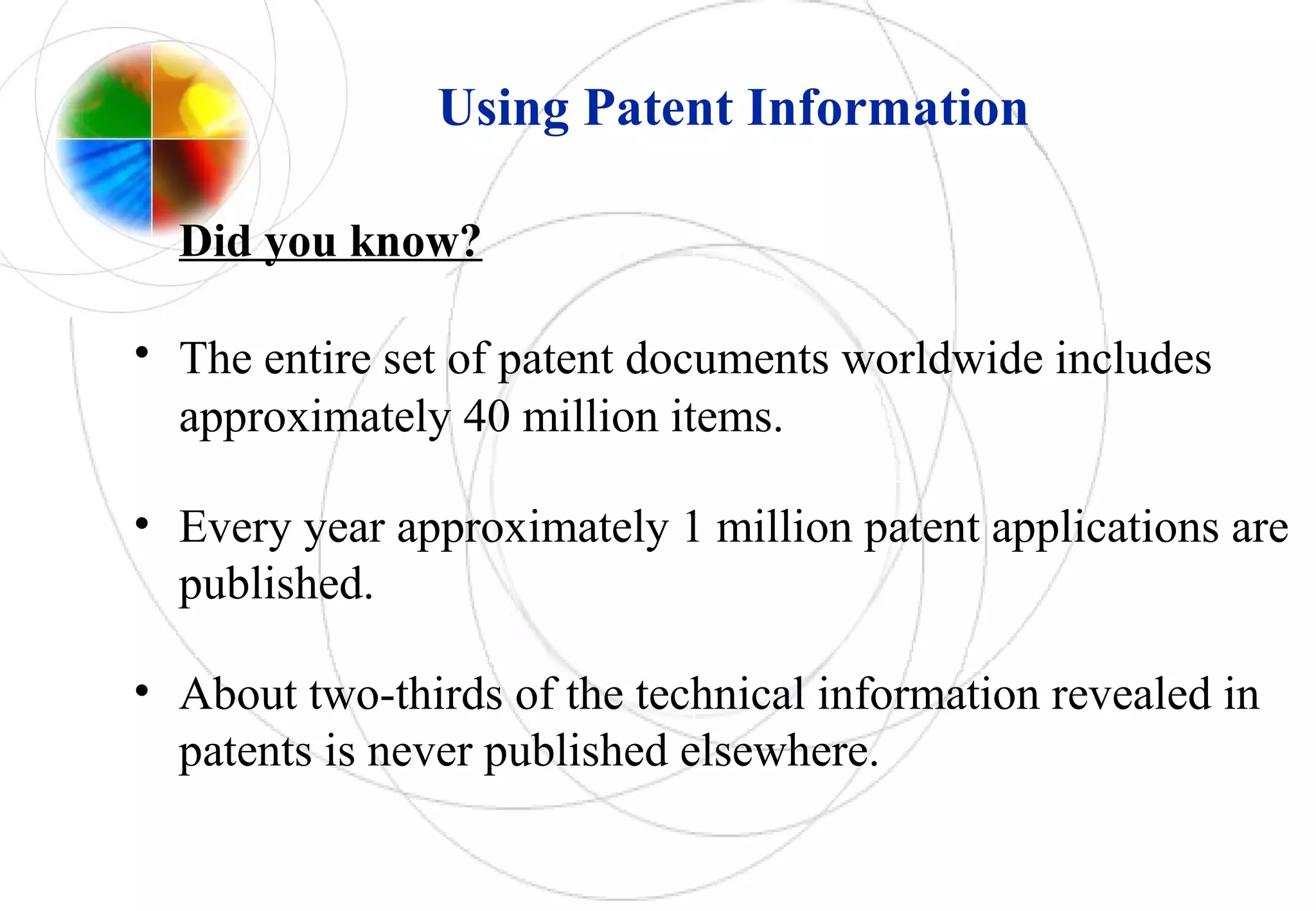
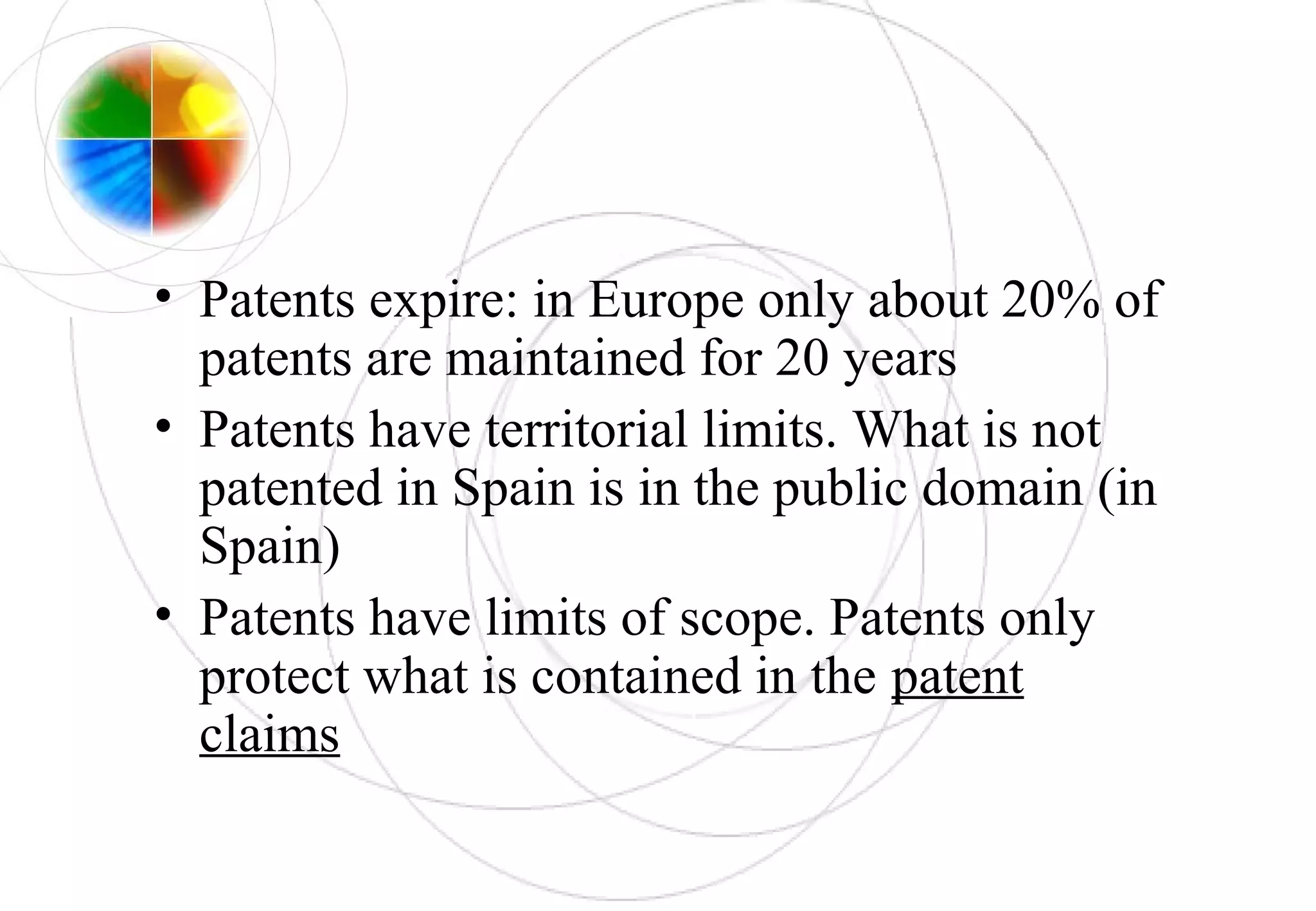
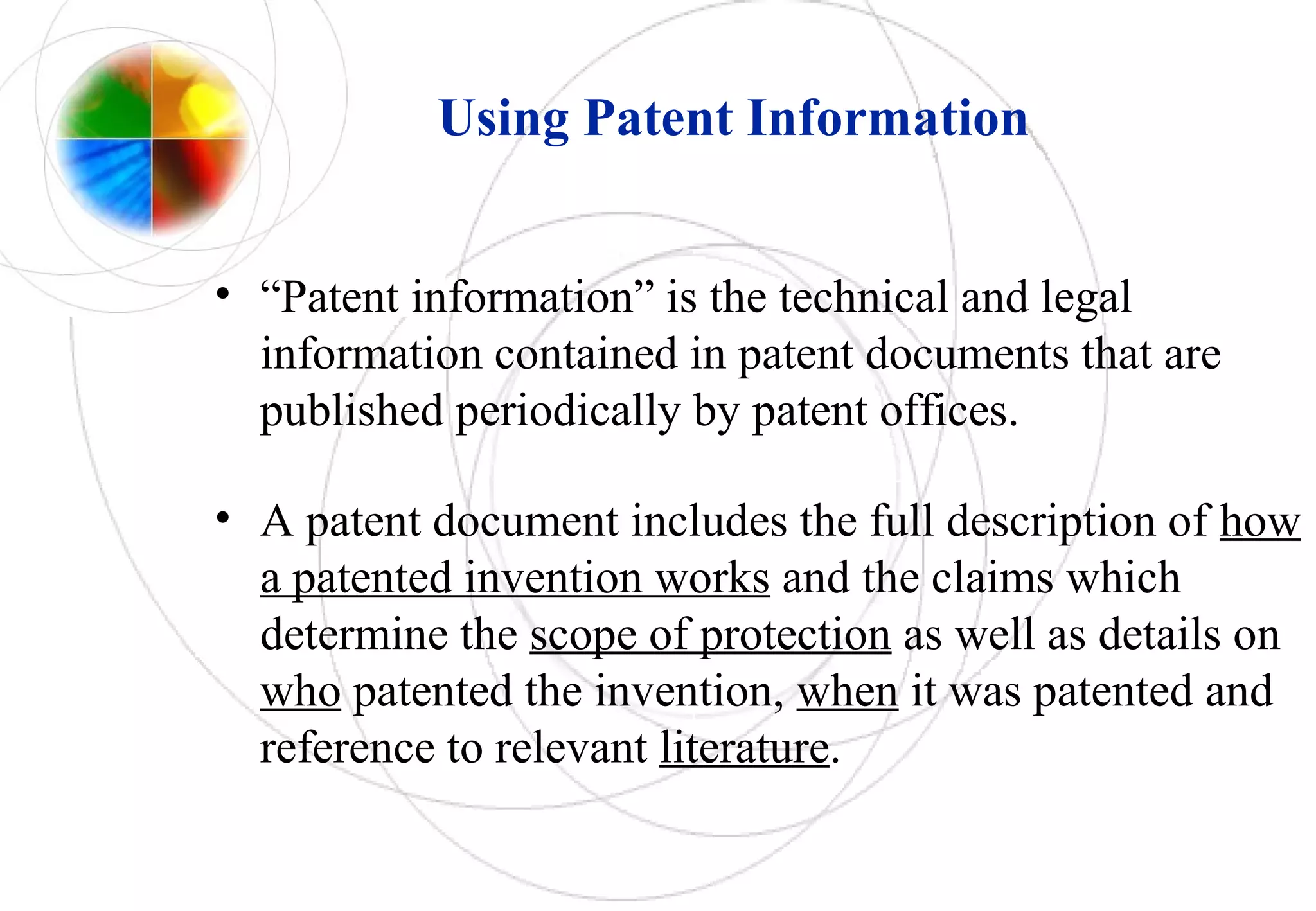
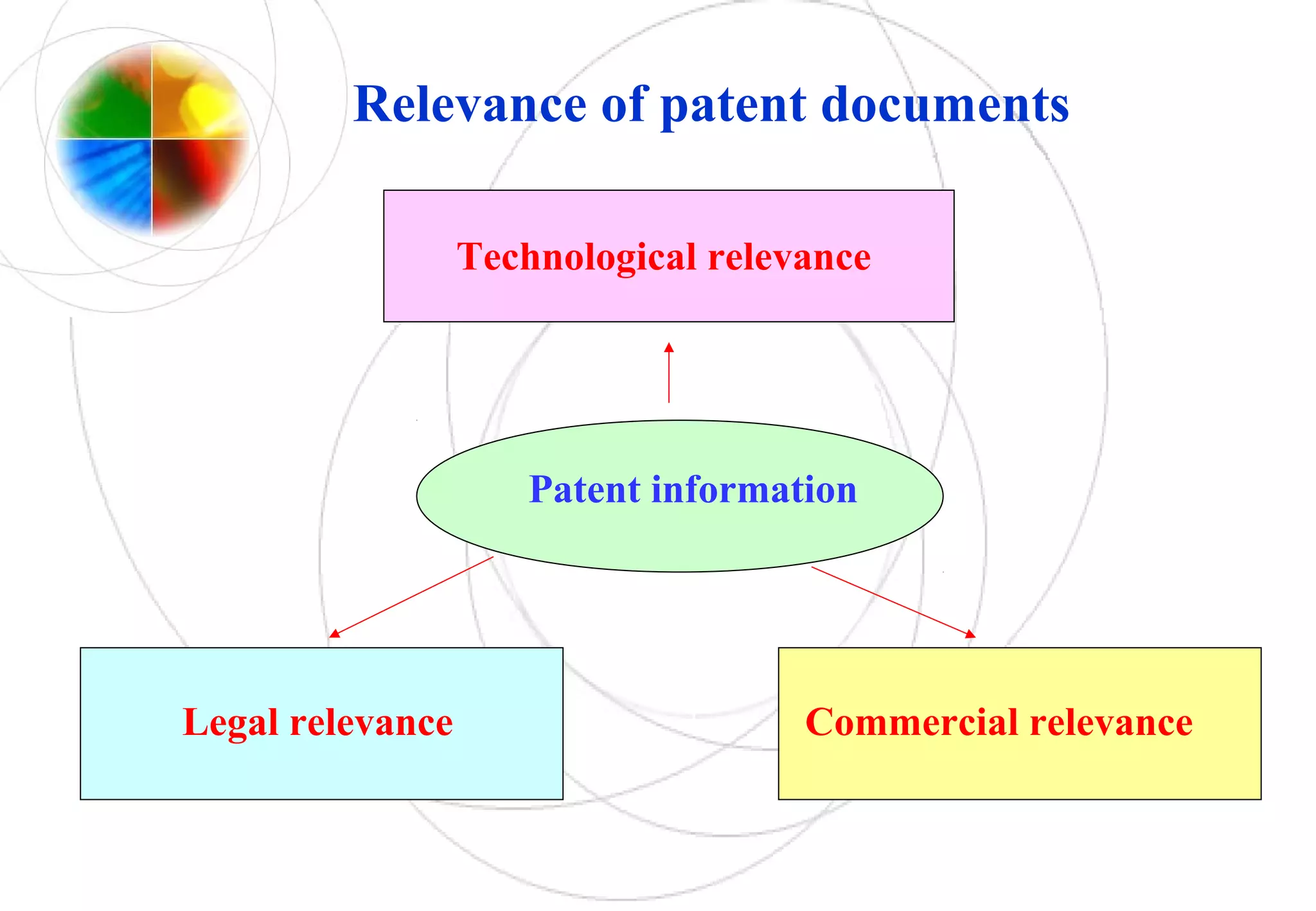
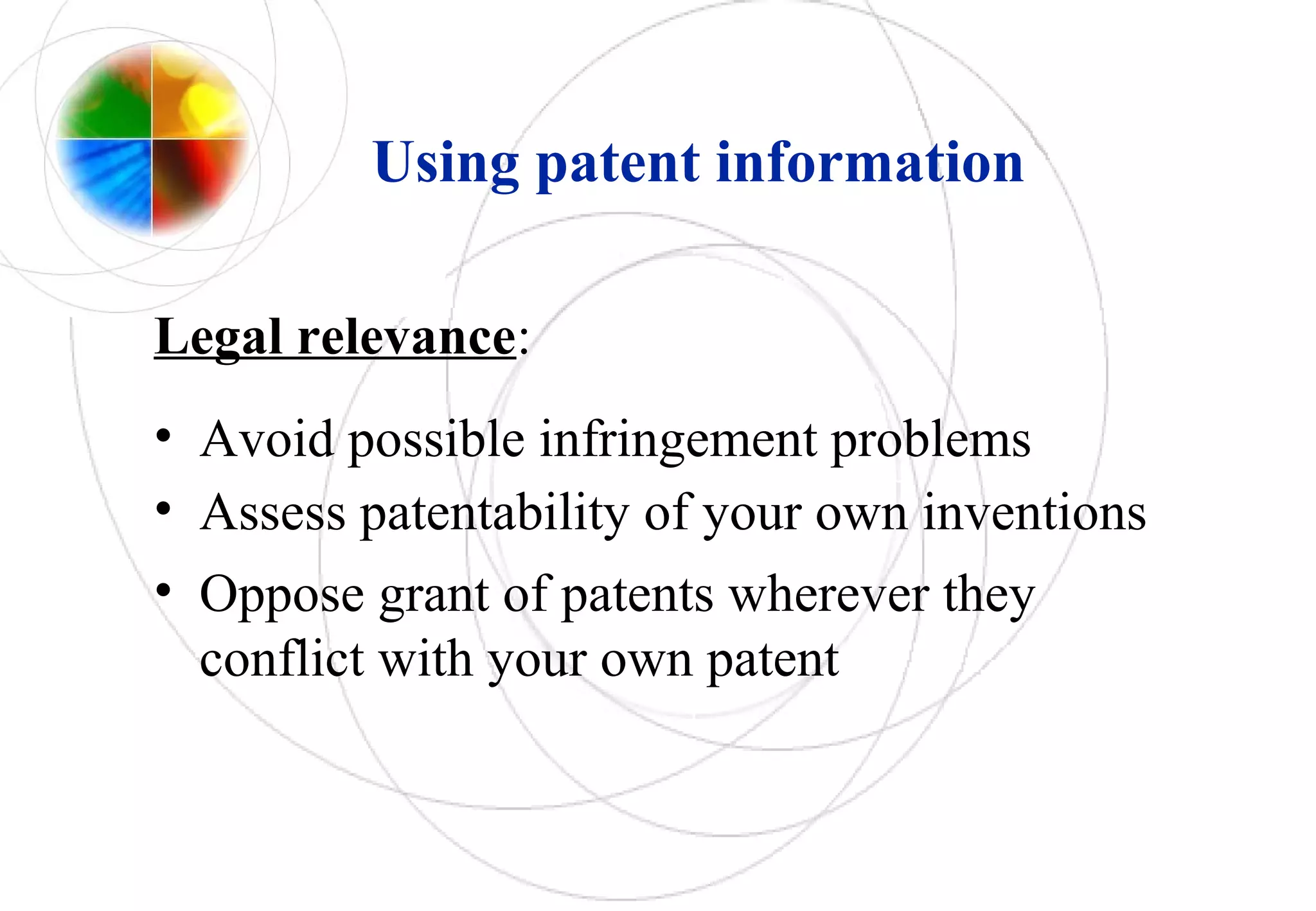
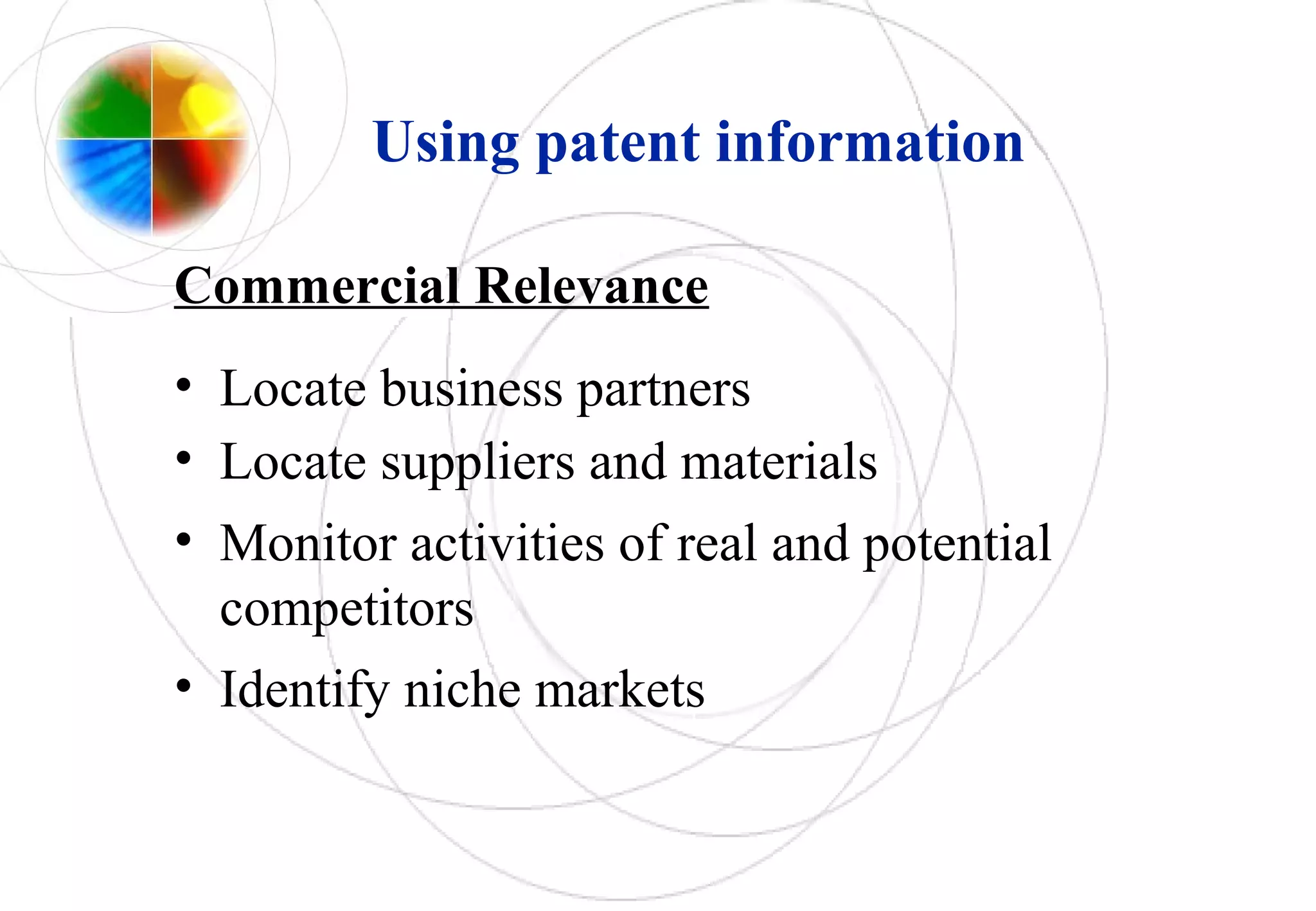
This document discusses intellectual property rights and innovation management. It provides information on patents, trademarks, and other intellectual property topics. Some key points:
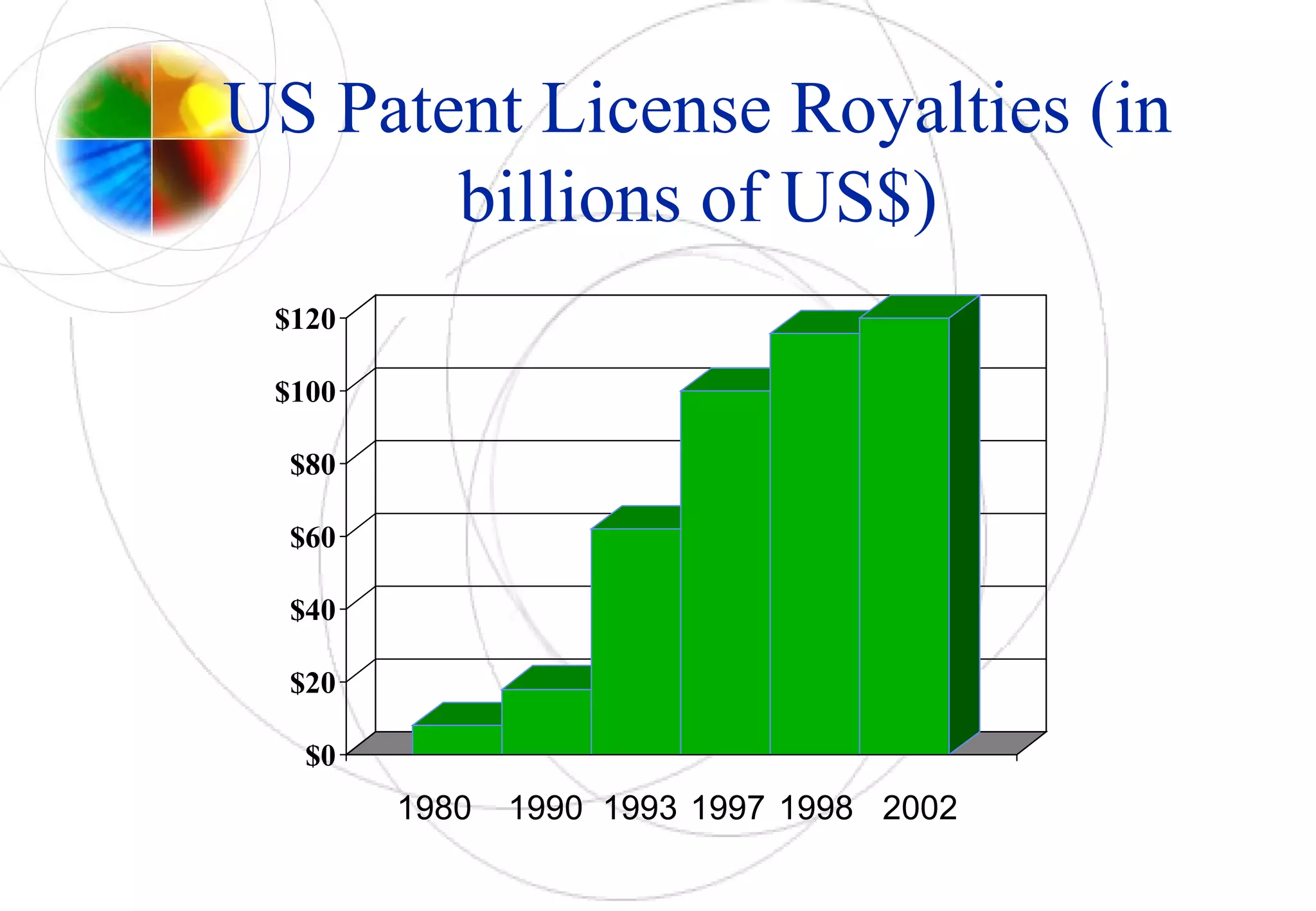
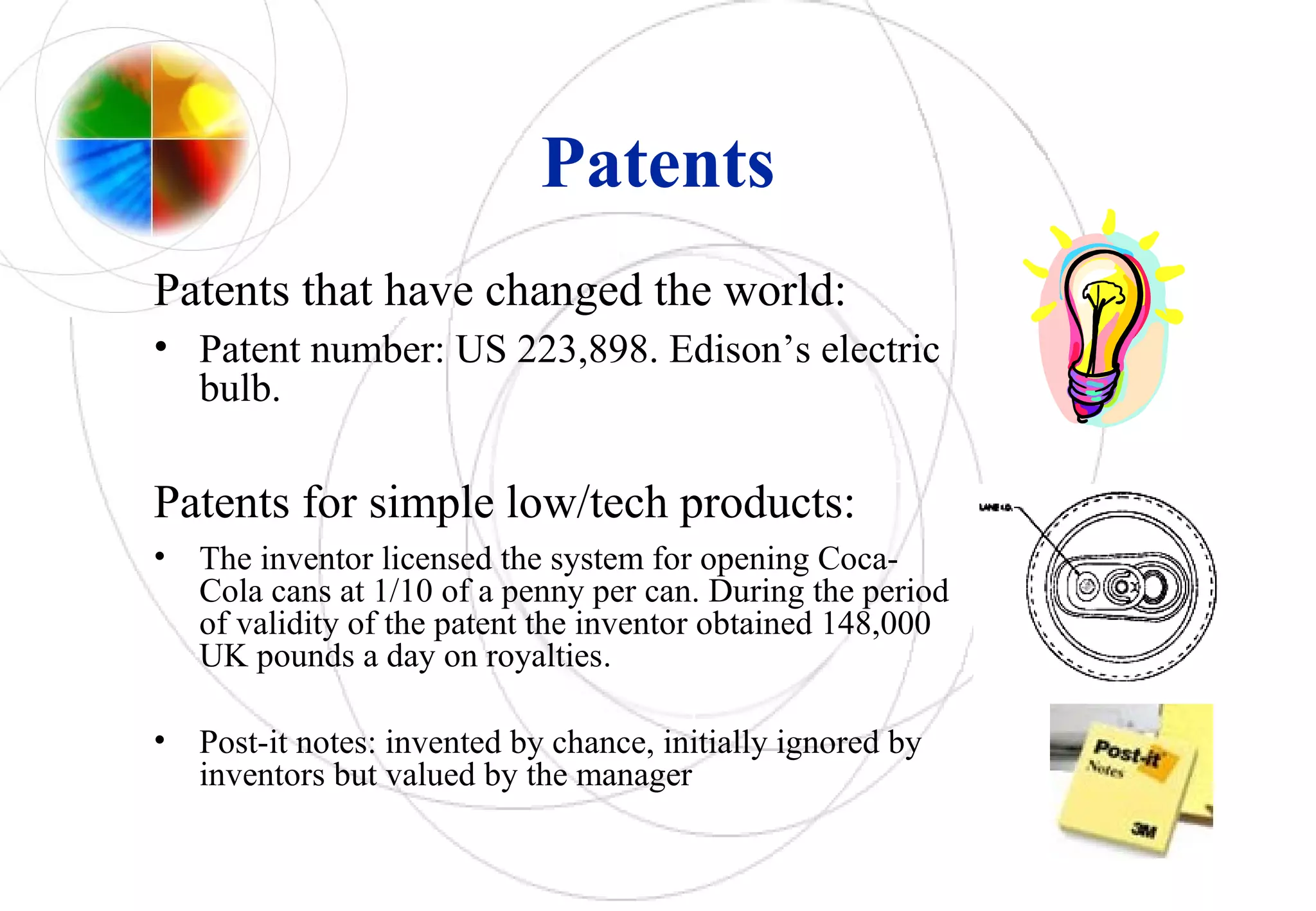
- Patents provide exclusivity for inventions and allow companies to profit from new products and technologies through licensing revenues or preventing copying.
- Factors like functional advantages, design, branding, and availability influence the success of new products in the market. Intellectual property rights like patents, trademarks, and designs can protect these features and maintain a company's exclusivity.
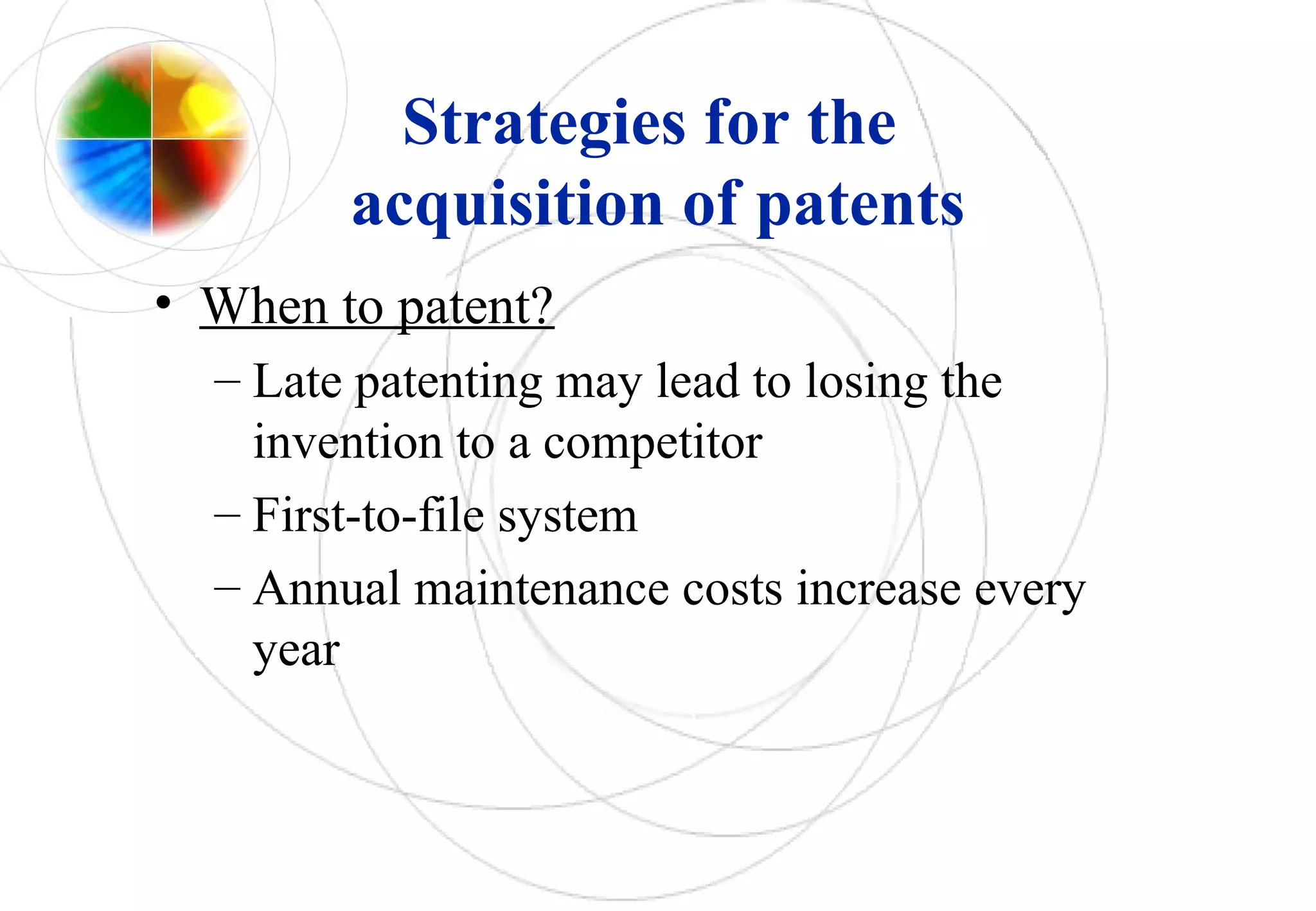
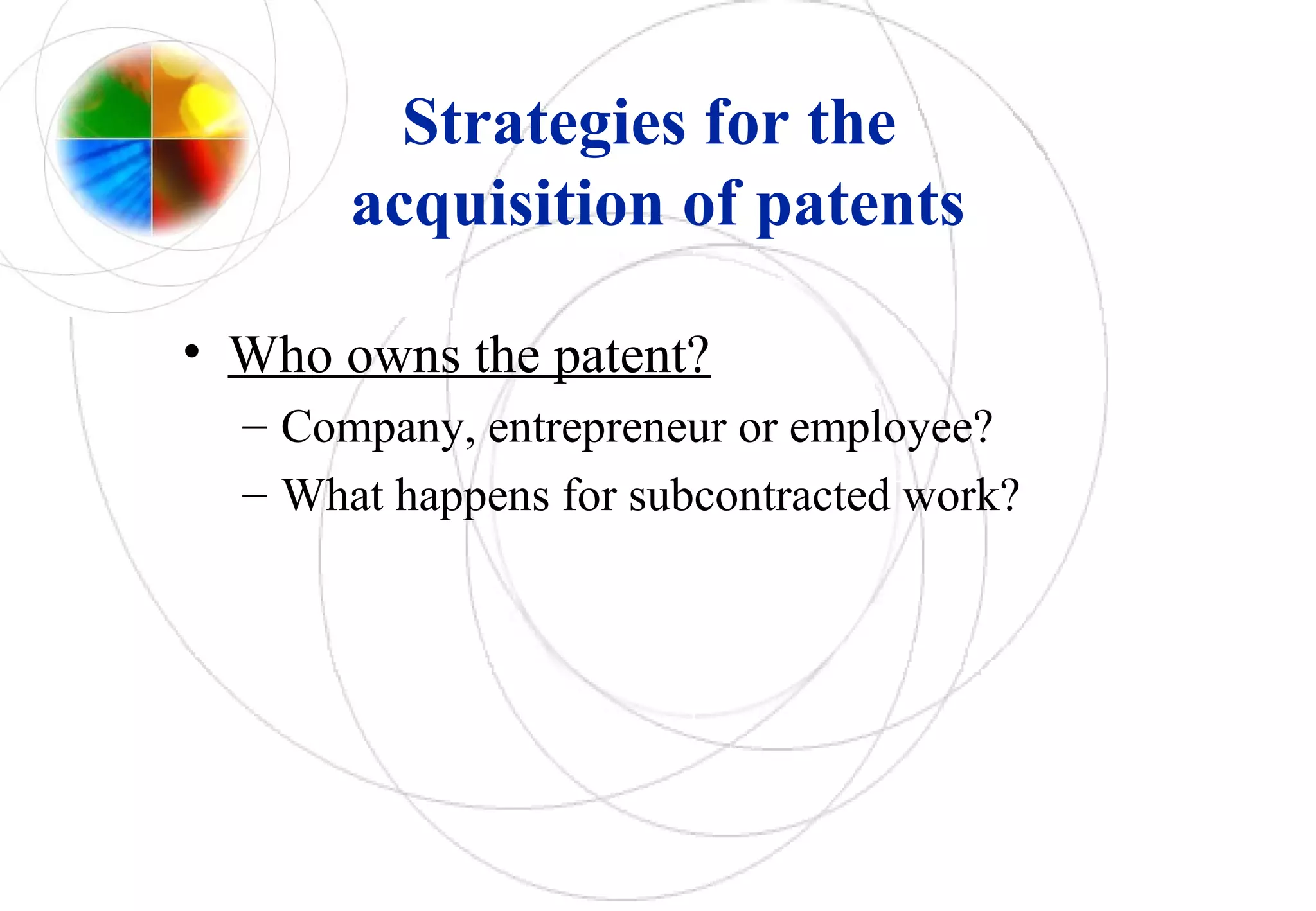
- Strategies for acquiring and exploiting patents include deciding what and when to patent, where to file, and whether to pursue own exploitation, licensing, or a combination. Patent information itself is publicly available and