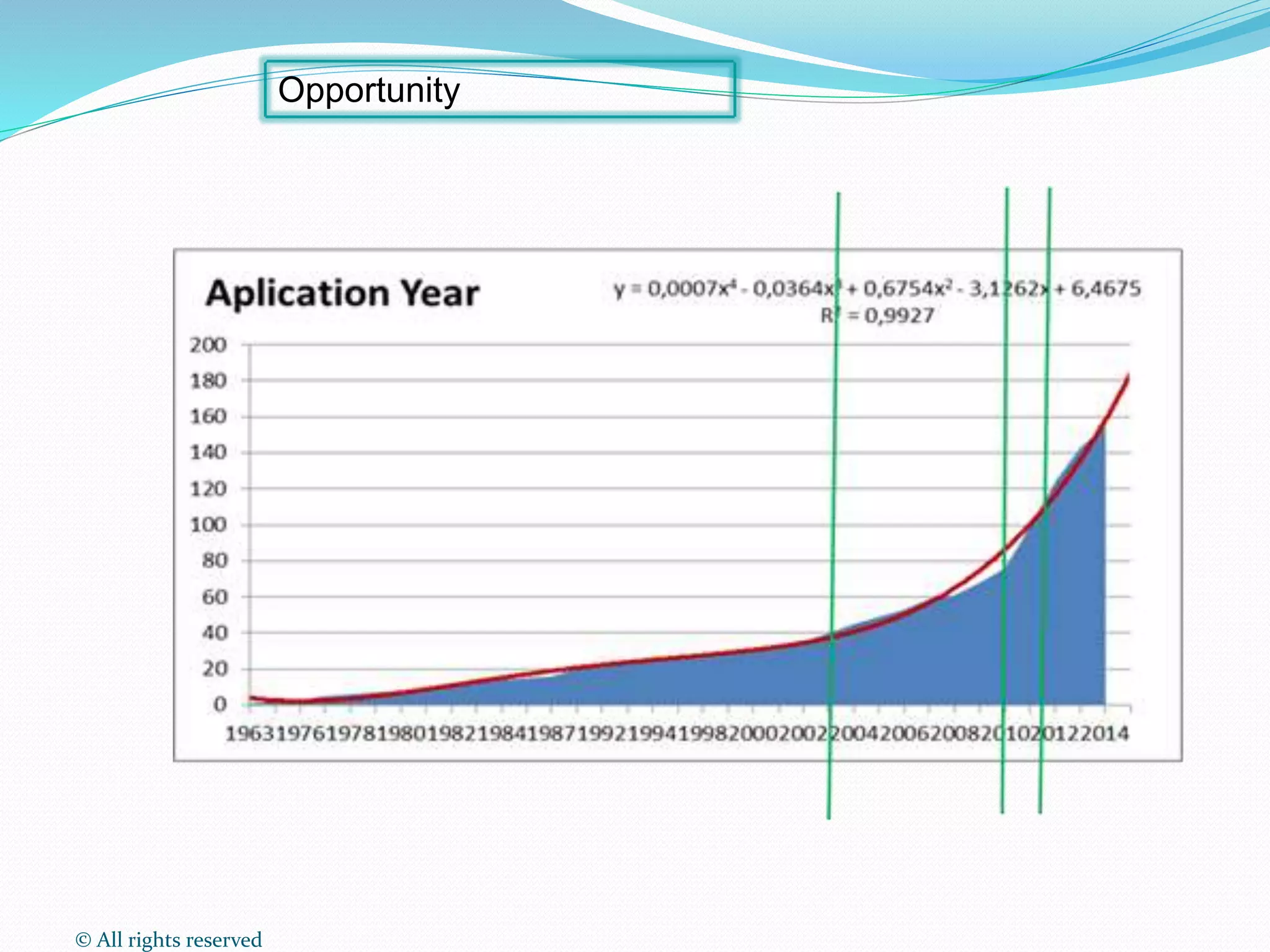
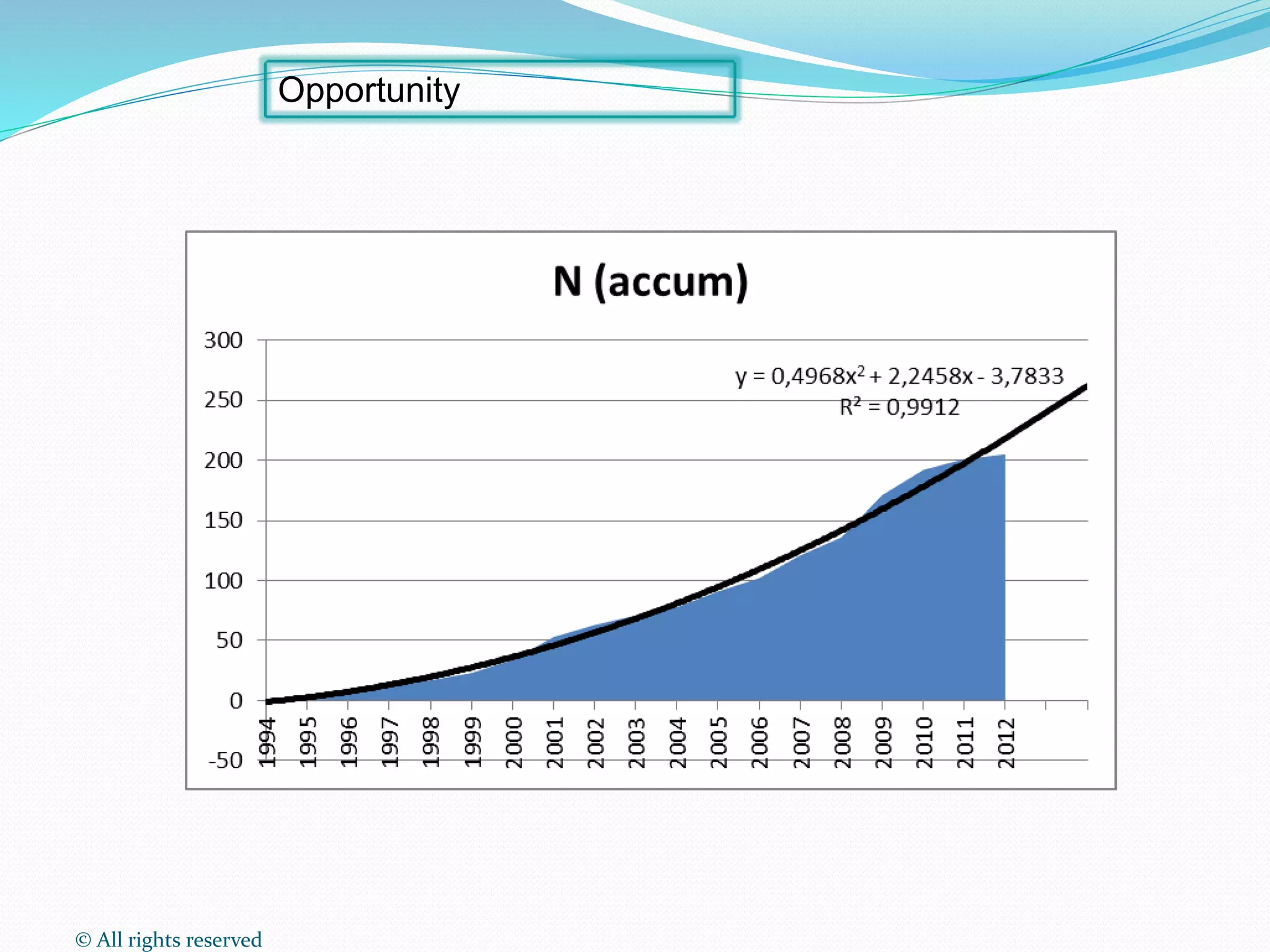
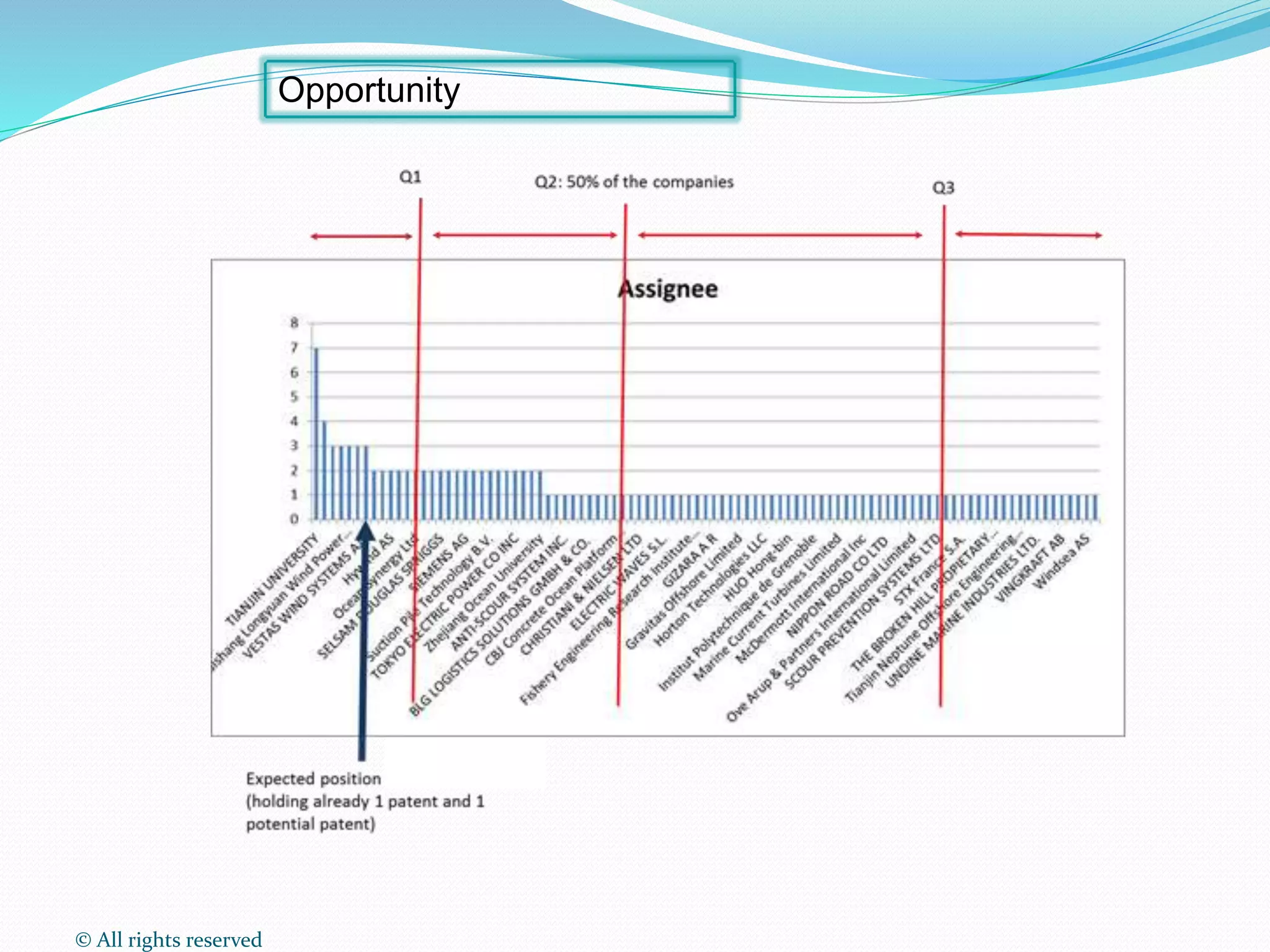
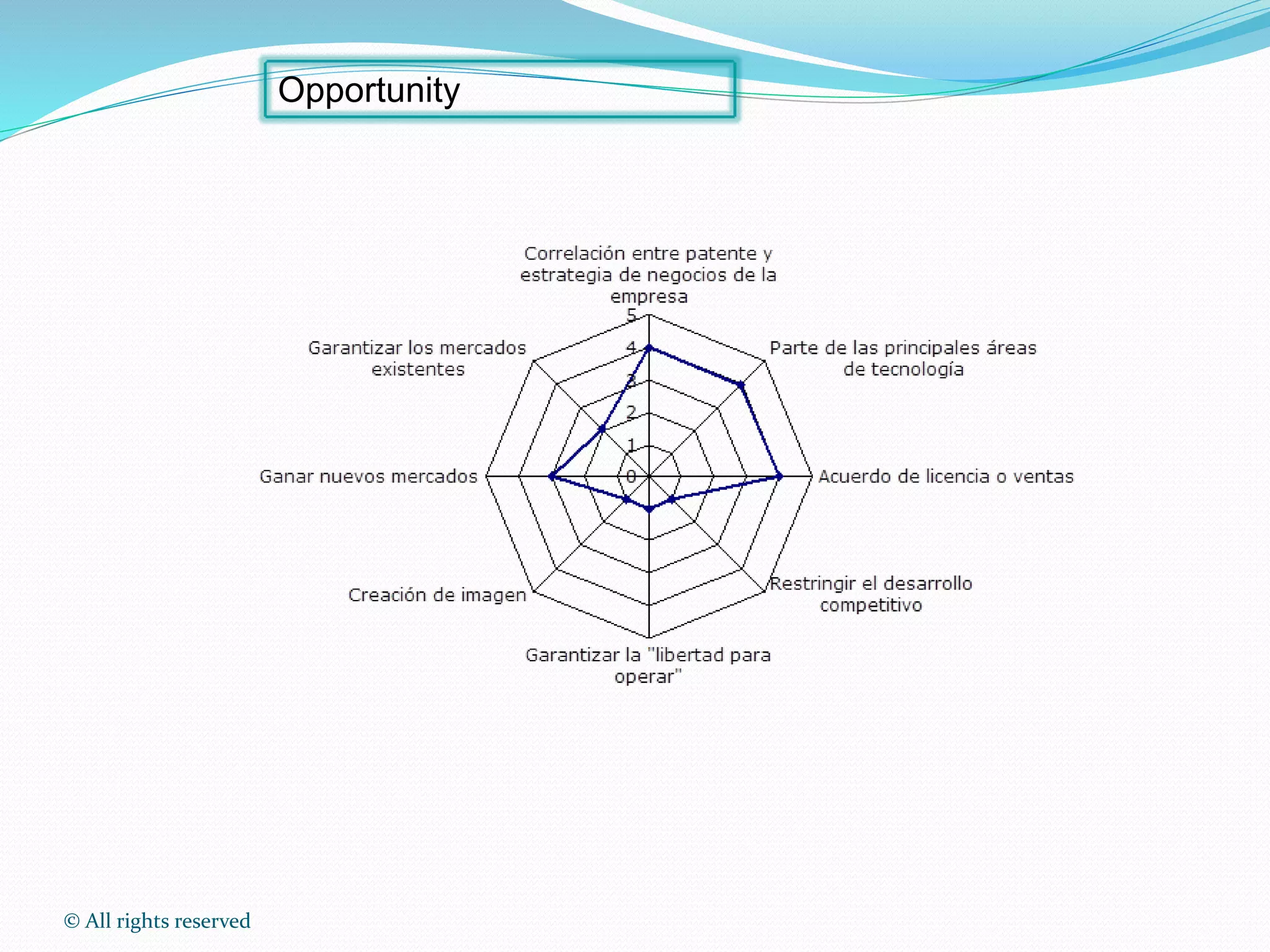
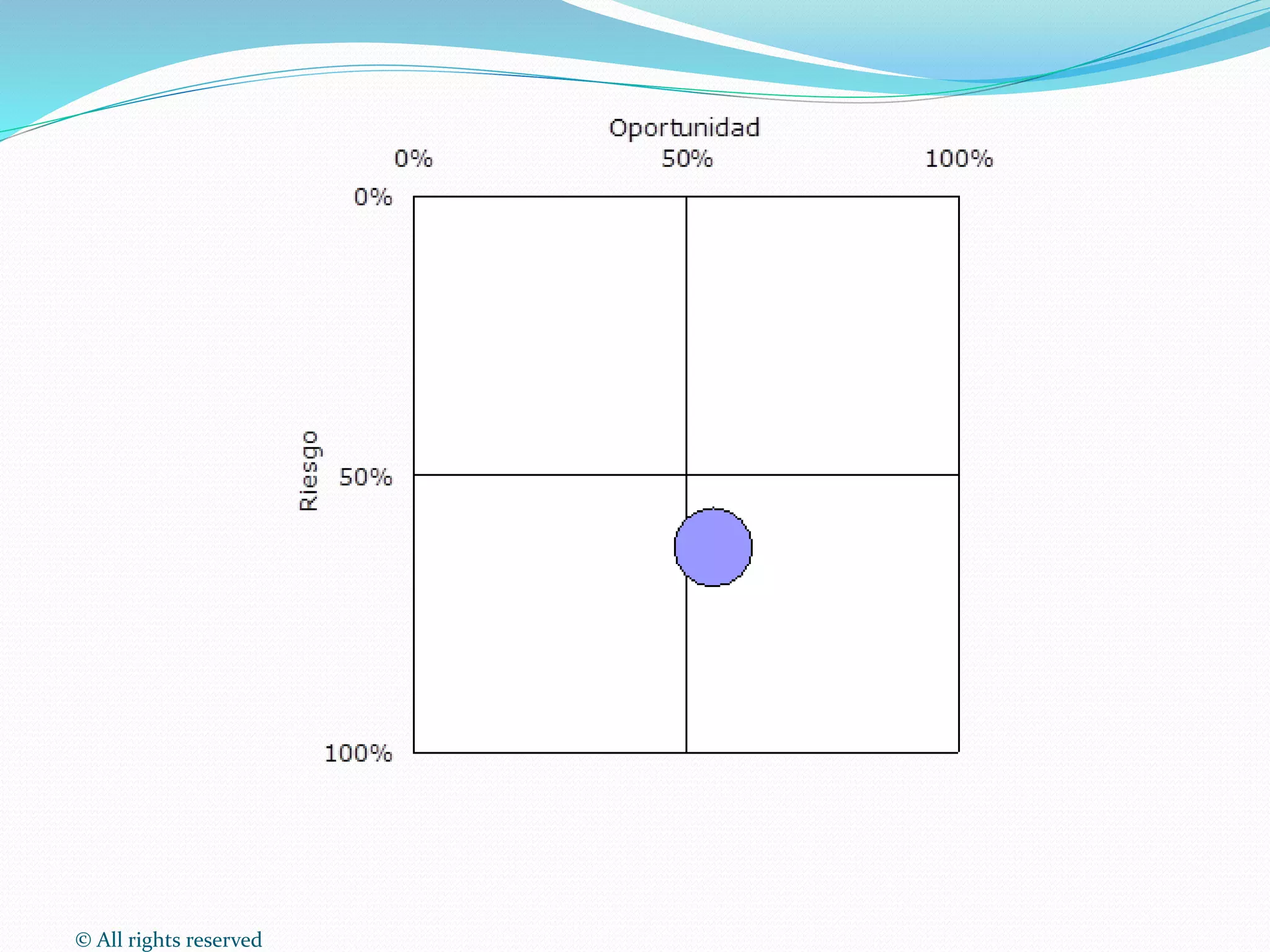
This document discusses intellectual property rights (IPR) and the importance of patent information. It defines what a patent is, including requirements for patentability. It outlines the patent application process and describes different types of IPR like trademarks, industrial designs, copyright, and personal data protection. The document emphasizes that patent information is a valuable source of technical information that can be used for competitive intelligence purposes like monitoring competitors, identifying new opportunities, and avoiding duplication of research efforts. Case studies are provided to illustrate how patent analysis can inform strategic decision making.