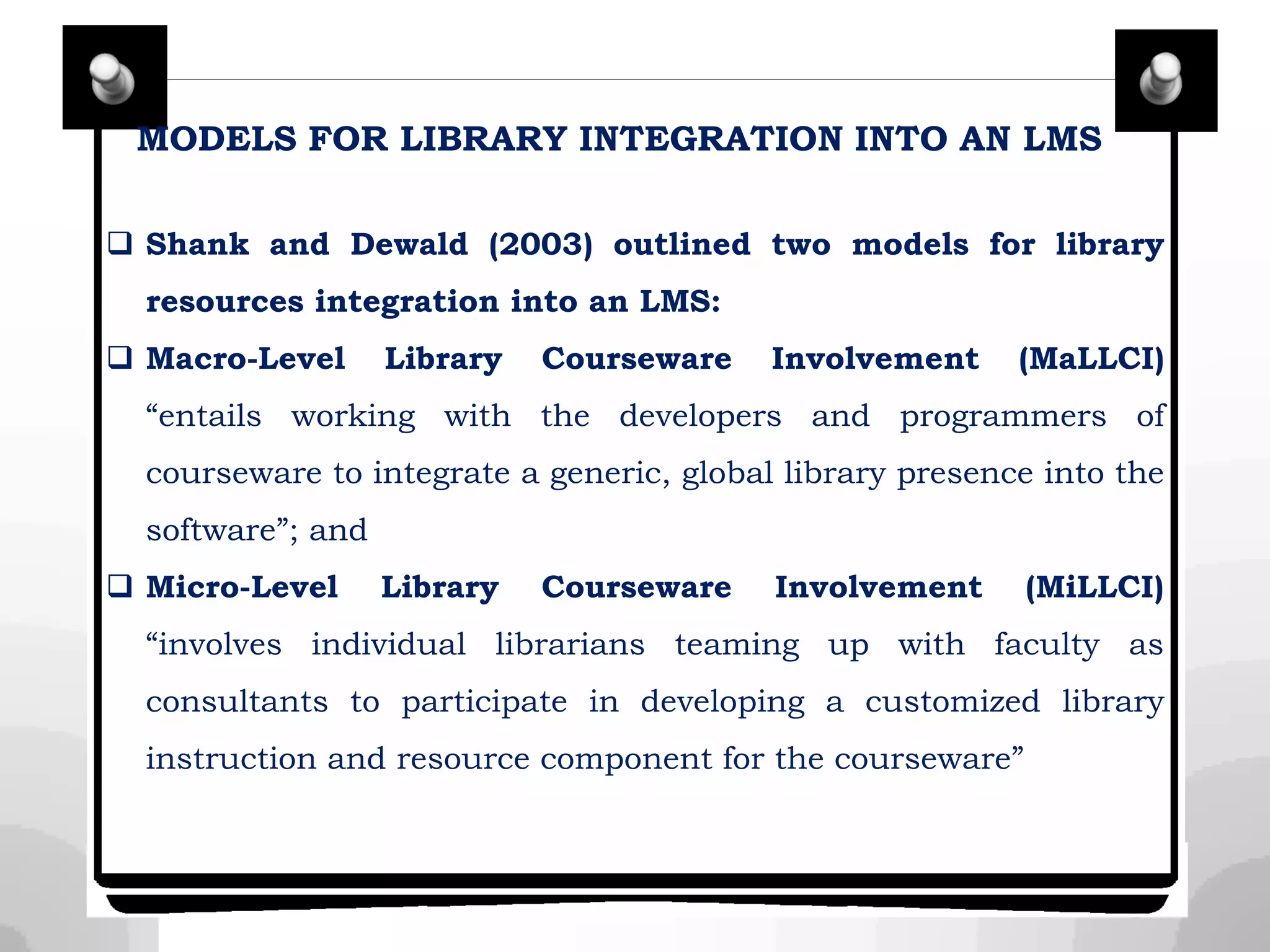
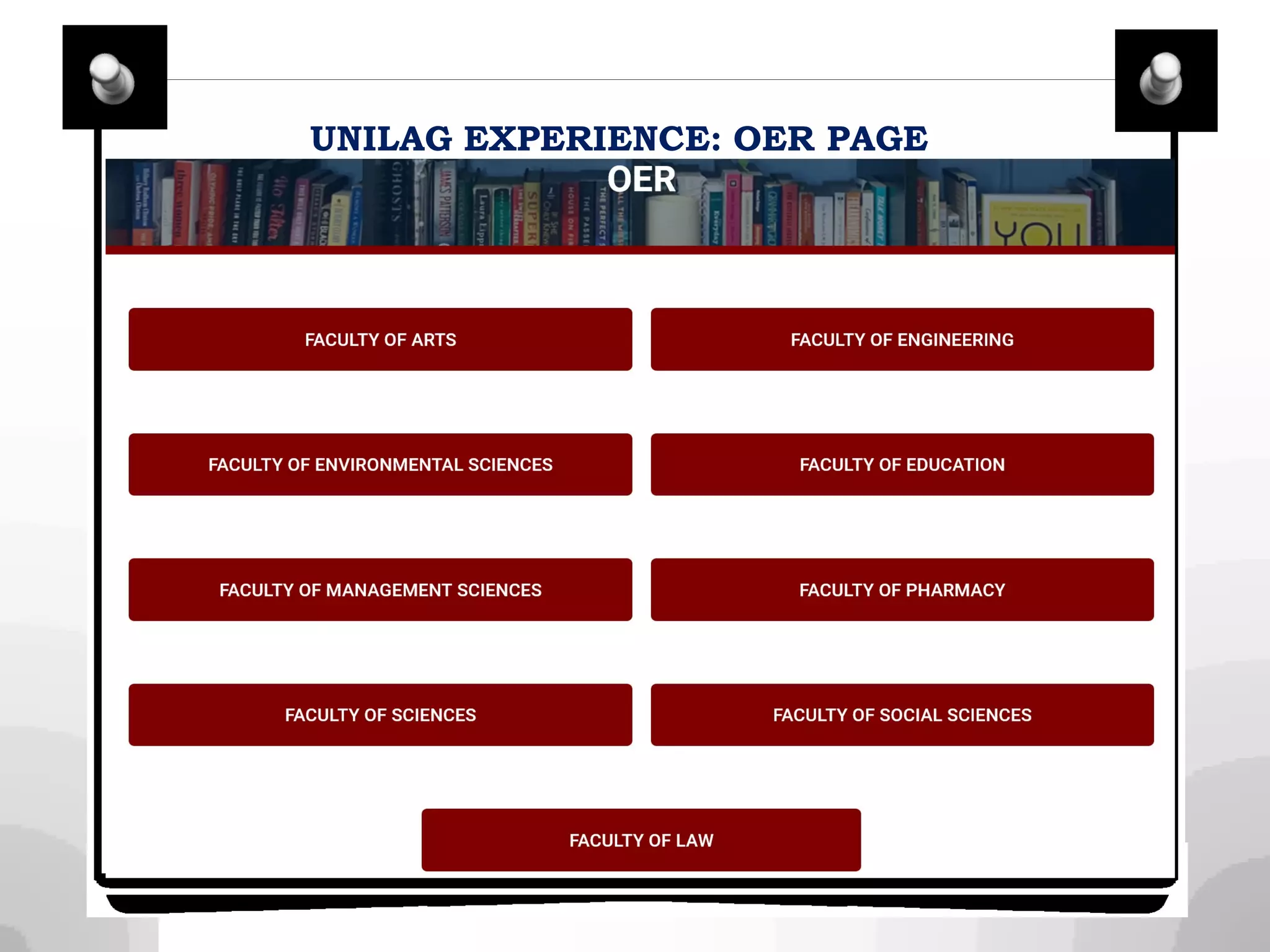
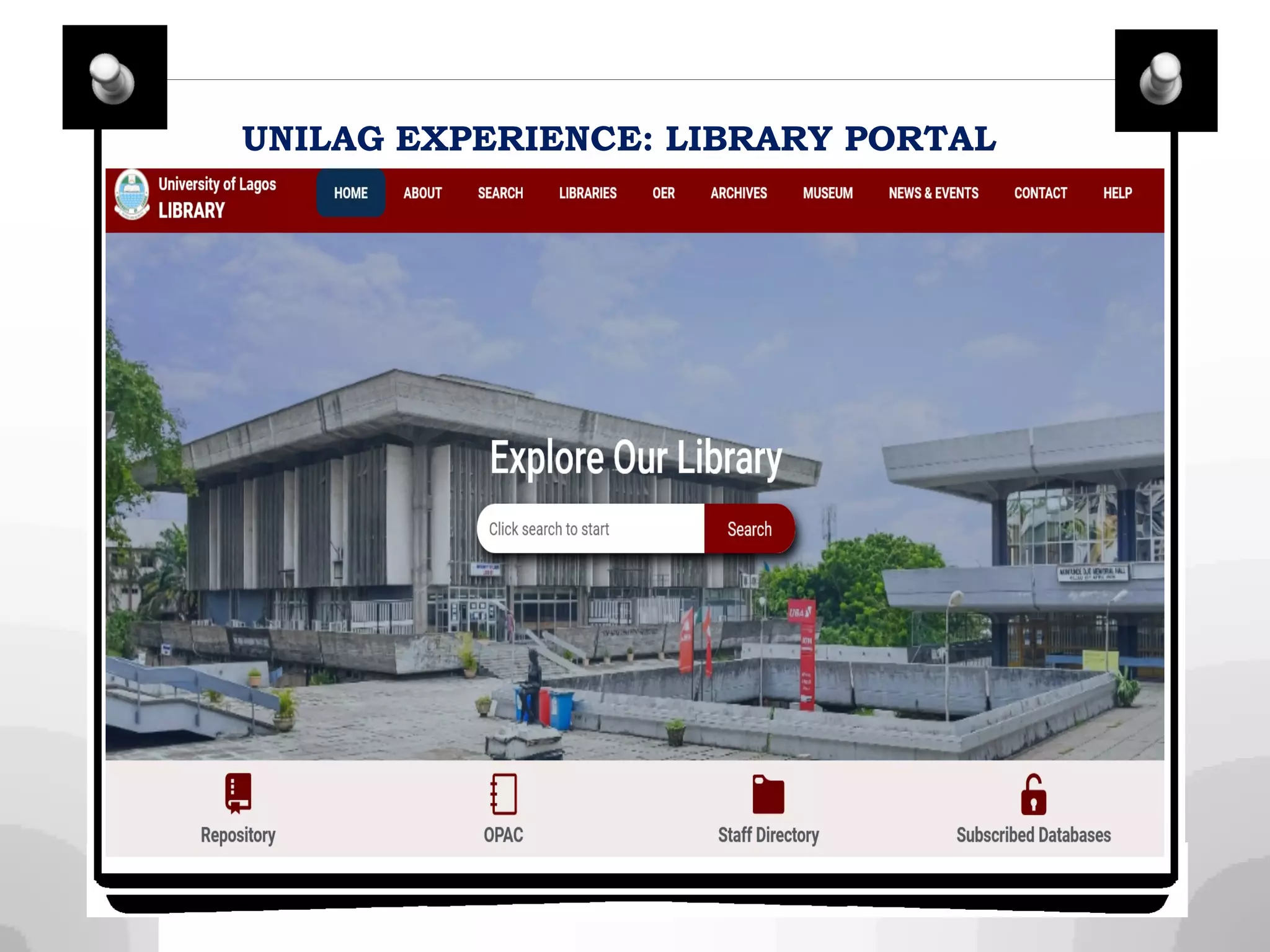
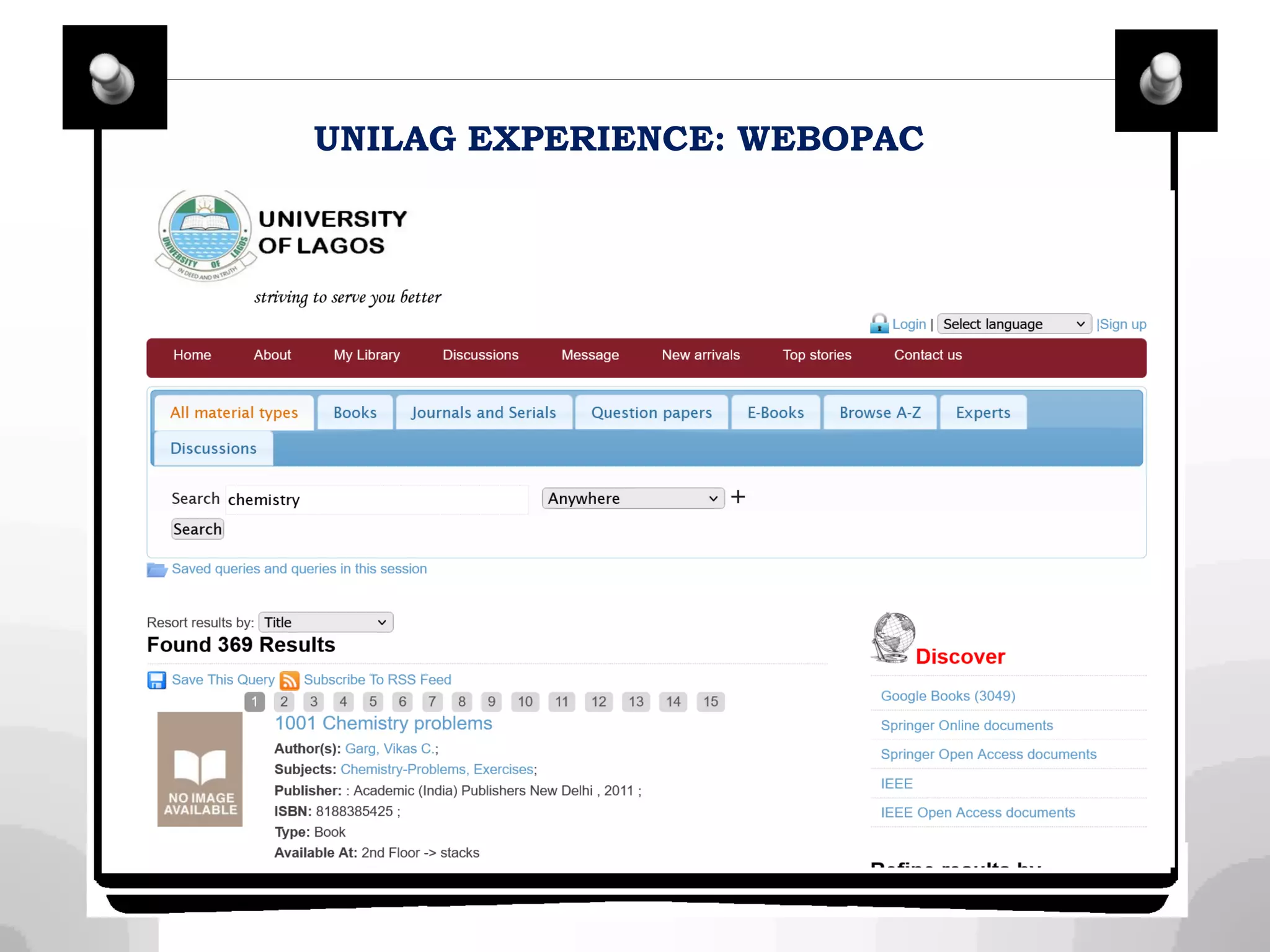
This document discusses integrating library services and resources into open and distance learning platforms. It outlines the need to provide equal access to library materials for online students. Two models of integration are described: macro-level integration of generic library tools across all courses, and micro-level customization for individual courses. Steps for integration include working with administrators, brainstorming content, and networking with faculty. The document also discusses procuring databases, curating open educational resources, and providing services like document delivery for distance learners.


















![OTHERS….
Projects
Carnegie Mellon Open Learning Initiative {http://oli.cmu.edu/}
Curriki [ https://www.curriki.org/]
edX [ https://www.edx.org/]
Khan Academy [ https://www.khanacademy.org/ ]
MITx [ https://www.edx.org/school/mitx/ ]
OER Commons [ https://www.oercommons.org/ ]
Online Education Database [ https://oedb.org/open/ ]
Open Education Consortium [ https://www.oeconsortium.org/ ]
Open Education Consortium Search Engine [ https://www.oeconsortium.org/courses/
Open Yale Courses [ https://oyc.yale.edu/ ]
Standard Engineering Everywhere [ https://see.stanford.edu/ ]
Ted Talks [ https://www.ted.com/ ]
The Encyclopedia of Life [ https://eol.org/ ]
UK’s OpenLearn Project [ https://www.open.edu/openlearn/ ]
Utah State OpenCourseWare [ https://digitalcommons.usu.edu/ocw/ ]
Wikieducator’s Learning4Content Project [ https://wikieducator.org/Learning4Content
]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/integratinglibraryservicesandoerintodistancelearning-211126164539/75/Integrating-library-services-and-oer-into-distance-learning-25-2048.jpg)
![OTHERS….
Digital Repositories:
Hippocampus [ http://www.hippocampus.org/ ]
Merlot [ https://www.merlot.org/merlot/index.htm ]
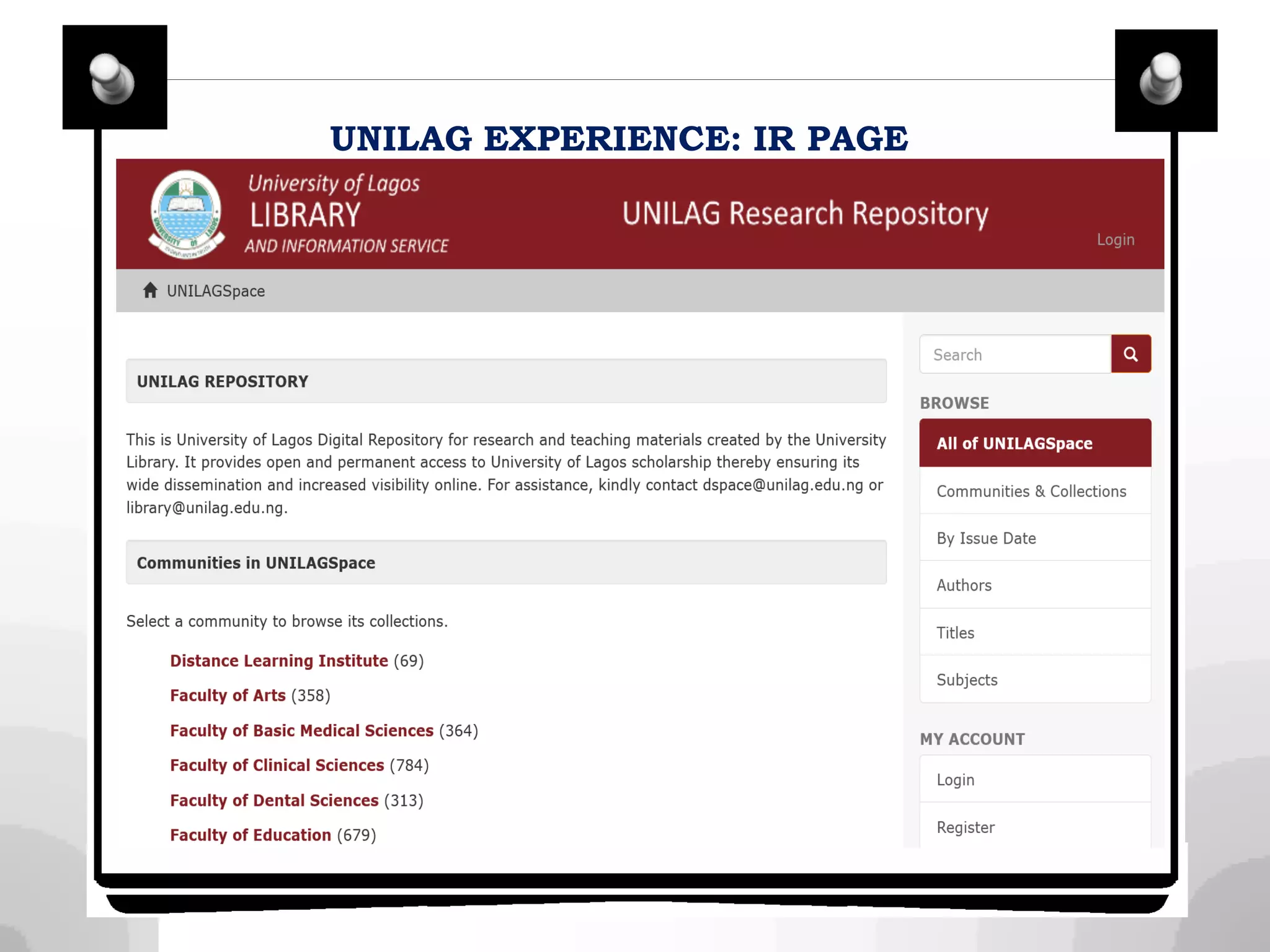
Unilag (https://ir.unilag.edu.ng/ )
Open Textbooks:
Bookboon [ http://bookboon.com/en ]
College Open Textbooks [
http://www.collegeopentextbooks.org/ ]
Community College Consortium for Open Educational
Resources [ http://oerconsortium.org/discipline-specific/ ]
Flat World Knowledge [
http://www1.flatworldknowledge.com/ ]
Textbook Revolution
http://textbookrevolution.org/index.php/Main_Page ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/integratinglibraryservicesandoerintodistancelearning-211126164539/75/Integrating-library-services-and-oer-into-distance-learning-26-2048.jpg)

