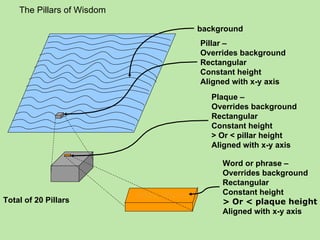
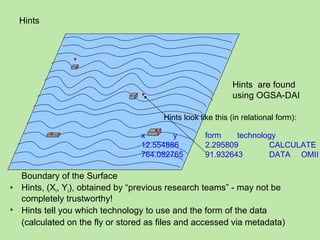
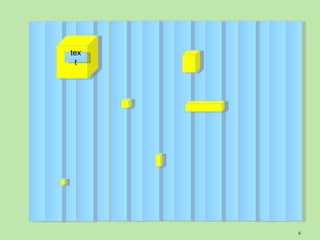
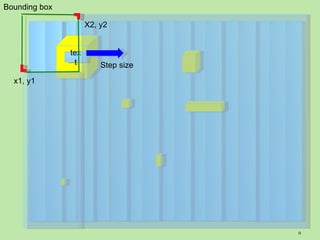
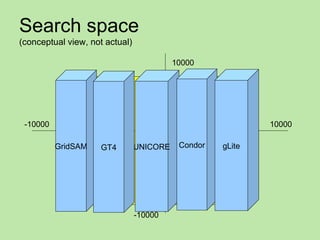
The document describes an integrating practical simulation involving searching for pillars on a surface to find words of wisdom. Participants are expected to write programs to interface tools to search across the surface for pillars and plaques, read words on the plaques, recognize patterns, and make use of capabilities. Instructions are provided for using scanner tools to search areas and submitting findings, as well as technology-specific instructions. Participants will report results and insights gained from searching strategies and technology evaluations.