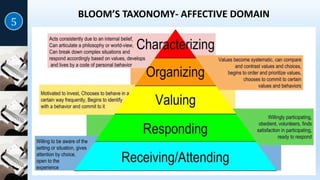
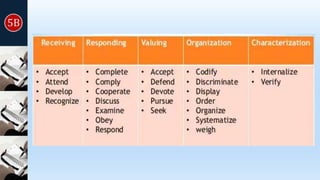
Instructional objectives define the intended outcomes of learning, help teachers plan lessons, and help students and teachers assess progress. They should be observable, measurable, and specify the performance, product, and conditions. Bloom's and SOLO taxonomies provide frameworks for categorizing objectives according to their cognitive complexity, from basic recall to higher-order thinking. Objectives can target the cognitive, affective, or psychomotor domains of learning.